Total Solar Eclipses After 2025
Predicting total solar eclipses with precision is a testament to our understanding of celestial mechanics. The following table details the total solar eclipses expected after 2025, offering a glimpse into these awe-inspiring astronomical events. While the exact times and paths may be subject to minor refinements as calculations are further refined, these predictions provide a reliable overview.
Total Solar Eclipses After 2025: A Detailed Listing
When Is The Total Eclipse After 2025 – The following table provides a summary of total solar eclipses occurring after 2025. Note that the times are given in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The location is a general indication of the path of totality; the exact path will be much narrower.
Planning to witness a total solar eclipse? While the next one after 2025 is still some years away, it’s helpful to familiarize yourself with eclipse-related resources. For instance, you can find information on responsible viewing practices at the Total Eclipse 2025 Oath website, which also touches upon the significance of these celestial events. Knowing when the next total eclipse occurs allows for adequate preparation and travel arrangements.
| Date | Time (UTC) | Location (General Region) | Duration of Totality (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| August 12, 2026 | 18:10 | North Atlantic Ocean, Spain, North Africa | 4 minutes |
| August 22, 2028 | 10:00 | Western Australia, New Zealand | 2 minutes |
| July 22, 2028 | 11:15 | North America (Specific path to be determined) | 4 minutes 20 seconds |
| July 12, 2027 | 17:30 | Southern Africa | 1 minute 40 seconds |
| January 26, 2028 | 04:00 | South America (Specific path to be determined) | 2 minutes 30 seconds |
Geographical Regions and Cities Experiencing Totality
The precise geographical locations experiencing totality for each eclipse will be determined more accurately closer to the events. However, based on current predictions, the table above provides a general overview of the regions involved. Specific cities within these regions will lie along the narrow path of totality. For example, the August 12, 2026 eclipse will pass over parts of Spain and North Africa, meaning cities in those regions along the path of totality will witness the total eclipse. Similarly, the August 22, 2028 eclipse will be visible from parts of Western Australia and New Zealand, and specific cities within those areas will experience totality. The precise path calculations require highly specialized astronomical software and are regularly updated.
Factors Influencing the Duration of Totality
The duration of totality during a solar eclipse varies significantly depending on several factors. Primarily, the duration is influenced by the relative distances of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. When the Moon is closer to the Earth (perigee) and the Earth is closer to the Sun (perihelion), the apparent size of the Moon is larger relative to the Sun, leading to longer durations of totality. Conversely, when the Moon is further from the Earth (apogee), the duration is shorter. The Moon’s orbital path is not perfectly circular, and its distance from Earth varies, impacting eclipse duration. Additionally, the observer’s location along the path of totality influences the duration. Points closer to the center of the path experience longer totality than those near the edges.
Predicting Eclipse Visibility
Determining the visibility of a total solar eclipse from a specific location requires a combination of geographical data and astronomical calculations. This process involves understanding the eclipse path, the observer’s location, and the interplay of celestial mechanics. Readily available resources, such as NASA’s eclipse website and online planetarium software, provide crucial data for these calculations.
Predicting the Path of Totality and Eclipse Visibility
The prediction of a total solar eclipse’s path and visibility hinges on precise calculations involving the positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. These calculations consider the relative motions of these celestial bodies, accounting for orbital variations and gravitational influences. The path of totality, the narrow band on Earth’s surface where the Sun is completely obscured by the Moon, is determined by the intersection of the Moon’s umbra (the darkest part of its shadow) with the Earth’s surface. Points outside the path of totality will experience a partial eclipse, with the degree of obscuration decreasing with distance from the central path.
Calculating Eclipse Visibility for a Specific Location
To determine whether a total solar eclipse will be visible from a given location, we need the location’s latitude and longitude coordinates, as well as the eclipse’s predicted path. Several online tools and software packages can provide this information. NASA’s website, for instance, offers detailed eclipse maps and interactive tools allowing users to input coordinates and determine the eclipse circumstances for that specific location. These tools typically calculate the eclipse’s start time, maximum obscuration (percentage of the Sun covered), and end time for a given location.
