Total Lunar Eclipse 2025
The year 2025 will witness a celestial event captivating skywatchers worldwide: a total lunar eclipse. This phenomenon, where the Earth passes directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow that completely obscures the lunar surface, offers a breathtaking spectacle. Understanding the date, visibility, and optimal viewing locations is crucial for anyone hoping to witness this astronomical marvel.
Total Lunar Eclipse 2025: Date and Time
While the precise date and time will vary slightly depending on the location, the total lunar eclipse of 2025 will occur on the night of September 7th and into the early morning hours of September 8th. The exact timing of totality (when the Moon is completely within the Earth’s umbral shadow) will depend on the observer’s geographical position. For example, observers in North America will experience the total eclipse later in the night than those in Europe or Africa. Detailed calculations for specific locations can be found on reputable astronomical websites and apps dedicated to celestial events.
Total Lunar Eclipse 2025: Global Visibility
A world map illustrating the visibility of the total lunar eclipse would show a large portion of the globe experiencing at least partial visibility. The Americas, Europe, Africa, and parts of Asia will have prime viewing opportunities. The duration of visibility will vary greatly depending on the observer’s location. For instance, those in central North America might witness the total eclipse for a longer duration compared to those on the eastern or western fringes of the visible area. Regions experiencing only partial eclipses will see a portion of the moon covered by the Earth’s shadow. A graphic representation would display varying shades of color, representing the degree of visibility, across different regions. The darkest areas would indicate complete visibility, while lighter areas would denote partial visibility or no visibility at all.
Optimal Viewing Locations for the Total Lunar Eclipse 2025
To ensure optimal viewing, several factors need to be considered. Firstly, weather conditions play a significant role. Clear skies are essential for a clear view of the eclipse. Locations with typically clear skies during September, such as high-altitude deserts or certain regions with low humidity, would be ideal. Secondly, light pollution significantly impacts visibility. Areas far from urban centers, with minimal artificial light, offer much darker skies, making the eclipse more visible and spectacular. Locations such as national parks or remote observatories are excellent choices. For example, areas in the southwestern United States, parts of the Andes Mountains, or certain areas of Australia are known for their dark skies and relatively predictable weather during September, making them potentially excellent viewing spots. However, one should always check local weather forecasts closer to the date of the eclipse to make an informed decision.
Understanding the Lunar Eclipse Phenomenon
A lunar eclipse is a celestial event that occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. This alignment, only possible during a full moon, results in a temporary obscuring of the Moon’s light, creating a visually striking spectacle in the night sky. The specifics of what we see depend on the degree to which the Earth’s shadow covers the Moon.
The mechanics of a total lunar eclipse hinge on the precise alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. The Sun’s rays illuminate the Earth, and the Earth, in turn, casts two shadows: the umbra and the penumbra. The umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, where sunlight is completely blocked by the Earth. The penumbra is the outer, fainter part of the shadow, where only a portion of the sunlight is blocked. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the full Moon passes entirely through the Earth’s umbra.
Stages of a Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse unfolds in distinct stages, each characterized by a different degree of shadow coverage on the Moon. The process begins with the penumbral phase, gradually progresses through a partial eclipse, and culminates in totality if the alignment is perfect. The reverse sequence then occurs as the Moon exits the Earth’s shadow.
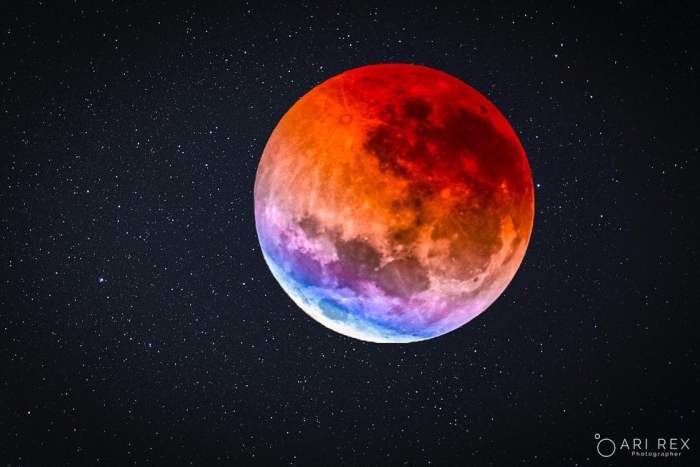
The penumbral phase is subtle; the Moon appears slightly dimmer, a change often imperceptible to the naked eye. The partial eclipse is more noticeable, as a portion of the Moon enters the umbra, creating a darkened area on its surface. The umbral phase reaches totality when the entire Moon is enveloped by the Earth’s umbra. During totality, the Moon doesn’t disappear completely; instead, it often takes on a reddish hue due to the scattering of sunlight through the Earth’s atmosphere. This phenomenon is often referred to as a “blood moon.”
