Path of the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse
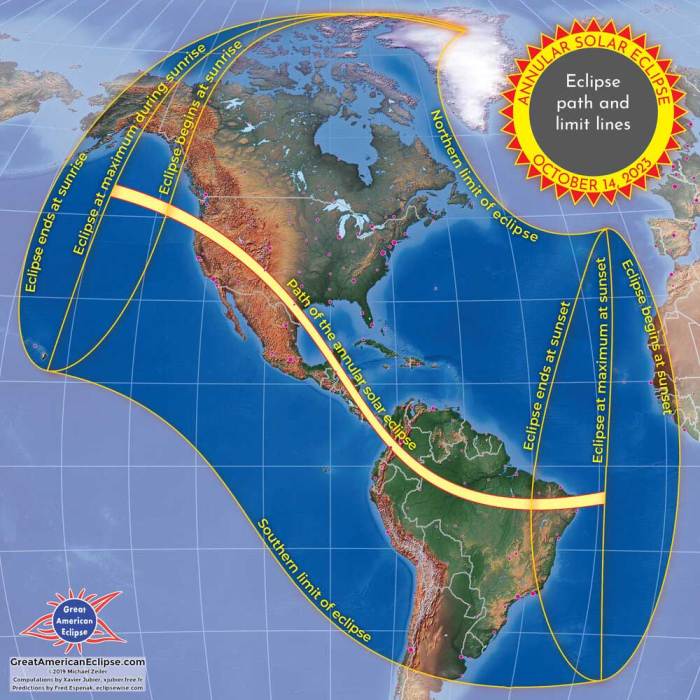
The total solar eclipse of April 8, 2025, will traverse a significant portion of the North American continent, offering a spectacular celestial event for millions. The path of totality, where the sun will be completely obscured by the moon, will begin in the Pacific Ocean and cross over land in several countries. This path offers diverse viewing opportunities, ranging from remote wilderness areas to bustling cityscapes.
Geographical Path of Totality
The path of totality for the April 8, 2025, total solar eclipse begins in the Pacific Ocean, making landfall in the western United States. It then sweeps across several states including California, Nevada, Utah, Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, North Carolina, and South Carolina before exiting over the Atlantic Ocean. Internationally, the eclipse will also be visible from Mexico. Specific cities along the path include, but are not limited to, Mazatlan, Mexico; Reno, Nevada; Denver, Colorado; Kansas City, Missouri; Nashville, Tennessee; and Charlotte, North Carolina. The precise timing and duration of totality will vary depending on the observer’s location within this path.
Map of the Eclipse Path
Imagine a map of North America. A relatively narrow band, representing the path of totality, stretches diagonally across the continent. The band begins in the Pacific Ocean, near the west coast of Mexico, and then crosses through the western United States, following a roughly northeast direction. Key cities, marked with small circles or stars, are clearly visible within this band, highlighting the major population centers where the total eclipse will be visible. The band continues to move eastward, passing through the central and southern United States, and eventually exiting into the Atlantic Ocean near the southeastern coast. The shading of the map would gradually darken from light gray at the edges to a deep shade of gray within the band of totality, clearly depicting the area of total eclipse visibility. Smaller, lighter gray areas surrounding the path of totality would indicate locations experiencing a partial solar eclipse.
Duration of Totality
The duration of totality, the period when the sun is completely blocked by the moon, varies along the eclipse path. Generally, the longest durations of totality will occur near the center of the path. For example, locations near the center line in central Kansas might experience totality for around 4 minutes, whereas locations closer to the edges of the path, perhaps in northern California or South Carolina, may see totality for only around 2 minutes or less. This difference is due to the geometry of the sun, moon, and Earth’s position during the eclipse. The precise duration at each location can be calculated using specialized astronomical software or eclipse prediction websites.
Peak Eclipse Time in Major Cities
The exact time of the peak eclipse will vary depending on the location. However, approximate peak times for several major cities along the path of totality might include: Mazatlan, Mexico, around midday; Reno, Nevada, in the early afternoon; Denver, Colorado, in the early afternoon; Kansas City, Missouri, in the mid-afternoon; Nashville, Tennessee, in the late afternoon; and Charlotte, North Carolina, in the late afternoon. These are approximate times and should be verified using precise astronomical calculations closer to the date of the eclipse. Local time zones will significantly influence the precise observation time.
Viewing the Eclipse Safely
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety. Looking directly at the sun, even for a short time, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. Never underestimate the sun’s power; safe viewing practices are paramount.