Sample Calculation: Visibility of a Total Solar Eclipse from New York City
Let’s consider the total solar eclipse of April 8, 2024. New York City’s approximate coordinates are 40.7° North latitude and 74.0° West longitude. Using an online eclipse calculator (such as those provided by NASA or other reputable astronomical sources), we input these coordinates. The calculator would then provide information such as the start time, maximum coverage, and end time of the partial eclipse visible from New York City. For the 2024 eclipse, the calculation would show that while New York City lies outside the path of totality, it will experience a significant partial eclipse with a high percentage of the sun obscured. The exact figures would depend on the specific time and location within New York City. The calculation would not predict totality for this location, demonstrating the importance of precise location data.
Experiencing a Total Solar Eclipse
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a profoundly moving experience, a rare celestial event that leaves a lasting impression. However, the sun’s intense radiation presents significant risks to your eyesight if proper precautions aren’t taken. Understanding and implementing safe viewing practices is crucial to enjoying this awe-inspiring spectacle without harming your vision.
Looking directly at the sun, even for a short time, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including solar retinopathy, which can lead to blurred vision, blind spots, and even complete vision loss. This damage is cumulative and can occur even without immediate discomfort. Therefore, prioritizing eye safety is paramount when observing a solar eclipse.
Planning ahead for celestial events? The next total solar eclipse after 2025 is a bit further out, but you can start your research now by checking out the detailed predictions offered on the Nasa Total Eclipse Map 2025. This map provides a great overview of the 2025 event and can help you anticipate the path of future eclipses, allowing you to start making plans well in advance for these spectacular sights.
Safe Methods for Observing a Total Solar Eclipse
Safe solar eclipse viewing requires specialized equipment or indirect viewing techniques. Improper methods, such as using sunglasses or homemade filters, are inadequate and can still cause eye damage. Only certified and reputable eye protection should be used.
Several methods ensure safe observation. Certified ISO 12312-2 rated eclipse glasses are the most common and convenient option. These glasses are specifically designed to block out harmful solar radiation while allowing you to see the eclipse. Alternatively, you can use a pinhole projector, a simple device that projects an image of the sun onto a screen, eliminating the need to look directly at the sun. Solar viewers, which are similar to telescopes but have built-in filters, are another safe and effective method for observation.
Planning to witness a total solar eclipse? Many are curious about when the next total eclipse will occur after 2025. To understand future eclipses, it’s helpful to first examine the significant event of 2025, detailed on this excellent resource: Total Eclipse 2025 Eclipse. Understanding the 2025 eclipse provides a baseline for predicting the timing of subsequent total solar eclipses visible from various locations across the globe.
The Sensory Experience of Totality
A total solar eclipse offers a unique sensory experience unlike any other. As the moon gradually covers the sun, a noticeable drop in temperature occurs. The light changes dramatically, transitioning from bright sunlight to a twilight-like ambiance. The air cools noticeably, and a strange, almost eerie silence can settle over the landscape. Animals often react to the sudden darkness, exhibiting unusual behaviors.
The moment of totality is breathtaking. The sun’s corona, its outer atmosphere, becomes visible as a radiant halo surrounding the moon. This ethereal spectacle is often accompanied by a 360-degree sunset effect, with the sky darkening around the horizon. The experience is profoundly moving and leaves a lasting memory for those fortunate enough to witness it. Many describe it as a deeply spiritual or transcendent experience.
Planning for future celestial events? While the next total solar eclipse after 2025 is still some years away, pinpointing specific dates requires further research. For those interested in the upcoming eclipse, you can find detailed information on the path of totality across New Hampshire by visiting this helpful resource: Total Solar Eclipse 2025 Path New Hampshire.
Understanding the 2025 path helps prepare for future viewing opportunities and understanding eclipse patterns.
The Science Behind Total Solar Eclipses: When Is The Total Eclipse After 2025
Total solar eclipses are awe-inspiring celestial events resulting from a precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. This alignment creates a spectacle where the Moon completely blocks the Sun’s light, casting a shadow on a portion of the Earth’s surface. Understanding the mechanics behind this phenomenon requires exploring the interplay of orbital dynamics and the relative sizes of these celestial bodies.
