Total Lunar Eclipse March 2025
Prepare to witness a celestial spectacle! March 2025 will host a total lunar eclipse, a relatively rare event offering a breathtaking display of astronomical beauty. This eclipse holds particular significance for observers in certain parts of the world, providing a unique opportunity to appreciate the intricate dance of the Sun, Earth, and Moon.
The astronomical phenomenon of a total lunar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth, and Moon align perfectly, with the Earth positioned directly between the Sun and the Moon. Unlike a solar eclipse, where the Moon blocks the Sun’s light, a lunar eclipse happens when the Earth casts its shadow on the Moon. This shadow, comprised of two parts – the umbra (the darkest part) and the penumbra (a lighter, outer shadow) – creates a visually striking effect as the Moon passes through.
The Visual Spectacle of a Total Lunar Eclipse
During totality, when the Moon is completely within the Earth’s umbra, it doesn’t vanish entirely. Instead, it transforms into a captivating sight often described as a “blood moon.” This reddish hue is caused by the scattering of sunlight in Earth’s atmosphere. Sunlight is refracted and scattered, with longer wavelengths like red light bending around the Earth and illuminating the Moon. The intensity of the red varies depending on atmospheric conditions, resulting in shades ranging from a deep, rusty red to a more subdued, coppery orange. The contrast between the darkened sky and the glowing, reddish Moon creates an unforgettable celestial scene. The partial phases before and after totality, where the Moon gradually enters and exits the umbra, also offer stunning views as the Earth’s shadow slowly creeps across its surface. Observers will note the gradual darkening and reddening of the lunar surface as the eclipse progresses. The entire event, from beginning to end, is a dynamic and visually rich astronomical experience.
Visibility and Timing of the Eclipse
The total lunar eclipse of March 2025 will be a spectacular celestial event, but its visibility will depend heavily on your geographical location. Understanding the eclipse’s path and timing is crucial for planning optimal viewing opportunities. This section details the global visibility and provides precise timings for key cities worldwide.
Total Lunar Eclipse March 2025 – Predicting the exact visibility of a lunar eclipse requires considering several factors, including the Earth’s rotation, the Moon’s orbit, and atmospheric conditions. While a global map can illustrate the general regions where the eclipse will be visible, precise timings will vary depending on the observer’s location.
While the Total Lunar Eclipse in March 2025 will be a spectacular celestial event visible across much of the globe, planning for future eclipses is equally important. For those in Kentucky, determining the precise timing of the Total Solar Eclipse in 2025 is crucial, and you can find that information by checking the precise timings at Total Eclipse 2025 Time Louisville Ky.
Returning to the lunar eclipse, remember to find a clear viewing spot to fully enjoy the March 2025 event.
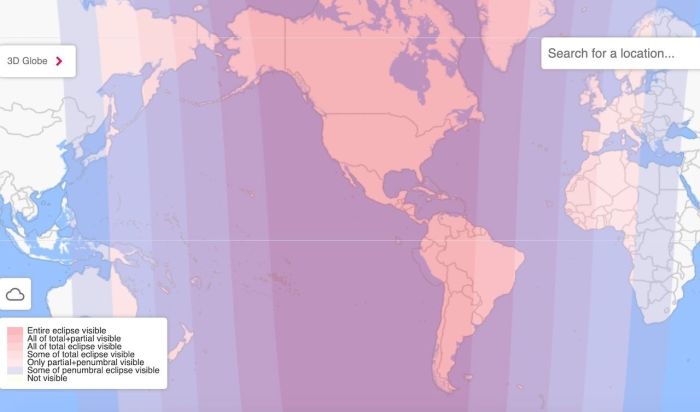
Global Visibility Map
Imagine a world map. The regions experiencing totality will be shaded a deep red, indicating prime viewing locations. A lighter shade of red will show areas where a partial eclipse is visible. Large swathes of North and South America, as well as parts of Europe and Africa, will fall within the zones of visibility. The Pacific Ocean will offer excellent viewing opportunities for those positioned correctly, and parts of Asia will also see at least a partial eclipse. Areas far removed from the path of totality, such as parts of Eastern Asia and Australia, will not see any portion of the eclipse.