Comparison of Lunar Eclipse Types
Total, partial, and penumbral lunar eclipses differ primarily in the extent to which the Moon enters the Earth’s shadow. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the entire Moon passes through the umbra, resulting in the characteristic reddish coloration. A partial lunar eclipse happens when only a portion of the Moon enters the umbra, leaving a part of the lunar surface illuminated. A penumbral lunar eclipse is the least dramatic, with the Moon passing only through the Earth’s penumbra, causing a subtle dimming that is often difficult to observe without specialized equipment. The duration of each type of eclipse also varies, with total lunar eclipses typically lasting longer than partial or penumbral eclipses. For example, a total lunar eclipse might last for several hours, including the time spent in the partial and umbral phases, while a penumbral eclipse might only show a slight dimming for a shorter period.
The Appearance of a Total Lunar Eclipse
A total lunar eclipse presents a breathtaking celestial spectacle, dramatically altering the Moon’s appearance. The transformation from a bright, silvery orb to a subtly colored celestial body is a captivating event driven by the interplay of sunlight, Earth’s atmosphere, and the Moon’s position within Earth’s shadow. Understanding these factors reveals the science behind the eclipse’s striking visuals.
The visual characteristics of a totally eclipsed Moon are far from uniform. While often described as “blood moon” due to its reddish hue, the exact shade can vary significantly from one eclipse to another, influenced by atmospheric conditions on Earth. The brightness also diminishes considerably, although the Moon never completely disappears. Instead, it takes on a subdued glow, its surface often displaying subtle variations in shading and color.
The Moon’s Color During Totality
The reddish color observed during totality is a consequence of Rayleigh scattering. Sunlight, which is comprised of all the colors of the visible spectrum, is scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere. Shorter wavelengths, like blue and green light, are scattered more effectively than longer wavelengths, like red and orange light. During a total lunar eclipse, the Earth blocks direct sunlight from reaching the Moon. However, some sunlight is refracted (bent) by the Earth’s atmosphere, and this refracted light reaches the Moon. Because the shorter wavelengths are scattered away, the longer wavelengths, predominantly red light, are able to reach the Moon and illuminate it. The intensity of the red color depends on the amount of dust and aerosols present in the Earth’s atmosphere at the time of the eclipse; volcanic eruptions, for example, can result in a darker, more reddish hue.
Phases of a Total Lunar Eclipse and Their Appearance
A total lunar eclipse unfolds in stages. Initially, the Moon enters the penumbra, the outer, fainter part of Earth’s shadow. This phase is generally subtle, with only a slight dimming of the Moon’s brightness. As the Moon progresses into the umbra, the Earth’s darker, central shadow, a noticeable darkening begins. This is the partial eclipse phase, where a portion of the Moon appears shadowed. The curvature of the Earth’s shadow becomes clearly visible on the Moon’s surface during this stage.
The most dramatic phase is totality, when the Moon is completely immersed in the umbra. This is when the characteristic reddish hue becomes apparent, though the exact shade can vary considerably. The intensity and color of the reddish glow can shift subtly throughout totality, sometimes even exhibiting a subtle banding effect. After totality, the Moon begins to emerge from the umbra, retracing the stages of the partial eclipse in reverse. Finally, it exits the penumbra, returning to its normal brightness. The entire process, from the initial penumbral phase to the final exit, can last for several hours. Observers should expect a gradual and mesmerizing transformation of the Moon’s appearance throughout the event.
Cultural and Historical Significance of Lunar Eclipses: Eclipse Lunar Total 2025
Lunar eclipses, throughout human history, have held profound cultural and religious significance across diverse societies. Their dramatic appearance in the night sky has often been interpreted as omens, divine messages, or indicators of significant events, shaping myths, rituals, and societal structures. The interpretations, however, varied greatly depending on the cultural context and the specific understanding of the cosmos prevalent at the time.