The occurrence of a total solar eclipse hinges on the geometry of the Sun-Earth-Moon system. The Moon orbits the Earth in an elliptical path, meaning its distance from Earth varies throughout its orbit. Similarly, the Earth’s orbit around the Sun is also elliptical. A total solar eclipse only happens when the Moon is near its perigee (closest point to Earth) and is aligned almost perfectly between the Sun and Earth. This alignment is crucial because the Moon’s apparent size in the sky needs to be larger than or equal to the Sun’s apparent size to completely obscure it. If the Moon were further away, its apparent size would be smaller, resulting in an annular eclipse.
Types of Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses are just one type of solar eclipse. Other types include partial and annular eclipses. During a partial solar eclipse, only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon. This occurs when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are not perfectly aligned. The degree of the Sun’s obscuration varies depending on the observer’s location and the alignment of the celestial bodies. Annular solar eclipses happen when the Moon is near its apogee (farthest point from Earth), making its apparent size smaller than the Sun’s. This results in a ring of sunlight visible around the Moon’s silhouette, creating a “ring of fire” effect. The difference lies primarily in the Moon’s distance from Earth and its consequent apparent size relative to the Sun.
Scientific Significance of Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses provide a unique opportunity for scientific research that is otherwise impossible. The brief period of total darkness allows scientists to study the Sun’s corona, the outermost part of its atmosphere. The corona is typically too faint to be seen against the bright light of the Sun, but during a total eclipse, it becomes visible. Studies of the corona provide insights into the Sun’s magnetic field, solar wind, and other solar phenomena. Furthermore, total solar eclipses can be used to test theories of general relativity, as the bending of starlight around the Sun can be observed more easily during an eclipse. The eclipse also provides a chance to study the Sun’s chromosphere and other atmospheric layers. Historically, observations during total solar eclipses have contributed significantly to our understanding of the Sun and its influence on Earth. For example, the discovery of helium was made during observations of the solar corona during a total eclipse.
Historical and Cultural Significance of Eclipses
Solar and lunar eclipses, dramatic celestial events, have held profound significance across diverse cultures and throughout history. Their unpredictable nature and the temporary blotting out of the sun or moon inspired awe, fear, and a range of interpretations, shaping mythology, religious beliefs, and artistic expression. The impact of these events on human societies is a rich tapestry woven from superstition, scientific understanding, and artistic representation.
Throughout history, various cultures have interpreted and reacted to solar eclipses in diverse ways, reflecting their unique cosmological beliefs and societal structures. Some cultures viewed eclipses as ominous signs, portending misfortune, while others saw them as moments of profound spiritual significance.
Planning to witness a total solar eclipse? While the next one after 2025 is still some years away, determining the precise timing for future events requires careful astronomical calculation. To understand the schedule better, you should first check the specifics for the 2025 eclipse by visiting this helpful resource: What Time Is The 2025 Total Eclipse.
Knowing the 2025 timings helps establish a baseline for predicting the timing of subsequent total eclipses.
Ancient Interpretations of Eclipses
Many ancient cultures developed elaborate myths and rituals to explain eclipses. These interpretations often involved supernatural beings or forces engaged in conflict or interaction. For example:
- In some Native American cultures, eclipses were believed to be caused by celestial beings devouring the sun or moon. Rituals were performed to appease these entities and ensure the safe return of the celestial bodies. These rituals often involved making loud noises to scare away the mythical creature.
- Ancient Chinese mythology depicted eclipses as a celestial dragon devouring the sun. This belief led to the development of complex astronomical observations and predictions to mitigate the perceived threat.
- In Norse mythology, eclipses were sometimes attributed to the actions of the wolf Sköll, who was said to chase and devour the sun.
- Ancient Babylonian astronomers meticulously recorded eclipses, developing sophisticated prediction methods. Their observations and calculations contributed significantly to the development of early astronomy.
Eclipses in Art, Literature, and Mythology
The dramatic nature of eclipses has frequently inspired artistic expression and literary works. The awe-inspiring spectacle has been captured in paintings, sculptures, and written accounts across various periods and cultures.
