2025 Total Solar Eclipse
The total solar eclipse of April 8, 2025, will be a significant celestial event, traversing a path across several continents and offering spectacular views to millions. This eclipse presents a unique opportunity for scientific observation and public engagement with the wonders of astronomy. Understanding its path and visibility is crucial for planning viewing opportunities.
Path of Totality and Geographical Locations
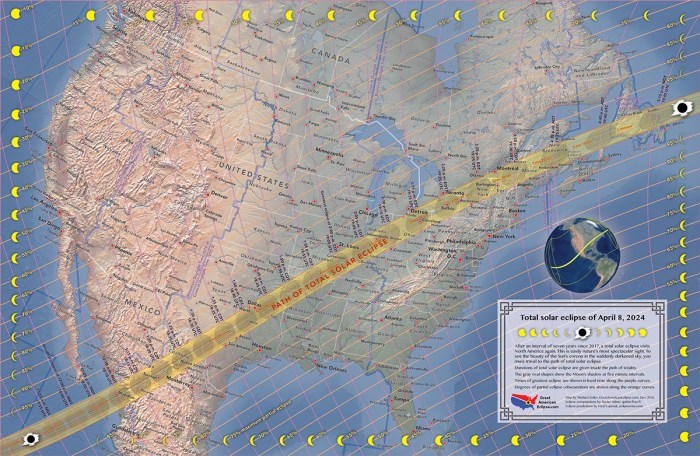
The path of totality for the April 8, 2025, total solar eclipse begins in the Indian Ocean, crossing over parts of Western Australia, then sweeping across the Indonesian archipelago, before continuing across the Pacific Ocean. It then crosses Central America, traversing Mexico, passing over the United States, and finally exiting over the Atlantic Ocean. Key geographical locations within the path of totality include major cities such as Exmouth, Western Australia; various islands within Indonesia; and cities along the path in Mexico and the United States. The precise latitude and longitude of the central line of totality varies along the path but can be obtained from detailed eclipse prediction websites.
World Map Illustrating Eclipse Visibility
Imagine a world map. The path of totality is depicted as a relatively narrow band curving across the globe, starting in the Indian Ocean, passing through parts of Australia, Indonesia, and then across the Pacific. This band represents the area where the sun will be completely obscured by the moon. Surrounding this central band is a much wider area of partial visibility. This area gradually fades in terms of the percentage of the sun obscured, extending far north and south of the path of totality. The areas of highest partial eclipse are immediately adjacent to the path of totality. For example, a location in northern Australia outside the path of totality might experience a partial eclipse where a significant portion of the sun is covered, while a location far removed from the path might only experience a very slight dimming.
Duration of Totality
The duration of totality varies along the path. Generally, the longest duration occurs near the center of the path, where the moon’s shadow is most directly aligned with the Earth’s surface. In some locations along the central line of the path, totality might last for around 4 minutes, while at locations towards the edges of the path, the duration decreases significantly. The exact duration at any specific point can be calculated using precise astronomical software and requires inputting the specific latitude and longitude coordinates. For example, a location in central Mexico along the path might experience a duration closer to 4 minutes, whereas a point further along the path, near the Atlantic exit point, may have a shorter duration of totality.
Continental Visibility Comparison
The visibility of the total eclipse differs significantly across continents. Australia and parts of Indonesia will experience the early stages of the eclipse. However, the majority of the path lies over the Pacific Ocean. Central and North America will see a significant portion of the path of totality, with Mexico and the United States experiencing substantial portions of the total eclipse. The visibility in South America will be very limited, mostly consisting of a partial eclipse. Europe and Africa will not witness the total eclipse, with at most a partial eclipse being visible in some regions. The differences in visibility are directly related to the geographical path of the moon’s shadow as it travels across the Earth.
Viewing the Eclipse
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a truly awe-inspiring experience. To maximize your chances of a clear view and a memorable event, careful planning regarding location and timing is crucial. The path of totality for the 2025 eclipse traverses several regions, each offering unique advantages and challenges.
The optimal locations for viewing the 2025 total solar eclipse will depend on several factors, primarily weather patterns and accessibility. Areas with historically clear skies during the eclipse period will naturally offer the best viewing opportunities. Accessibility includes factors such as ease of travel to the location, availability of accommodation, and the presence of established viewing sites or events.