Many ancient cultures viewed lunar eclipses as ominous events. These celestial occurrences, often unexpected and unpredictable, were frequently associated with fear and superstition. The temporary disappearance of the moon, a celestial body crucial to many cultures’ timekeeping and agricultural practices, could be understandably alarming. The perceived disruption of the natural order led to the development of diverse explanations, ranging from mythical battles to divine displeasure.
Interpretations of Lunar Eclipses in Different Cultures
The interpretation of lunar eclipses varied widely across different cultures and time periods. For example, some ancient cultures believed that a celestial being or animal was devouring the moon. In some Native American traditions, the eclipse was seen as a time when the moon needed protection and healing, leading to rituals and ceremonies aimed at restoring its celestial health. Conversely, other cultures interpreted the event as a time of spiritual renewal or a harbinger of good fortune. The Inca, for instance, believed a jaguar was attacking the moon, leading to rituals involving noise-making to scare the creature away. In contrast, some East Asian cultures associated the event with the cyclical nature of life, death, and rebirth.
Historical Events and Myths Associated with Lunar Eclipses
Numerous historical events and myths are linked to lunar eclipses. The ancient Greeks, for instance, associated lunar eclipses with the wrath of the gods, often attributing them to divine interventions in human affairs. Their myths often depicted eclipses as moments of intense cosmic drama, reflecting the anxieties and uncertainties of their time. Similarly, many historical accounts describe widespread panic and fear during lunar eclipses, with people engaging in various rituals to appease their gods or ward off perceived evil. The chronicles of several ancient civilizations frequently record lunar eclipses, often alongside significant political or social events, reinforcing the perception of their importance. This correlation, however, is likely a reflection of the tendency to record significant events, rather than a direct causal link.
Comparison of Cultural Interpretations Across Regions and Time Periods
A comparison of cultural interpretations reveals a fascinating spectrum of beliefs and practices. While many ancient cultures shared a common thread of fear and superstition surrounding lunar eclipses, the specific narratives and rituals varied considerably. The interpretation of the event was heavily influenced by the prevailing cosmological beliefs, religious doctrines, and societal structures of each culture. While some cultures saw the eclipse as a negative omen, others viewed it as a time of spiritual reflection or renewal. The evolution of scientific understanding has significantly altered the perception of lunar eclipses, transforming them from ominous events into predictable celestial phenomena. However, the enduring cultural significance of these events continues to resonate in various traditions and artistic expressions.
Photography and Observation Tips

Capturing the beauty of a total lunar eclipse, whether through a camera lens or with the naked eye, requires some planning and understanding of the celestial event. This section provides guidance on photographing the eclipse and observing it safely and effectively. Remember that safety and enjoyment are paramount.
Eclipse Lunar Total 2025 – Photographing a lunar eclipse presents a unique challenge due to the low light conditions. Success depends on choosing the right equipment and employing suitable techniques. Even a simple setup can yield impressive results, provided you understand the basic principles of astrophotography.
The upcoming Total Lunar Eclipse in 2025 promises a spectacular celestial display, a captivating event for astronomy enthusiasts. However, it’s worth noting the relative rarity of total solar eclipses, as highlighted in this informative article on the Total Solar Eclipse 2025 Rarity , which makes the lunar eclipse even more significant in comparison. Both events offer unique opportunities for observation and understanding celestial mechanics, making 2025 a year of notable astronomical occurrences.
Camera and Telescope Settings for Lunar Eclipse Photography
Achieving sharp, detailed images of the eclipsed moon necessitates careful consideration of camera and telescope settings. The key is to balance sufficient exposure time with minimal image blurring caused by the Earth’s rotation. A tripod is absolutely essential for stability.
For cameras, a DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual controls is ideal. Start with a relatively fast shutter speed (e.g., 1/125th of a second to 1/250th of a second) and a high ISO (e.g., ISO 800 to ISO 3200, depending on your camera’s capabilities and the ambient light). Adjust the aperture to a value that balances sharpness and light gathering (e.g., f/5.6 to f/8). Use a telephoto lens (at least 200mm focal length) or a teleconverter to magnify the moon significantly. Consider using a remote shutter release to avoid camera shake.