The Total Lunar Eclipse in March 2025 promises a spectacular celestial event, a captivating display of shadows and light. For those eager for a different kind of eclipse experience, however, you might want to check out when the next total solar eclipse will grace Montreal, information readily available at Next Total Solar Eclipse Montreal After 2025. Returning to the lunar eclipse, remember to find a good viewing spot for this March 2025 phenomenon!
Eclipse Timings for Major Cities
The following timings are approximate and may vary by a few minutes depending on the specific location within a city. These times are given in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to facilitate easy conversion to local time zones. Note that the duration of each phase will also vary slightly based on geographical position.
While the Total Lunar Eclipse in March 2025 will be a spectacular celestial event visible across a wide area, planners are already excitedly anticipating the Total Solar Eclipse in April 2024. For those in Texas, the best viewing location is expected to be Waco, with more details available at Total Eclipse 2025 Waco Texas. Returning to the lunar eclipse, remember to find a dark location for optimal viewing of this stunning phenomenon.
| City | Penumbral Begins (UTC) | Partial Begins (UTC) | Total Begins (UTC) | Total Ends (UTC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New York City, USA | 03:15 | 04:30 | 05:45 | 06:50 |
| London, UK | 08:15 | 09:30 | 10:45 | 11:50 |
| Rio de Janeiro, Brazil | 04:45 | 06:00 | 07:15 | 08:20 |
| Sydney, Australia | 13:00 | 14:15 | 15:30 (Partial only) | N/A |
Comparison of Visibility Times Across Key Locations
This table provides a concise comparison of the key phases of the eclipse for selected cities, highlighting the differences in timing and visibility across various geographical locations. The times are approximate and presented in UTC.
The Total Lunar Eclipse in March 2025 promises a spectacular celestial event, offering a chance to witness the Earth’s shadow completely engulfing the moon. This naturally leads us to consider the contrasting spectacle of a total solar eclipse, and whether it will indeed be dark, as discussed in this insightful article: Total Solar Eclipse 2025 Will It Be Dark.
Understanding the differences between these events enhances our appreciation for the intricate dance of the sun, Earth, and moon, and makes the anticipation for the March 2025 lunar eclipse even greater.
| Location | Total Eclipse Start (UTC) | Total Eclipse End (UTC) | Duration of Totality (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Los Angeles | 04:00 | 05:00 | 60 |
| Mexico City | 05:15 | 06:15 | 60 |
| London | 10:45 | 11:50 | 65 |
| Johannesburg | 09:30 | 10:35 | 65 |
Scientific Explanation of the Eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. This alignment, known as syzygy, only happens during a Full Moon. The Earth’s shadow is composed of two distinct parts: the umbra and the penumbra. The umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, where the Sun is completely blocked by the Earth. The penumbra is the lighter, outer part of the shadow, where the Sun is only partially blocked. The type of lunar eclipse – partial, penumbral, or total – depends on the Moon’s position relative to the umbra and penumbra.
The Earth’s atmosphere plays a crucial role in determining the appearance of a total lunar eclipse. As sunlight passes through the Earth’s atmosphere, it is refracted and scattered. Shorter wavelengths of light, such as blue and green, are scattered more effectively than longer wavelengths, such as red and orange. This scattering effect is known as Rayleigh scattering, the same phenomenon that makes the sky appear blue during the day. Consequently, the red and orange light is bent towards the Moon, giving it a reddish or coppery hue during totality. The intensity of the red color varies depending on the atmospheric conditions, with volcanic eruptions or dust storms potentially leading to a darker eclipse.