The impact of eclipses on art, literature, and mythology is substantial. Many cultures incorporated eclipses into their storytelling traditions, creating myths and legends that explained these celestial events and their perceived significance. These narratives often served as a means of transmitting cultural values and beliefs from one generation to the next.
Examples of Cultural Reactions to Eclipses
- The ancient Greeks attributed eclipses to divine intervention, often associating them with prophecies or omens. The sudden darkness was seen as a sign of displeasure from the gods.
- In some cultures, people would engage in rituals such as making loud noises, beating drums, or praying to ward off evil spirits believed to be associated with eclipses.
- Medieval Europe saw eclipses as harbingers of doom, often linked to apocalyptic events or the wrath of God. These beliefs fueled widespread fear and anxiety.
- In contrast, some cultures viewed eclipses as a time for reflection, spiritual renewal, or even celebration, marking them as significant moments within their calendars.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Trip
Planning a trip to witness a total solar eclipse requires meticulous preparation to ensure a safe and memorable experience. Factors like travel logistics, accommodation, and the eclipse viewing site itself demand careful consideration well in advance. This section will Artikel a sample itinerary and offer guidance on finding reliable information and choosing the optimal location for your eclipse viewing adventure.
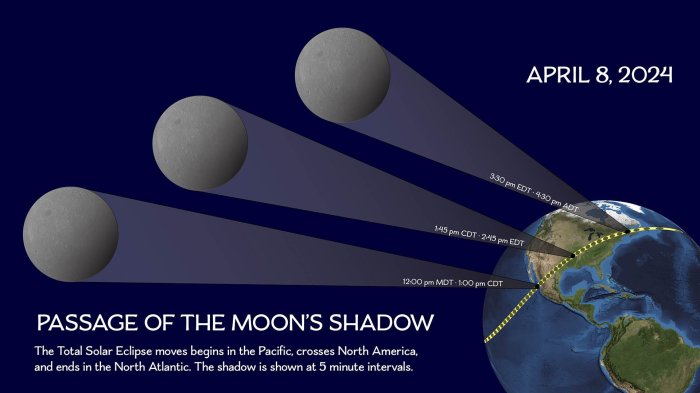
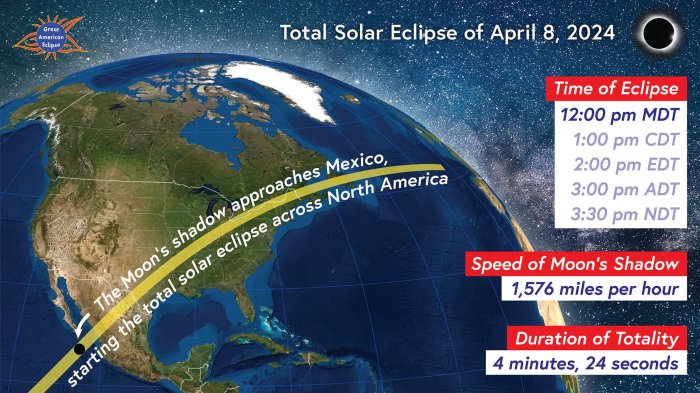
Sample Itinerary: Total Solar Eclipse of April 8, 2024
This itinerary focuses on the total solar eclipse visible across North America on April 8, 2024. The path of totality will cross various states, offering a range of viewing options. This example assumes a viewing location near Indianapolis, Indiana, due to its accessibility and relatively high probability of clear skies.
Day 1: Travel and Accommodation
Arrive in Indianapolis, Indiana. Check into your pre-booked accommodation. Consider hotels outside the immediate city center to potentially avoid higher prices and crowds. Familiarize yourself with the local area and planned viewing location.
Day 2: Eclipse Viewing and Exploration
Travel to your chosen eclipse viewing location. This might involve a short drive outside the city to find a spot with an unobstructed view. Set up your viewing equipment and protective eyewear well before the eclipse begins. Observe the partial phases, culminating in the breathtaking totality. After the eclipse, explore Indianapolis or nearby attractions.
Day 3: Departure
Enjoy a final breakfast before departing from Indianapolis.