Safe Methods for Viewing the Total Solar Eclipse
Directly viewing any portion of the sun during a partial eclipse is extremely dangerous. Only during the brief period of totality – when the moon completely blocks the sun’s disk – is it safe to view the eclipse without eye protection. Even then, it is advisable to use ISO 12312-2 certified solar filters. During the partial phases of the eclipse, and at all other times except totality, you must use appropriate eye protection.
Certified Solar Eclipse Glasses
Certified solar eclipse glasses are essential for safe viewing of the partial phases of a solar eclipse. These glasses are specifically designed to filter out harmful ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation, as well as a significant portion of visible light, reducing the sun’s brightness to safe levels. Look for glasses with the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard printed on them. These glasses should be free from scratches or damage. Discard any glasses that are more than three years old or show any signs of wear and tear.
Path Of Next Total Solar Eclipse 2025 – Safe Viewing Checklist:
- Use only ISO 12312-2 certified solar eclipse glasses.
- Inspect glasses for any damage before use.
- Supervise children carefully while they are wearing eclipse glasses.
- Remove glasses only during the total phase of a total solar eclipse (if applicable).
- Never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection.
Creating a Pinhole Projector
A pinhole projector offers a safe and simple method for indirectly viewing the solar eclipse. This method projects an image of the sun onto a surface, eliminating the need to look directly at the sun.
Construction and Use:
To create a pinhole projector, you will need two pieces of cardboard, a pin or needle, and a sheet of white paper. Make a small hole (approximately 1mm in diameter) in the center of one piece of cardboard. This will be your pinhole. Then, hold the cardboard with the pinhole in front of a sheet of white paper, positioning it so that sunlight shines through the pinhole. The image of the sun will be projected onto the paper. You can adjust the distance between the cardboard and the paper to adjust the size of the projected image. For better results, use a larger cardboard box, creating a darker environment to enhance the projected image.
Diagram (Description): Imagine a small box, perhaps a shoebox, with one end open. A small hole is carefully punched in the center of the opposite end. The sunlight passes through this pinhole and projects a tiny, inverted image of the sun onto the inside of the open end of the box, where a sheet of white paper is placed. This projected image shows the sun’s shape and the progression of the eclipse safely and clearly.
The path of the next total solar eclipse in 2025 will traverse across North America, offering a spectacular celestial event. To help you plan your viewing, consider checking out this helpful resource for finding the Best Place To See Total Eclipse April 8 2025 , ensuring optimal viewing conditions. Securing a location along the eclipse’s path is crucial for witnessing this rare phenomenon.
Partial vs. Total Eclipse Viewing
Viewing a partial eclipse requires the use of certified solar eclipse glasses at all times. Looking directly at the sun during a partial eclipse, even for a few seconds, can cause severe eye damage. During a total solar eclipse, it is only safe to remove your eye protection during the brief period of totality, when the sun’s corona is visible. Before and after totality, certified solar filters must be used. The difference is crucial: during totality, you can see the sun’s corona, but during a partial eclipse, you are still looking at the intensely bright sun. Always prioritize safety.
The Science Behind the Eclipse
A total solar eclipse is a breathtaking celestial event resulting from a precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. Understanding the mechanics behind this phenomenon requires exploring the interplay of these three bodies and the resulting shadow cast upon our planet.
The astronomical mechanics of a total solar eclipse are governed by the relative positions and sizes of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light from reaching a specific region on Earth’s surface. This alignment is possible because, although the Sun is vastly larger than the Moon, the Moon is significantly closer to Earth. This creates a situation where the Moon’s apparent size in the sky is approximately equal to the Sun’s, allowing for a complete blockage of sunlight. The Earth’s curvature means that the total eclipse is only visible within a relatively narrow path on the surface of the planet.
Phases of a Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse unfolds in distinct phases. The partial phase begins as the Moon starts to encroach upon the Sun’s disk, gradually obscuring a portion of its light. As the Moon continues its transit, the partial phase progresses until the Moon completely covers the Sun, marking the onset of totality. Totality is a brief period of darkness, where the Sun’s corona—its outer atmosphere—becomes visible as a radiant halo. The eerie darkness during totality can be strikingly beautiful and often reveals stars and planets in the daytime sky. Following totality, the Moon begins to move away from the Sun’s disk, initiating the end of totality and the reverse of the partial phase. The partial phase continues until the Moon is no longer obstructing any part of the Sun, concluding the eclipse.
Total Solar Eclipses versus Annular Solar Eclipses
While both total and annular solar eclipses involve the Moon passing between the Sun and Earth, a key difference lies in the Moon’s distance from Earth. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon is close enough to Earth that its apparent size completely covers the Sun. In an annular eclipse, the Moon is farther away, resulting in its apparent size being smaller than the Sun’s. This means that during an annular eclipse, the Moon appears as a dark disk against the bright background of the Sun, creating a “ring of fire” effect. The difference in the Moon’s distance is due to the Moon’s elliptical orbit around the Earth.