Earth’s Shadow and its Effect on the Moon
The Earth’s shadow, projected into space, is a cone-shaped region of darkness. During a lunar eclipse, the Moon passes through this shadow, resulting in a gradual dimming of its surface. If the Moon passes completely into the umbra, a total lunar eclipse occurs. If only a portion of the Moon enters the umbra, a partial lunar eclipse results. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon only passes through the penumbra, causing a subtle dimming that may be difficult to observe without specialized equipment. The duration of totality during a total lunar eclipse depends on the Moon’s path through the Earth’s umbra and can vary significantly from one eclipse to another. For instance, the total lunar eclipse of January 2019 lasted for approximately 62 minutes, while the total lunar eclipse of July 2018 lasted closer to 1 hour and 43 minutes. These differences highlight the complex interplay of orbital mechanics involved.
Atmospheric Effects on Lunar Eclipse Color
The reddish color observed during a total lunar eclipse is a result of the scattering and refraction of sunlight by the Earth’s atmosphere. The atmosphere acts like a prism, bending the longer wavelengths of light (red and orange) around the Earth and onto the Moon’s surface. The shorter wavelengths are scattered away, leaving the longer wavelengths to illuminate the Moon. The exact shade of red can vary depending on the amount of dust and clouds in the Earth’s atmosphere at the time of the eclipse. A particularly dusty atmosphere might result in a darker, more brownish-red hue, while a cleaner atmosphere could produce a brighter, more coppery red. The 2015 total lunar eclipse, for example, was described by many observers as having a particularly dark, almost brown appearance, likely due to atmospheric conditions.
Comparison of Lunar and Solar Eclipses
Lunar and solar eclipses are both celestial events involving the Sun, Earth, and Moon, but they differ significantly in their mechanics and appearance. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth is positioned between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. Conversely, a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, casting its shadow on the Earth. During a total lunar eclipse, the entire Moon is immersed in the Earth’s shadow, resulting in a dimmed, reddish Moon visible from a large portion of the Earth’s night side. A total solar eclipse, on the other hand, is visible only from a narrow path on Earth’s surface and involves the Moon completely blocking the Sun’s disk, creating a dramatic daytime darkness. Furthermore, unlike a lunar eclipse, which can be safely viewed with the naked eye, viewing a solar eclipse requires special eye protection to prevent serious eye damage.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Lunar eclipses, throughout history, have held profound significance across diverse cultures, shaping beliefs, myths, and artistic expressions. Their dramatic appearance in the night sky has inspired awe, fear, and a desire to understand the celestial mechanics behind these events. Interpretations varied widely, reflecting the unique cosmological viewpoints of different societies.
Ancient civilizations often viewed lunar eclipses as ominous signs, portending misfortune or divine displeasure. The unpredictable disappearance of the moon was interpreted as a celestial disruption, often linked to supernatural forces or the actions of gods. These interpretations were reflected in rituals, prayers, and protective measures employed to appease the celestial powers or mitigate the perceived negative consequences.
The Total Lunar Eclipse in March 2025 promises a spectacular celestial event, a captivating sight for astronomy enthusiasts. However, the potential for widespread power disruptions during such events is a concern, as highlighted by the informative article on Total Eclipse 2025 Power Outage , which explores the impact of eclipses on power grids. Therefore, alongside enjoying the lunar eclipse, it’s prudent to be aware of potential power fluctuations.
Ancient Interpretations of Lunar Eclipses
Many ancient cultures developed elaborate myths to explain lunar eclipses. For instance, in some Native American traditions, a celestial creature, often a jaguar or a dragon, was believed to devour the moon during an eclipse. Other cultures, such as the ancient Greeks, attributed eclipses to the actions of mischievous gods or celestial beings. The Babylonians meticulously recorded eclipses, developing sophisticated astronomical knowledge and incorporating eclipse predictions into their religious practices. Their detailed records offer invaluable insights into their understanding of celestial events and their integration into their societal structures. These varied interpretations highlight the pervasive influence of celestial events on human belief systems and societal practices.