While the upcoming Total Lunar Eclipse of 2025 promises a spectacular celestial event, planning for viewing a different kind of eclipse is also underway. For those interested in witnessing a Total Solar Eclipse, a helpful resource is available: Total Eclipse 2025 Canada Map , which details the path of totality across Canada. Returning to the lunar eclipse, remember to check local times for optimal viewing of this captivating astronomical phenomenon.
When using a telescope, you will likely need a camera adapter to connect your camera to the telescope’s eyepiece. The settings will depend on your telescope’s focal length and the camera’s sensitivity. Experimentation is key. Start with shorter exposure times to avoid overexposure and gradually increase them as the eclipse progresses. Astrophotography software can be helpful in stacking multiple images to reduce noise and improve image quality.
While the upcoming Total Lunar Eclipse of 2025 promises a spectacular celestial event visible across large portions of the globe, planning for the 2025 solar eclipse is also crucial for those in specific locations. For those in San Antonio, Texas, the optimal viewing locations can be found using this helpful resource: Total Eclipse 2025 San Antonio Map.
Understanding optimal viewing points for the solar eclipse enhances the overall astronomical experience, making the contrast with the lunar eclipse all the more interesting.
Step-by-Step Guide for Observing a Lunar Eclipse
Observing a lunar eclipse is a safe and rewarding experience that requires minimal equipment. The naked eye is sufficient for appreciating the event’s progression, but binoculars or telescopes can enhance the viewing experience.
For naked-eye observation, find a location with minimal light pollution. Allow your eyes to adjust to the darkness for about 15-20 minutes. The eclipse unfolds gradually, so patience is crucial. Observe the changes in the moon’s appearance as it moves into and out of the Earth’s shadow. Note the varying shades of red and brown that the moon takes on during totality.
While the upcoming total lunar eclipse in 2025 promises a spectacular celestial event visible across much of the globe, planning for viewing the 2024 total solar eclipse is also crucial. For those in Texas hoping to witness this rarer phenomenon, a helpful resource is the detailed Total Eclipse Texas Map 2025 , which pinpoints optimal viewing locations.
Understanding the path of totality is key to maximizing your experience of either eclipse, whether lunar or solar.
Binoculars or telescopes will provide a closer and more detailed view. With binoculars, you can see the subtle variations in the moon’s surface texture and the Earth’s shadow more clearly. A telescope will offer an even more magnified view, allowing you to appreciate the lunar landscape in greater detail during the eclipse. Remember to use appropriate filters to protect your eyes, especially during the partial phases.
The upcoming Total Lunar Eclipse in 2025 promises a spectacular celestial event, a breathtaking display of shadow play across the night sky. However, for those interested in a different kind of eclipse experience, consider checking out the details on the Vt Total Solar Eclipse 2025 , which offers a completely different perspective on these celestial phenomena. Then, after witnessing (or learning about) the solar eclipse, you can eagerly anticipate the lunar eclipse’s unique beauty.
Safety Precautions During Eclipse Viewing
Witnessing a total lunar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize safety, particularly when observing the celestial event. While a total lunar eclipse doesn’t pose the same dangers as a solar eclipse, it’s still important to be mindful of your surroundings and take precautions to ensure a comfortable and safe viewing experience.
Directly viewing the sun, even during a partial phase of a solar eclipse (which does not apply to a lunar eclipse), is extremely dangerous and can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. A total lunar eclipse, however, involves the Earth passing between the sun and the moon, casting a shadow on the moon. Therefore, unlike a solar eclipse, observing a lunar eclipse with the naked eye is perfectly safe. However, using optical aids can enhance the viewing experience, but even then, specific precautions should be taken to avoid eye strain.
Recommended Eye Protection for Lunar Eclipse Viewing
While not strictly necessary for viewing a total lunar eclipse, using binoculars or a telescope can significantly enhance the viewing experience by allowing you to see the subtle changes in the moon’s appearance during the eclipse. However, prolonged use of optical devices can cause eye strain. To mitigate this, it is recommended to take frequent breaks and avoid prolonged, uninterrupted observation. If using binoculars or a telescope, ensure they are properly focused to avoid eye strain. Remember that the moon itself is not emitting intense light during the eclipse; the danger lies solely in potential eye strain from extended use of optical equipment.