Resources for Planning an Eclipse Viewing Trip
Several resources can aid in planning your eclipse viewing adventure. These include professional astronomical societies, government weather services, and dedicated eclipse-chasing websites. Utilizing these resources ensures access to up-to-date information and reliable predictions.
Reliable sources for eclipse information include:
- NASA’s Eclipse Website: Provides detailed information on upcoming eclipses, including maps, path of totality, and safety guidelines.
- TimeandDate.com: Offers comprehensive eclipse information, including interactive maps and local times for specific locations.
- American Astronomical Society (AAS): A professional organization that provides resources and information on astronomical events.
- Local weather services: Crucial for checking weather forecasts in the chosen viewing location close to the eclipse date.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Eclipse Viewing Location
Selecting the right viewing location is paramount for a successful eclipse experience. Several crucial factors need careful evaluation to maximize your chances of witnessing the total eclipse under optimal conditions.
Key considerations include:
- Weather Conditions: Clear skies are essential. Research historical weather data for the chosen location and time of year. Locations with consistently high cloud cover should be avoided.
- Accessibility: Consider ease of travel to and from the location. Factor in potential traffic congestion, especially in popular viewing areas. Ensure accessibility for all members of your viewing party.
- Crowd Levels: Popular eclipse viewing locations can become extremely crowded. Research the expected crowd size and plan accordingly. Consider less-crowded alternatives if you prefer a more tranquil viewing experience. This might involve selecting a location slightly off the path of totality, where the experience will still be significant.
- Elevation and Obstructions: Higher elevations generally offer better visibility and reduced atmospheric distortion. Ensure the viewing location offers an unobstructed view of the sun, free from trees, buildings, or mountains.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section addresses some common queries regarding total solar eclipses occurring after 2025, covering their frequency, duration, viewing safety, and optimal viewing locations. Understanding these aspects enhances the experience and ensures safe observation of this awe-inspiring celestial event.
Best Places to View a Total Solar Eclipse After 2025
Several locations worldwide offer excellent viewing opportunities for total solar eclipses after 2025. North America, South America, and parts of Asia and Africa will experience these events. For example, the path of totality for a future eclipse might cross through regions of the United States offering clear skies and established infrastructure for eclipse tourism. Other promising locations include parts of South America known for their relatively low light pollution and potentially favorable weather conditions during eclipse season. Specific locations will depend on the exact date and path of the eclipse. Choosing a location with minimal cloud cover and readily accessible viewing sites is crucial for a successful observation.
Frequency of Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events at any given location. While a total solar eclipse occurs somewhere on Earth approximately every 18 months, any specific location may not witness one for decades, or even centuries. This rarity is due to the precise alignment required between the Sun, Moon, and Earth. The Moon’s orbit is not perfectly aligned with the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, so perfect alignment—necessary for a total eclipse—is infrequent. Furthermore, the Moon’s shadow is relatively small, meaning totality is only visible from a narrow path on Earth’s surface.
Duration of a Total Solar Eclipse
The duration of totality—the period when the Sun is completely obscured by the Moon—varies considerably, ranging from a few seconds to a maximum of about 7.5 minutes. The duration depends on several factors, including the relative distances between the Sun, Moon, and Earth, and the Moon’s apparent size in the sky. A longer duration of totality occurs when the Moon is closer to the Earth (perigee) and the Sun is farther away (apogee). The specific location within the path of totality also affects the duration, with the longest durations occurring near the center of the path.
Safety Precautions for Viewing a Total Solar Eclipse, When Is The Total Eclipse After 2025
Viewing a solar eclipse without proper eye protection can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. It is crucial to never look directly at the Sun during any phase of a solar eclipse, except during the brief period of totality (when the Sun is completely covered). Safe viewing methods include using certified solar eclipse glasses that meet the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard. These glasses significantly reduce the intensity of sunlight, protecting your eyes. Alternatively, indirect viewing methods such as pinhole projectors can also be used. These methods project an image of the Sun onto a surface, allowing safe observation without direct eye exposure. It’s essential to prioritize eye safety and use appropriate viewing techniques to fully enjoy this extraordinary celestial event without risking vision impairment.