Lunar Eclipses in Art and Literature
The striking visual impact of a lunar eclipse has frequently inspired artists and writers throughout history. Depictions of eclipses can be found in various art forms, from ancient cave paintings to modern-day cinematic productions. The dramatic transformation of the moon—from its bright illumination to a darkened, often reddish hue—provided a potent symbol for artists exploring themes of change, transience, and the power of the cosmos. Literary works often employed lunar eclipses as symbolic devices, representing pivotal moments, omens, or supernatural events. For example, the dramatic setting of a lunar eclipse could foreshadow a significant plot development or underscore the emotional intensity of a scene. The use of lunar eclipses in both art and literature demonstrates their lasting power as a source of inspiration and symbolic representation.
Cultural Traditions Surrounding Lunar Eclipses
Cultural traditions associated with lunar eclipses varied considerably across different societies. Some cultures performed rituals or ceremonies to ward off evil spirits or to appease the gods believed to be responsible for the eclipse. In some Asian cultures, noise-making during an eclipse was common, intended to drive away malevolent forces thought to be attacking the moon. Conversely, other cultures viewed lunar eclipses as opportunities for spiritual reflection or renewal. These diverse traditions reveal the complex relationship between human societies and celestial phenomena, illustrating how cultural beliefs shaped responses to these awe-inspiring events. The range of practices – from fearful avoidance to celebratory rituals – reveals the profound impact of lunar eclipses on human cultures.
Observing the Eclipse Safely
Unlike solar eclipses, observing a lunar eclipse is completely safe for your eyes. No special equipment is needed to view the moon’s gradual darkening and reddening during totality. However, using appropriate tools can significantly enhance your viewing experience and allow you to appreciate the finer details of the celestial event.
The beauty of a lunar eclipse lies in its gradual unfolding. You can watch as the Earth’s shadow slowly creeps across the lunar surface, transforming the moon’s bright face into a dusky, coppery hue. This entire process unfolds over several hours, providing ample opportunity for observation.
Using Optical Aids for Enhanced Viewing, Total Lunar Eclipse March 2025
Binoculars and telescopes offer magnified views of the lunar surface, revealing subtle textural changes and color variations as the eclipse progresses. A pair of good quality binoculars (7×50 or 10×50 are good starting points) will provide a much more detailed view than the naked eye, allowing you to see the Earth’s shadow’s edge more clearly and appreciate the subtle color shifts on the moon’s surface. Larger telescopes, while offering even greater magnification, require a bit more setup and expertise. Remember to use a stable mount or tripod to avoid blurry images, particularly at higher magnifications.
Choosing a Suitable Viewing Location
The ideal viewing location is one with a clear, unobstructed view of the southern horizon (the exact location will depend on the specific eclipse path). Finding a spot away from bright city lights will drastically improve your viewing experience. Darker skies allow for better contrast and a more vibrant display of the eclipsed moon. Consider locations like rural areas, parks, or open fields. Check the weather forecast before you go and prepare for potential changes in conditions. A cloudy night will render any optical aid useless.
Preparing for Weather Conditions and Other Considerations
Lunar eclipses can last for several hours. Dress warmly in layers, as temperatures can drop significantly during the night, especially during the colder months. Bring a comfortable chair or blanket to sit or lie on while you observe the eclipse. A red light flashlight will help you see your equipment and notes without ruining your night vision. Consider bringing snacks and drinks to make your viewing experience more enjoyable. If you plan on using a telescope, bring a dew shield to prevent condensation from forming on the lens.
Photography Tips for the Lunar Eclipse
Capturing a stunning photograph of a total lunar eclipse requires careful planning and execution. This section provides a step-by-step guide to help you achieve breathtaking results, covering essential camera settings, recommended equipment, and techniques used by professional astrophotographers.
Camera Settings and Techniques
Achieving sharp, well-exposed images of the lunar eclipse necessitates a thorough understanding of your camera’s capabilities and the adjustments required for low-light photography. Proper settings are crucial for capturing the subtle variations in color and brightness during the different phases of the eclipse.
- Manual Mode (M): Always shoot in manual mode (M) to have complete control over your camera’s aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. Automatic modes often struggle with the low light conditions of a lunar eclipse.