Additional Safety Considerations for Eclipse Viewing
Beyond eye protection, several other safety precautions should be considered for a pleasant and safe eclipse viewing experience. Finding a location with a clear view of the night sky, away from light pollution, will significantly enhance the visibility of the eclipse. Checking the weather forecast beforehand will help you prepare for potential rain or cloud cover. Bringing a comfortable chair or blanket will allow for relaxed and prolonged viewing. Finally, remember to dress appropriately for the weather conditions, especially if you are planning to be outdoors for an extended period.
Future Lunar Eclipses
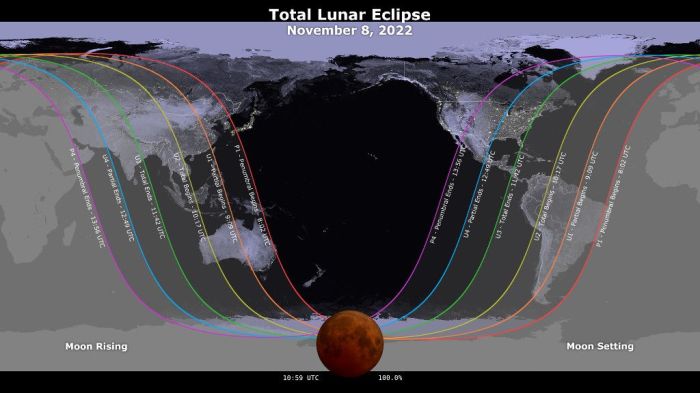
Predicting lunar eclipses is a relatively straightforward process thanks to our understanding of celestial mechanics. While pinpointing the exact time and visibility requires sophisticated calculations, general predictions for the next decade are readily available from reputable astronomical sources. These predictions allow enthusiasts to plan viewing events and researchers to prepare for observations.
The following information summarizes predicted total lunar eclipses for the next decade, focusing on their global visibility and anticipated characteristics. It’s important to note that these predictions are based on current models and may be subject to minor adjustments as our understanding improves.
Upcoming Total Lunar Eclipses (2026-2035)
Predicting the precise path and timing of future lunar eclipses requires detailed astronomical calculations. However, we can provide a general overview of expected total lunar eclipses over the next decade, highlighting their potential visibility across different regions. The data below represents a summary and may differ slightly depending on the source. Precise times and visibility zones should be confirmed closer to each event using specialized astronomical software or websites.
| Date | Visibility | Anticipated Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| [Insert Date of Next Total Lunar Eclipse after 2025] | [Regions with good visibility, e.g., North America, parts of Europe] | [Description of expected umbral shadow, color, duration, etc. Example: “A relatively short eclipse with a deep, reddish-brown umbra, visible for approximately 1 hour and 30 minutes from optimal viewing locations.”] |
| [Insert Date of Next Total Lunar Eclipse after the previous one] | [Regions with good visibility, e.g., Asia, Australia] | [Description of expected umbral shadow, color, duration, etc. Example: “A longer eclipse with a slightly lighter umbral shadow, possibly appearing more of a copper or brick-red color, visible for approximately 1 hour and 45 minutes in optimal locations.”] |
| [Insert Date of a third Total Lunar Eclipse in the next decade] | [Regions with good visibility, e.g., South America, parts of Africa] | [Description of expected umbral shadow, color, duration, etc. Example: “A deep, dark eclipse with a long duration of the total phase, possibly exhibiting a darker red hue due to atmospheric conditions.”] |
Comparison with the 2025 Eclipse
Comparing future total lunar eclipses with the 2025 event requires specific data regarding the 2025 eclipse’s duration, umbral shadow characteristics, and path of totality. However, we can generally expect variations in these factors. For example, the length of totality can differ significantly depending on the alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. The color of the Moon during totality is also influenced by atmospheric conditions, resulting in variations from a deep red to a lighter, coppery hue. Furthermore, the geographic regions with optimal viewing conditions will vary for each eclipse. The 2025 eclipse served as a benchmark, providing a point of comparison for future events. Future eclipses may be shorter or longer, exhibit different shades of red, and be visible from different parts of the globe. The precise differences will be determined by the specific orbital positions of the celestial bodies involved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section addresses some common questions about total lunar eclipses, providing clear and concise answers based on scientific understanding and observable phenomena. Understanding these frequently asked questions can enhance your appreciation and enjoyment of this celestial event.