Scientific Impact of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses provide invaluable opportunities for scientific research across multiple disciplines. For astronomers, totality offers a rare chance to study the Sun’s corona, a region normally obscured by the Sun’s intense brightness. Atmospheric scientists utilize eclipses to study changes in the Earth’s atmosphere, particularly temperature and wind patterns, as the sudden decrease in solar radiation creates a measurable impact. Furthermore, the precise alignment during an eclipse can contribute to advancements in gravitational physics and the testing of Einstein’s theory of general relativity. The shadow’s path, predicted with high accuracy, serves as a crucial validation of our understanding of celestial mechanics.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Solar eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events, have held profound significance across diverse cultures and throughout human history. Their dramatic appearance, transforming midday into twilight, has invariably sparked wonder, fear, and attempts at understanding their causes and implications. Interpretations varied widely, reflecting the cosmological beliefs and societal structures of each civilization.
From ancient times to the present, societies have grappled with the mystery of eclipses, developing unique responses based on their prevailing worldviews. Some cultures viewed them as ominous signs, portending disaster or the wrath of the gods, while others attributed them to celestial battles or the actions of mythical beings. These varied interpretations shaped rituals, myths, and societal reactions to these extraordinary events.
Ancient Mesopotamian Interpretations
Ancient Mesopotamians, meticulous record-keepers, meticulously documented eclipses in their cuneiform tablets. They viewed eclipses as negative omens, often associating them with the potential downfall of rulers or societal upheaval. Their detailed records, however, also provide valuable insights into their astronomical observations and attempts to predict these celestial events. The regularity of eclipse occurrences, noted over centuries, gradually allowed them to develop rudimentary prediction methods. For example, the appearance of a solar eclipse might trigger elaborate rituals aimed at appeasing the gods and averting calamity.
Chinese Mythology and Eclipses
In ancient China, eclipses were interpreted as a celestial dragon devouring the sun. This belief led to the development of unique customs designed to scare the dragon away. The beating of drums and gongs, along with the firing of arrows into the sky, were common practices intended to drive away the mythical beast and restore the sun’s light. These rituals highlight the deep-seated fear and anxiety eclipses could evoke, even while simultaneously demonstrating an attempt to exert control over the seemingly uncontrollable forces of nature. Furthermore, Chinese astronomers developed sophisticated methods for predicting eclipses, using sophisticated mathematical models to calculate their occurrence.
Eclipse Myths in the Americas
Various indigenous cultures in the Americas developed rich mythologies surrounding eclipses. For instance, some cultures believed that the sun and moon were engaged in a celestial battle during an eclipse. Others viewed the event as a sign of a significant shift in the cosmic order, requiring specific rituals to restore balance. These narratives, passed down through generations, reveal a complex interplay between astronomical observation and spiritual beliefs. These myths, often intertwined with creation stories, shaped cultural understanding and provided a framework for interpreting the world around them. The specific narratives varied greatly depending on the region and specific indigenous group.
Modern Understanding and Prediction
Today, our understanding of solar eclipses is rooted in scientific principles. We know they occur when the moon passes between the sun and the earth, casting a shadow on the planet’s surface. Accurate predictions are now possible thanks to advanced astronomical models and computational tools, allowing us to know precisely when and where a total solar eclipse will occur, years in advance. While the awe and wonder associated with these events remain, the fear and uncertainty of the past have been largely replaced by scientific curiosity and appreciation for the intricate mechanics of the cosmos.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Trip
Planning a trip to witness a total solar eclipse is an exciting endeavor, requiring careful consideration of various factors to ensure a safe and memorable experience. This section will guide you through the process, providing practical advice and resources to make your eclipse-viewing adventure a success. Remember that careful planning is key to maximizing your enjoyment and minimizing potential disruptions.
Sample Itinerary: A Trip to Mazatlan, Mexico for the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse
Let’s assume you’re planning to view the total solar eclipse of April 8, 2025, from Mazatlan, Mexico, a city along the path of totality. This itinerary provides a framework; you can adjust it based on your preferences and budget.
Day 1: Arrival and Exploration
Arrive at General Rafael Buelna International Airport (MZT) in Mazatlan. Check into your pre-booked hotel near the beach or in the historic center. Spend the afternoon exploring the city, visiting the Malecon (boardwalk), and enjoying the local cuisine.