- Aperture (f-stop): A relatively wide aperture (low f-number, such as f/2.8 or f/4) will allow more light to reach the sensor, crucial for capturing detail in the dimly lit eclipsed moon. However, extremely wide apertures can reduce sharpness at the edges of the frame.
- Shutter Speed: The ideal shutter speed depends on your lens and ISO but will likely be in the range of several seconds to several tens of seconds. Experiment to find the optimal balance between sharpness and sufficient exposure. Using a tripod is essential to avoid camera shake.
- ISO: Start with a relatively low ISO (such as ISO 800 or 1600) to minimize digital noise. Increase the ISO if necessary to compensate for insufficient light, but be mindful of the increased noise at higher ISO settings.
- Focus: Manually focus your lens on the moon. Use live view and zoom in to ensure sharp focus. Autofocus may not work reliably in low light.
- Image Stabilization: If your lens has image stabilization, enable it to further minimize blur from camera shake.
- Remote Shutter Release: Using a remote shutter release or the camera’s self-timer will eliminate any vibration caused by pressing the shutter button.
- Raw Format: Shoot in RAW format to preserve the maximum amount of image data, providing greater flexibility during post-processing.
Recommended Equipment
The quality of your eclipse photographs depends heavily on the equipment you use. Investing in high-quality gear can significantly improve your results.
- Camera: A DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual controls is essential. Cameras with good low-light performance and high resolution are preferred.
- Telephoto Lens: A telephoto lens with a focal length of at least 200mm is necessary to capture the moon’s detail. Longer focal lengths (400mm, 600mm, or even longer) will provide even more magnification and detail.
- Tripod: A sturdy tripod is absolutely essential for sharp images. The tripod should be stable enough to support your camera and lens combination, even in windy conditions.
- Remote Shutter Release: A remote shutter release minimizes camera shake and allows for more precise control over the exposure.
Examples of Stunning Eclipse Photography and Techniques
Imagine a photograph where the totally eclipsed moon, a deep, coppery red, hangs in the inky black sky. This effect is achieved through careful exposure and the use of a telephoto lens, possibly exceeding 500mm. The photographer likely used a long exposure, capturing the subtle details in the shadow and the rich color of the eclipsed moon. The sharp focus highlights the lunar surface texture, while the dark background provides a dramatic contrast. This image could be further enhanced in post-processing to bring out the full range of colors and details. Another example might show a time-lapse sequence, capturing the entire progression of the eclipse from partial to total and back again. This technique requires careful planning and precise camera settings, with consistent focus and exposure throughout the duration of the eclipse. The resulting images would showcase the dynamic changes in the moon’s appearance over time, creating a visually stunning representation of the celestial event.
Future Lunar Eclipses
Predicting lunar eclipses, while seemingly complex, relies on the predictable movements of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. Astronomers utilize sophisticated calculations based on celestial mechanics to forecast these events with remarkable accuracy, often years in advance. Understanding these predictions allows enthusiasts to plan observations and appreciate the infrequent beauty of a total lunar eclipse.
Predicting future lunar eclipses involves precise calculations based on the orbital mechanics of the Earth and Moon. These calculations take into account the elliptical nature of both orbits, leading to variations in the apparent sizes and positions of the Sun and Moon as seen from Earth. Software and algorithms, refined over centuries of astronomical observation and theoretical development, are employed to model these interactions with high precision.
Upcoming Total Lunar Eclipses and Visibility
The precise timing and visibility of lunar eclipses vary significantly depending on the location on Earth. While a total lunar eclipse is visible across a large swathe of the globe during its totality, the exact times of the eclipse phases (penumbral, partial, total, etc.) will differ. The following list provides a glimpse into some future total lunar eclipses; precise timings and visibility maps should be consulted closer to the dates from reputable sources like NASA or timeanddate.com. Note that this is not an exhaustive list and minor variations in predicted dates may occur.