A Total Lunar Eclipse
A total lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. Unlike a solar eclipse, which requires special eye protection, a lunar eclipse is perfectly safe to view with the naked eye. The entire Moon passes through the Earth’s umbra (the darkest part of its shadow), resulting in a dramatic darkening and often a reddish hue.
Visibility of the 2025 Total Lunar Eclipse
The precise timing and visibility of the 2025 total lunar eclipse will depend on the specific date and time of the event, which requires consulting astronomical resources closer to the date. However, generally, the eclipse will be visible from locations where the Moon is above the horizon during the eclipse. Predictive maps and online tools provided by astronomical organizations will offer detailed information on visibility in specific geographic regions.
Eye Safety During a Lunar Eclipse
It is completely safe to view a lunar eclipse without any special eye protection. Unlike solar eclipses, where looking directly at the Sun can cause serious eye damage, a lunar eclipse involves observing the reflected light of the Sun from the Moon. This reflected light is not harmful to the eyes.
The Red Moon During a Total Lunar Eclipse
The reddish hue observed during a total lunar eclipse is due to a phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering. As sunlight passes through the Earth’s atmosphere, shorter wavelengths of light (like blue and green) are scattered more effectively than longer wavelengths (like red and orange). This means that during a total lunar eclipse, the only sunlight reaching the Moon is the red light that has been bent and refracted by the Earth’s atmosphere. This process casts a reddish glow onto the Moon’s surface, often resulting in the spectacular sight of a “blood moon.”
Illustrative Content
Visual aids significantly enhance understanding of complex astronomical events like lunar eclipses. Illustrations can clarify the geometrical relationships between the Sun, Earth, and Moon, and effectively demonstrate the progression of the eclipse phases. Two key illustrations are described below.
Orbital Mechanics of a Lunar Eclipse, Eclipse Lunar Total 2025
This illustration depicts the alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon during a total lunar eclipse. The Sun is shown as a large yellow circle on the left, emitting rays of light. The Earth is represented as a large blue and green sphere in the center, with its axis slightly tilted. The Moon, a smaller grey sphere, is positioned directly behind the Earth, in the Earth’s umbral shadow. The illustration clearly shows the Earth’s umbra (the darkest part of its shadow) and penumbra (the lighter, outer part of its shadow). A curved arrow indicates the direction of the Moon’s orbit around the Earth. Labels clearly identify the Sun, Earth, Moon, umbra, and penumbra. The illustration should also highlight the approximate scale and relative distances between these celestial bodies. This visual representation effectively communicates the necessary alignment for a lunar eclipse to occur.
Phases of a Lunar Eclipse
This illustration shows the different stages of a total lunar eclipse. It is divided into four main panels, each representing a distinct phase.
Panel 1: Penumbral Eclipse. The Moon is shown slightly darkened as it enters the Earth’s penumbra. A caption explains that this phase is often subtle and difficult to observe without specialized equipment. The Moon appears only slightly shaded.
Panel 2: Partial Lunar Eclipse. A portion of the Moon is now clearly within the Earth’s umbra, appearing noticeably darker. The illustration clearly shows the dividing line between the umbra and the illuminated portion of the Moon. A caption states that the shadow gradually deepens as more of the Moon enters the umbra.
Panel 3: Total Lunar Eclipse. The entire Moon is completely immersed in the Earth’s umbra. The Moon takes on a reddish hue, often referred to as a “blood moon,” due to the scattering of sunlight in the Earth’s atmosphere. The caption explains the reddish color and the duration of totality.
Panel 4: Partial Lunar Eclipse (Exiting Umbra). The Moon begins to emerge from the Earth’s umbra, with the illuminated portion gradually increasing. The illustration mirrors Panel 2 but shows the progression of the Moon exiting the umbra. A caption indicates that the eclipse is nearing its end.
Each panel includes a small diagram showing the relative positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon during that specific phase. This allows viewers to understand the geometry behind the changes in the Moon’s appearance. The entire illustration uses consistent scaling and color coding to ensure clarity and visual coherence.