The path of the next total solar eclipse in 2025 will traverse across North America, offering a spectacular celestial event. Planning your viewing location is crucial, but equally important is considering what to wear for optimal comfort and protection. For practical advice on appropriate attire, consult this helpful guide: Total Eclipse 2025 What To Wear. Remember to dress in layers for varying temperatures and choose clothing that protects you from the sun.
Careful preparation will ensure you fully enjoy the Path of Next Total Solar Eclipse 2025.
Day 2: Eclipse Day!
Wake up early and secure your viewing spot. Many locations in Mazatlan offer excellent views. Remember to wear your eclipse glasses at all times except during the brief period of totality. After the eclipse, celebrate with a festive meal and reflect on the awe-inspiring event.
The path of the next total solar eclipse in 2025 will be a remarkable event, traversing several continents. A key date to remember within this celestial journey is the April 8th, 2025, total eclipse, details of which you can find on this informative website: April 8th 2025 Total Eclipse. Understanding this specific event helps us better appreciate the broader scope of the 2025 eclipse path and its global impact.
Day 3: Departure
The path of the next total solar eclipse in 2025 traverses North America, offering a spectacular celestial event for many. A significant portion of this path crosses through Canada, with prime viewing locations readily available; for those interested in Ontario specifically, check out this helpful resource on the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse Ontario for detailed information.
Planning your viewing spot along the eclipse’s path will ensure you witness this incredible natural phenomenon.
Enjoy a final breakfast in Mazatlan before heading to the airport for your departure.
Eclipse Trip Resources
Planning a successful eclipse viewing trip involves utilizing several reliable resources.
Websites offering valuable information include:
- NASA’s Eclipse Website: Provides detailed information on eclipse paths, timings, and safety guidelines.
- TimeandDate.com: Offers precise eclipse times for specific locations and interactive maps.
- EclipseWise.com: A comprehensive resource for eclipse enthusiasts, featuring historical data and future predictions.
Consider contacting specialized travel agencies that organize eclipse-viewing tours. These agencies often handle logistics, accommodation, and transportation, making your trip more convenient.
The path of the next total solar eclipse in 2025 will traverse North America, offering a spectacular celestial event. Scientists are already preparing, and you can learn more about their early findings from NASA in this insightful article: Nasa Scientists Share Early Findings From 2025 North American Total Solar Eclipse. This research will undoubtedly enhance our understanding and appreciation of this upcoming astronomical phenomenon, making planning for optimal viewing along the eclipse’s path even more precise.
Logistical Aspects of Planning an Eclipse Viewing Trip
Several key logistical elements need careful consideration.
Travel Arrangements: Book flights and transportation well in advance, especially if traveling during peak season. Consider various transportation options, including flights, trains, buses, or rental cars, depending on your destination and budget. Secure your travel insurance.
Accommodation: Book your hotel or other accommodation well in advance, as prices tend to surge during eclipse events. Research locations along the path of totality and choose accommodations based on your preferences and budget. Confirm cancellation policies.
Safety Considerations: Prioritize your safety. This includes obtaining and using certified ISO 12312-2 compliant eclipse glasses. Research the local weather forecast and pack accordingly. Be aware of your surroundings and take necessary precautions to protect yourself from the elements and potential hazards.
Utilizing Online Resources for Weather Forecasts and Eclipse Viewing Locations
The internet provides invaluable tools for planning your eclipse viewing trip.
Weather Forecasts: Utilize reputable weather websites such as AccuWeather, The Weather Channel, or local meteorological services to check weather forecasts for your chosen viewing location in the days leading up to the eclipse. Look for forecasts that predict clear skies for optimal viewing conditions. Remember that weather can be unpredictable, so having a backup plan is advisable.
Eclipse Viewing Locations: Use interactive maps provided by NASA’s eclipse website or TimeandDate.com to identify locations along the path of totality. Consider factors such as accessibility, crowd size, and potential obstructions when choosing your viewing spot. Explore images and videos of previous eclipses from the location to get an idea of what to expect.
Photography and Astrophotography: Path Of Next Total Solar Eclipse 2025
Capturing a total solar eclipse is a rewarding photographic challenge, demanding careful planning and the right equipment. The fleeting nature of totality, coupled with the extreme brightness contrast between the sun and its corona, presents unique difficulties for both casual photographers and astrophotographers. This section will explore techniques and strategies for successfully documenting this celestial event.
Photographing the different phases of a solar eclipse requires a nuanced approach, varying the equipment and settings as the event progresses. The partial phases, before and after totality, require specialized solar filters to protect both your equipment and your eyes. Totality, however, offers a brief window of opportunity to photograph the sun’s corona without filters, revealing its intricate structure.