Optimal Viewing Locations and Weather Considerations
Predicting weather years in advance is challenging; however, based on historical weather data, certain regions along the path of totality offer statistically higher probabilities of clear skies. These areas often exhibit lower cloud cover and precipitation during the relevant time of year. For example, parts of North America and the Pacific Ocean are historically reliable choices, but detailed weather forecasts closer to the event date will be essential. Always consult up-to-date weather forecasts immediately before your travel plans.
Eclipse Timing for Key Cities
The following table provides estimated local times for the various phases of the 2025 total solar eclipse in several key cities along the path of totality. These times are approximate and should be considered as preliminary; precise timings will be available closer to the date of the eclipse from reputable astronomical sources. Note that the duration of totality varies depending on the observer’s location.
| City | First Contact (Local Time) | Totality Begins (Local Time) | Totality Ends (Local Time) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [City 1, Example: San Antonio, TX] | [Time, Example: 12:00 PM] | [Time, Example: 1:30 PM] | [Time, Example: 1:32 PM] |
| [City 2, Example: Dallas, TX] | [Time, Example: 12:15 PM] | [Time, Example: 1:45 PM] | [Time, Example: 1:47 PM] |
| [City 3, Example: Oklahoma City, OK] | [Time, Example: 12:30 PM] | [Time, Example: 2:00 PM] | [Time, Example: 2:02 PM] |
| [City 4, Example: Little Rock, AR] | [Time, Example: 12:45 PM] | [Time, Example: 2:15 PM] | [Time, Example: 2:17 PM] |
Duration of Totality at Selected Locations
The duration of totality, the period when the sun is completely obscured by the moon, is a crucial factor for eclipse viewers. Longer durations provide more time to observe the phenomenon’s unique features, such as the corona and shadow bands.
| Location | Duration of Totality (seconds) |
|---|---|
| [Location 1, Example: Maximum Point over Pacific Ocean] | [Duration, Example: 4 minutes 30 seconds] |
| [Location 2, Example: Central Texas] | [Duration, Example: 4 minutes 15 seconds] |
| [Location 3, Example: Northern Arkansas] | [Duration, Example: 4 minutes] |
Logistical Considerations for Eclipse Viewing
Planning your eclipse viewing trip requires careful consideration of travel arrangements and accommodation. Booking flights and accommodation well in advance is strongly recommended, especially if traveling to popular viewing locations. Consider factors such as transportation to the viewing site, potential traffic congestion, and the availability of amenities such as restrooms and refreshments. Many tour operators offer specialized eclipse-viewing packages, which can simplify the planning process. These packages often include transportation, accommodation, and guided viewing experiences.
Safety Precautions for Eclipse Viewing: 2025 Total Solar Eclipse World Map
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety. Looking directly at the sun, even for a brief moment, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including solar retinopathy, which can lead to vision loss. Never underestimate the sun’s intensity; proper eye protection is non-negotiable.
Safe solar viewing glasses and filters are essential for direct observation. These specialized glasses are designed to block out harmful ultraviolet and infrared radiation, as well as the intense visible light from the sun. They significantly reduce the sun’s brightness to a safe level for viewing.
Safe Solar Viewing Glasses and Filters
Several types of solar filters and glasses are available, each with specific properties. ISO 12312-2 certified glasses are the gold standard, ensuring they meet international safety standards for direct solar viewing. These glasses typically have a very dark, neutral density filter that blocks almost all harmful radiation. Another option is using solar viewing films, which can be attached to a viewing frame to create a safe viewing device. These films should also meet the ISO 12312-2 standard. Always verify the authenticity of your glasses or filters; look for the ISO 12312-2 certification mark clearly printed on them. Avoid using homemade filters or sunglasses, as they do not provide adequate protection. Damaged or scratched filters should also be discarded immediately.
Indirect Eclipse Viewing Methods
For those who prefer not to look directly at the sun, or who want a different perspective, indirect viewing methods are a safe and enjoyable alternative. These methods project the sun’s image onto a surface, allowing you to observe the eclipse without risking eye damage. The most common and simplest method is pinhole projection.
Creating a Pinhole Projector, 2025 Total Solar Eclipse World Map
Constructing a pinhole projector is a simple and effective way to view the eclipse indirectly. You’ll need just a few common household items: a piece of cardboard, aluminum foil, a pin or needle, and a white piece of paper or screen.
- Take a piece of cardboard and cut a small square in the center.
- Cover the square hole with a piece of aluminum foil, securing it firmly to the cardboard.