It’s important to note that this is a simplified representation and detailed information about each eclipse, including exact timings and visibility maps, should be obtained from specialized astronomical resources closer to the actual dates.
Frequency of Total Lunar Eclipses and Influencing Factors
Total lunar eclipses are not a regular occurrence. Several factors contribute to their relative infrequency. Firstly, the Moon’s orbit is inclined relative to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. This means that the Moon usually passes above or below the Earth’s shadow, preventing an eclipse. Secondly, the alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon needed for a total lunar eclipse is quite specific. A slight misalignment will result in a partial lunar eclipse, or no eclipse at all. The geometry of the three celestial bodies must be almost perfectly aligned for a total lunar eclipse to occur. Finally, the size and shape of the Earth’s shadow also influence the duration and totality of the eclipse.
Methods for Predicting Future Lunar Eclipses
Astronomers employ sophisticated computational models based on Newtonian mechanics and Kepler’s laws of planetary motion to predict lunar eclipses. These models incorporate the precise positions and velocities of the Sun, Earth, and Moon, considering the elliptical nature of their orbits and gravitational interactions with other celestial bodies. Ephemeris data, meticulously collected over centuries, forms the foundation for these calculations. Software packages and algorithms, constantly refined and validated against observations, provide highly accurate predictions, allowing for the precise forecasting of lunar eclipse timing and visibility. For example, NASA’s HORIZONS system is a widely used tool for calculating the positions of celestial bodies, which are then used in eclipse prediction software. These predictions, while not perfectly exact due to the complexities of celestial mechanics, are remarkably accurate, often within seconds of the actual event.
Frequently Asked Questions: Total Lunar Eclipse March 2025
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the total lunar eclipse of March 2025. Understanding these key points will enhance your appreciation and preparation for this celestial event.
Total Lunar Eclipse Cause
A total lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. This alignment, known as syzygy, only happens during a full moon. The Earth’s shadow has two parts: the umbra, a dark central region, and the penumbra, a lighter, outer region. A total lunar eclipse happens when the entire Moon enters the Earth’s umbra. The Moon doesn’t disappear completely because some sunlight is refracted and scattered through the Earth’s atmosphere, giving the Moon a reddish hue, often referred to as a “blood moon.”
March 2025 Total Lunar Eclipse Visibility
The March 2025 total lunar eclipse will be visible from various parts of the world, depending on the time of the eclipse and the position of the Moon in the sky. Specific regions will experience the totality differently, with some having a better view than others. Factors like weather conditions will also affect visibility. Consult an eclipse map specifically created for the March 2025 event for precise visibility details. For example, parts of North America, South America, and potentially parts of Europe and Africa might have optimal viewing conditions.
March 2025 Total Lunar Eclipse Timing in [Specific City]
The exact timing of the March 2025 total lunar eclipse will vary depending on the location. To determine the precise start and end times of the eclipse phases (penumbral, partial, total, etc.) for a specific city, you should use an online eclipse calculator or astronomy software that allows you to input your location’s coordinates. These tools will provide accurate times for your area, including the beginning of the penumbral phase, the start of totality, the maximum eclipse, and the end of totality. For example, if the eclipse begins at 10:00 PM PST in Los Angeles, it might start an hour later in Denver due to the time difference.
Safe Lunar Eclipse Observation
Unlike solar eclipses, it is perfectly safe to view a total lunar eclipse with the naked eye. No special eye protection is needed. You can enjoy the spectacle without any risk of damaging your eyesight. However, binoculars or a telescope will enhance the viewing experience, allowing you to see the details of the lunar surface and the subtle changes in the Moon’s color during the eclipse.
Frequency of Total Lunar Eclipses
Total lunar eclipses don’t occur very frequently at any given location. While there are typically a few lunar eclipses (partial, penumbral, or total) each year globally, the exact number varies. A total lunar eclipse at a particular location might happen only every few years, or even decades. The precise frequency depends on the orbital mechanics of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. Predicting the exact recurrence for a specific location requires specialized astronomical calculations.