Equipment Recommendations and Settings
Choosing the right equipment is crucial for capturing stunning eclipse images. A DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual control over aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is ideal. For the partial phases, a telephoto lens (at least 300mm) with a securely attached solar filter is essential. Consider using a sturdy tripod to avoid camera shake. During totality, you can remove the solar filter to capture the corona, but be mindful of the sudden increase in light intensity. Experiment with different shutter speeds and ISO settings to find the optimal balance between exposure and image quality. For wider shots incorporating the landscape, a shorter lens can be used, again with a solar filter during the partial phases.
Capturing the Different Phases of the Eclipse
The partial phases require careful exposure adjustments to avoid overexposing the bright sun. Start with a fast shutter speed (e.g., 1/4000th of a second) and a small aperture (e.g., f/8-f/11) and a low ISO (e.g., 100). As the eclipse progresses, you may need to adjust these settings to maintain proper exposure. During totality, the exposure settings will change drastically. You’ll need to significantly increase the exposure time (several seconds) to capture the faint corona. Experimentation is key; test shots before totality are highly recommended. Remember to refit your solar filter immediately after totality ends. Using a smartphone, dedicated apps offering manual control and the use of a suitable solar filter attachment can provide decent results, but the quality will be limited by the smartphone’s camera capabilities.
Challenges of Astrophotography During a Solar Eclipse and Strategies to Overcome Them
Astrophotography during a solar eclipse presents several unique challenges. The extreme brightness contrast between the sun and the corona makes achieving proper exposure difficult. Precise focusing is also crucial, as the corona’s details are easily lost with a slightly out-of-focus image. Atmospheric conditions, including haze and turbulence, can significantly impact image quality. To overcome these challenges, careful planning and precise technique are vital. Using a sturdy tripod, remote shutter release, and image stabilization techniques are crucial. Post-processing techniques, such as stacking multiple images, can help to reduce noise and enhance details. Knowing the predicted weather conditions at your viewing location is also critical for success.
Examples of Stunning Images of Previous Total Solar Eclipses
Many stunning images of past total solar eclipses showcase the dramatic beauty of the event. For example, images from the 2017 total solar eclipse across the United States often showed the sun’s corona extending far beyond the eclipsed sun, displaying intricate streamers and delicate structures. These images were likely captured using high-quality telephoto lenses and long exposures during totality. The photographer’s skill in choosing the right composition and adjusting exposure settings is evident in the rich detail and dynamic range of these images. Other notable examples from various eclipses showcase the diverse beauty of the corona, influenced by the sun’s activity and atmospheric conditions. The careful composition of the images, often incorporating the landscape, further enhances their visual impact. Many of these images would have involved post-processing to bring out subtle details and enhance color.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses some common questions about the 2025 total solar eclipse, providing clear and concise answers to help you prepare for this celestial event. Understanding the phenomenon, its frequency, safe viewing practices, and necessary equipment will ensure a safe and memorable experience.
Total Solar Eclipses Explained
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and the Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light. This only happens when the Moon is at its closest point to Earth in its orbit (perigee), creating an apparent size large enough to cover the Sun’s disk. The result is a dramatic darkening of the sky, revealing the Sun’s corona – its outer atmosphere – which is usually invisible to the naked eye. During totality, the temperature drops noticeably, and animals often react to the sudden change in light.
Frequency of Total Solar Eclipses, Path Of Next Total Solar Eclipse 2025
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events at any given location. While they occur somewhere on Earth roughly every 18 months, a specific location might only experience one every few hundred years. This rarity is due to the precise alignment required between the Sun, Moon, and Earth. The path of totality, where the total eclipse is visible, is also quite narrow, typically only a few hundred kilometers wide.
Safe Viewing Locations for the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse
The 2025 total solar eclipse will traverse a path across several regions. Specific locations within the path of totality, offering optimal viewing conditions, will be widely publicized closer to the date. However, remember that *safe viewing practices are paramount regardless of location*. This means using certified solar eclipse glasses at all times when viewing the partial phases of the eclipse, even in locations with indirect sunlight. Never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection. Regions along the path of totality in North America, for instance, will experience peak viewing conditions, but appropriate safety precautions must be followed everywhere.
Essential Equipment for Safe Eclipse Viewing
Safe viewing of a solar eclipse requires specialized equipment. Crucially, this means using only certified ISO 12312-2 rated solar eclipse glasses. These glasses are specifically designed to filter out harmful solar radiation, preventing eye damage. Regular sunglasses, even very dark ones, are *not* sufficient and should never be used to view the sun. Improper eye protection can lead to serious and permanent vision impairment. Ensure your glasses are from a reputable supplier and check for the ISO certification before using them.