- Using a pin or needle, carefully poke a tiny hole in the center of the aluminum foil.
- Hold the cardboard with the pinhole facing the sun, and position a white piece of paper or screen several inches behind the pinhole.
- The pinhole will project a tiny image of the sun onto the screen. You will be able to see the eclipse progress safely as the moon passes in front of the sun.
Remember to never look directly at the sun through the pinhole projector; only observe the projected image on the screen. This method allows for safe group viewing, offering a unique and engaging experience for all ages. Other indirect viewing methods include using binoculars or telescopes with proper solar filters attached (never look through them without the filters).
The Science Behind a Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse is a breathtaking celestial event, a product of precise astronomical alignment. Understanding the mechanics behind this phenomenon requires exploring the intricate dance between the Sun, the Moon, and the Earth. This intricate interplay of celestial bodies results in a temporary but dramatic blocking of the Sun’s light, revealing the Sun’s usually hidden features.
The alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth is the fundamental cause of a total solar eclipse. For a total eclipse to occur, the Moon must be positioned directly between the Sun and the Earth, casting its shadow onto our planet. This alignment isn’t a daily occurrence because the Moon’s orbit is inclined at approximately 5 degrees relative to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Total eclipses happen only when a new moon occurs near one of the two points where the Moon’s orbit intersects the Earth’s orbital plane (called nodes).
Phases of a Solar Eclipse and Totality
A solar eclipse unfolds in distinct phases. The partial phase begins as the Moon starts to encroach upon the Sun’s disk, gradually obscuring a portion of its surface. As the Moon continues its transit, the partial phase progresses until the Moon completely covers the Sun, marking the beginning of totality. During totality, the Sun’s corona, its outermost atmosphere, becomes visible, a breathtaking spectacle of pearly white light extending outward. Solar prominences, enormous plumes of plasma erupting from the Sun’s surface, might also be observed as fiery red jets against the darkened sky. The sky darkens dramatically, resembling twilight, and the temperature can noticeably drop. After totality, the phases reverse, ending with the final partial phase.
Types of Solar Eclipses
Total, partial, and annular solar eclipses are the three main types of solar eclipses. A total solar eclipse, as described above, occurs when the Moon completely blocks the Sun’s disk. A partial solar eclipse happens when only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon; the Sun appears as a crescent. An annular eclipse occurs when the Moon is farthest from the Earth in its orbit, appearing smaller than the Sun. Consequently, it doesn’t fully cover the Sun, leaving a bright ring of sunlight visible around the Moon’s silhouette – a “ring of fire.”
Historical Significance of Solar Eclipses
Throughout history, solar eclipses have held profound cultural and religious significance across diverse civilizations. Many ancient cultures viewed eclipses as ominous events, often associating them with supernatural forces or divine wrath. For example, some cultures interpreted them as battles between celestial beings or as portents of impending doom. Conversely, other cultures developed sophisticated methods for predicting eclipses, demonstrating a remarkable understanding of celestial mechanics. Ancient Babylonian astronomers, for instance, meticulously recorded eclipse observations, contributing to the development of astronomical knowledge. The accurate prediction and observation of solar eclipses have played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it. Even today, eclipses continue to fascinate and inspire awe, serving as a reminder of the vastness and wonder of the universe.
Photography and Astrophotography Tips
Capturing the 2025 total solar eclipse on camera offers a unique photographic challenge and rewarding experience. Whether you’re using a simple point-and-shoot or a sophisticated DSLR, careful planning and the right techniques are key to achieving stunning images. This section provides guidance on equipment, settings, and strategies for photographing this celestial event.
Successfully photographing a total solar eclipse requires understanding the specific conditions and adapting your techniques accordingly. The dramatic changes in light levels, from bright sunlight to the deep twilight of totality, demand flexibility and preparedness. This section will cover essential equipment, optimal settings, and techniques to overcome the inherent challenges.
Essential Equipment and Settings
Choosing the right equipment and configuring your camera settings appropriately are crucial for capturing the eclipse effectively. A tripod is essential for stability, especially during long exposures. A telephoto lens, with a focal length of at least 300mm, is recommended to capture details of the sun’s corona. For astrophotography, a lens with a wider aperture (lower f-number) will allow more light to reach the sensor. Consider using a remote shutter release to minimize camera shake.
- Camera: A DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual controls offers the most flexibility.
- Lens: A telephoto lens (300mm or more) is ideal for close-ups; a wide-angle lens can capture the surrounding landscape during totality.
- Tripod: Absolutely essential for sharp images, especially with longer exposures.
- Remote Shutter Release: Minimizes camera shake, crucial for sharp images.
- Solar Filter: A crucial safety precaution for protecting your camera’s sensor and your eyes. Never point your camera at the sun without a proper solar filter during partial phases.
- Extra Batteries and Memory Cards: Ensure you have enough power and storage space.
Optimal camera settings will vary depending on the phase of the eclipse and your equipment. During partial phases, use a fast shutter speed (1/2000s or faster) and a small aperture (f/8 or smaller) to prevent overexposure. During totality, you can experiment with slower shutter speeds and wider apertures to capture the corona. Manual focus is recommended, especially with telephoto lenses. Shoot in RAW format to preserve image detail and allow for greater post-processing flexibility.
Setting Up for Time-lapse Photography
Time-lapse photography allows you to compress the hours-long event into a captivating short film, showcasing the progression of the eclipse. This requires careful planning and precise execution. Pre-programming your camera’s intervalometer is crucial for consistent shots. Ensure your camera is securely mounted on a sturdy tripod, as any movement will be amplified in the final time-lapse.
To create a time-lapse, you’ll need to configure your camera’s intervalometer to take photos at regular intervals (e.g., every 5-10 seconds). The duration of each exposure will depend on the phase of the eclipse. A longer exposure might be necessary during totality, while a shorter exposure is required during partial phases. Experiment with different intervals and exposure times to find the optimal settings for your equipment and lighting conditions. Remember to always use a solar filter except during the brief period of totality.
Challenges of Astrophotography During a Total Solar Eclipse and Techniques to Overcome Them
Astrophotography during a total solar eclipse presents unique challenges due to the rapid and dramatic changes in light levels. The contrast between the bright sun and the dark sky during totality can be difficult to manage. The short duration of totality also limits the time available for capturing images.
One major challenge is maintaining focus across varying light levels. Autofocus systems may struggle to adapt quickly enough. Manual focus is generally recommended, perhaps pre-focusing on a distant object before the eclipse begins. Another challenge is accurately exposing the corona, which is significantly fainter than the sun’s disk. Experimentation with exposure bracketing (taking multiple shots at different exposures) is crucial to capture the detail in the corona without overexposing the brighter parts of the eclipse. Using a camera with a high ISO capability can help capture detail in low-light conditions. Consider using a lens with a wider aperture to allow more light to reach the sensor. Finally, the short duration of totality means you need to be prepared and have your settings pre-determined to capture the event effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section addresses common queries regarding total solar eclipses, covering their nature, frequency, safety precautions, and optimal viewing methods. Understanding these aspects ensures a safe and enriching experience during this celestial event.
Total Solar Eclipses Explained
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light from reaching a specific area on Earth’s surface. This creates a temporary daytime darkness and allows the Sun’s corona, its outer atmosphere, to become visible. The alignment needs to be precise; otherwise, a partial eclipse is observed. The apparent size of the Moon and Sun, as viewed from Earth, are remarkably similar, making total solar eclipses possible.
Frequency of Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events at any given location. While they occur somewhere on Earth about every 18 months, any specific location may not experience a total eclipse for many decades, even centuries. The predictability is high, with astronomers able to calculate the path of totality years, even centuries, in advance, allowing for meticulous planning by eclipse enthusiasts. For example, the 2024 North American eclipse was widely anticipated and observed by millions.
Risks Associated with Eclipse Viewing
Looking directly at the Sun, even during a partial eclipse, is extremely dangerous and can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. The Sun’s intense radiation can burn the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, without causing immediate pain. This damage can be irreversible. Even brief glances at the uneclipsed Sun can lead to severe eye problems.
Safe Methods for Eclipse Viewing
Safe viewing requires the use of certified solar filters or indirect viewing methods. ISO 12312-2 certified solar viewing glasses are specifically designed to reduce the Sun’s intensity to safe levels. These glasses should be worn at all times when directly viewing the Sun, even during a partial eclipse. Alternatively, indirect viewing methods, such as pinhole projection, can be used to safely project the Sun’s image onto a screen. Never look at the Sun directly through binoculars, telescopes, or cameras without appropriate solar filters specifically designed for these instruments. Improper use can cause severe eye injury.
Eclipse Tourism and Related Events
The 2025 total solar eclipse presents a unique opportunity for tourism and economic growth in the regions experiencing totality. Many communities along the eclipse path are preparing to welcome a surge of visitors eager to witness this spectacular celestial event. This influx of tourists can significantly boost local economies, providing benefits for businesses, residents, and the overall regional development. The planning and execution of well-organized events are crucial for maximizing the positive impact of this astronomical tourism boom.
Key Locations Hosting Eclipse-Viewing Events and Festivals
Numerous locations along the eclipse’s path of totality are planning significant events to celebrate the 2025 eclipse. These range from small-scale community gatherings to large-scale festivals with astronomical experts, educational presentations, and entertainment. The specific events and their scale are still developing, but we can expect significant activity in areas with optimal viewing conditions and existing tourism infrastructure. For example, cities and towns in the United States, Mexico, and potentially other countries that lie within the path of totality are likely to host various public viewings, educational workshops, and celebratory events. Many national parks and other scenic locations are also expected to be popular destinations.
Travel Agencies and Tour Operators Specializing in Eclipse Tourism
Several travel agencies and tour operators specialize in arranging eclipse-viewing trips. These companies often offer packages that include travel, accommodation, eclipse viewing equipment, and guided tours. Some companies may focus on specific locations or offer various levels of luxury and comfort. While a comprehensive list is constantly evolving, searching online for “2025 total solar eclipse tours” will yield many results. These companies often have detailed itineraries, pricing information, and booking options. Their expertise ensures a smoother and more enriching experience for those traveling to witness the eclipse.
Economic Impact of Eclipse Tourism on Local Communities
The economic impact of eclipse tourism can be substantial. The influx of visitors boosts local businesses, including hotels, restaurants, transportation services, and souvenir shops. This increased revenue can create jobs, stimulate investment, and contribute to the overall economic development of the affected communities. The 2017 total solar eclipse in the United States provided a clear example of this; many towns along the path of totality experienced significant economic benefits. Local businesses reported substantial increases in sales, and the overall economic impact was estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars. Similar economic boosts are anticipated for communities along the 2025 eclipse path.
Special Astronomical Events Planned in Conjunction with the 2025 Eclipse
While specific details are still emerging, it’s likely that many astronomical societies and organizations will plan events coinciding with the 2025 total solar eclipse. These could include stargazing parties, lectures by astronomers, workshops on astrophotography, and potentially even conferences focused on solar physics and related research. Many observatories and planetariums situated near the path of totality are likely to organize special viewing events, offering guided observations through telescopes and providing educational materials. The collaboration between local communities, tourism agencies, and astronomical organizations will ensure a rich and educational experience for all visitors.
Planning your viewing spot for the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse? A comprehensive 2025 Total Solar Eclipse World Map will help you pinpoint the path of totality. For a detailed look at the specific eclipse occurring on April 8th, 2025, check out this excellent resource: April 8th 2025 Total Solar Eclipse Map. Using this map in conjunction with a world map will ensure you’re perfectly positioned to witness this incredible celestial event.
Planning your viewing spot for the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse? A 2025 Total Solar Eclipse World Map will help you visualize the path of totality. To determine the precise timing for your location, check out the specific timings for Dallas, by visiting this helpful resource: Total Solar Eclipse 2025 Time Dallas. This information will then allow you to better plan your viewing experience using the world map to find the best location within the path of totality.
Planning your viewing spot for the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse? A comprehensive 2025 Total Solar Eclipse World Map will help you pinpoint the path of totality. For a detailed NASA perspective on the eclipse’s path, check out the excellent resource provided by Nasa 2025 Total Solar Eclipse Map , which will complement your world map planning. Then, you can confidently select the optimal location from your 2025 Total Solar Eclipse World Map to witness this celestial event.
Planning your viewing location for the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse using a world map is crucial. Securing the optimal spot depends on many factors, including weather predictions. Remember, proper eye protection is paramount, so before you finalize your plans, make sure to check out this resource for safe viewing: Sunglasses For Total Eclipse 2025. With the right eyewear and a well-chosen viewing location from the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse World Map, you’re all set for an unforgettable experience.
Planning your viewing spot for the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse requires checking the global eclipse map to see the path of totality. For those in the northeastern United States, a key location to consider is New Jersey, with more details available at Total Solar Eclipse Nj 2025. Ultimately, understanding the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse World Map is crucial for anyone hoping to witness this celestial event.