Last Total Solar Eclipse Before 2025
Total solar eclipses, where the moon completely blocks the sun’s disk, are awe-inspiring celestial events. Their significance extends beyond mere spectacle; they offer invaluable opportunities for scientific research, particularly in studying the sun’s corona and testing theories of relativity. Beyond the scientific realm, these events hold cultural and spiritual importance for many societies throughout history.
These breathtaking events are, however, remarkably rare occurrences at any given location. The precise alignment of the sun, moon, and Earth required for a total solar eclipse means that they are only visible from a relatively narrow path across the Earth’s surface. Millions may live within range of a partial eclipse, but the experience of totality – the complete obscuring of the sun – is limited to a much smaller, and often sparsely populated, area.
The Total Solar Eclipse of April 20, 2023
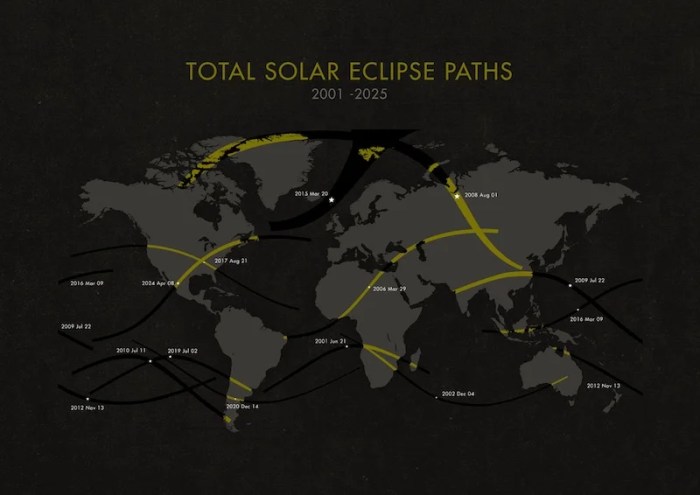
The last total solar eclipse before 2025 occurred on April 20, 2023. This eclipse’s path of totality traversed a swathe of the Earth, beginning in the South Pacific Ocean, then passing over parts of Western Australia, East Timor, and West Papua, Indonesia before ending in the Pacific Ocean. The exact time of totality varied depending on the location, with the maximum duration of totality reaching approximately 1 minute and 16 seconds. The eclipse was visible as a partial eclipse over a much wider area, including parts of Australia, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific Islands. This specific eclipse provided a unique opportunity for observers in these relatively isolated regions to witness this spectacular natural phenomenon.
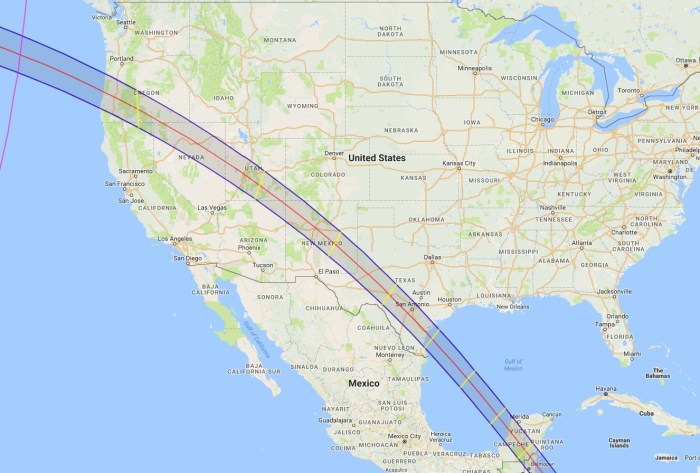
Path of Totality
The path of totality for the last total solar eclipse before 2025 traces a relatively narrow band across the Earth’s surface. Understanding this path is crucial for anyone hoping to witness the full spectacle of the eclipse, as only those within this specific area will experience the total obscuration of the sun. The precise coordinates of this path vary slightly depending on the specific time and location, but generally, it follows a predictable trajectory.
The path’s precise location is determined by complex astronomical calculations that consider the relative positions of the sun, moon, and Earth. Small variations in these positions can subtly alter the path’s exact location from year to year, making each eclipse unique.
Path of Totality Map
Imagine a map of the Earth showing a curved line stretching across a portion of the globe. This line represents the path of totality. The line isn’t perfectly straight; it curves due to the Earth’s curvature and the moon’s orbit. Along this path, the moon completely blocks the sun’s disk, creating a breathtaking total solar eclipse. The width of this path varies; it is typically narrowest near the beginning and end of the eclipse’s path and widest near the middle. Precise latitude and longitude coordinates would be needed to pinpoint specific locations within this path, but these would vary greatly depending on the specific eclipse in question. For example, the path might pass through specific cities, crossing geographic landmarks and varying in width. A visual representation would be a world map with a clearly marked, curving line representing the path of totality. The line would be thicker in the middle of the path and taper off towards the edges, indicating the varying width of the path. Key geographic locations along the path could be labelled for easy identification.
Eclipse Duration and Visibility Comparison, Last Total Solar Eclipse Before 2025
This table compares the duration and visibility conditions of the eclipse at different locations along the path of totality. The values provided are illustrative and would need to be replaced with actual data for a specific eclipse.
| Location | Date/Time (Local Time) | Duration (Seconds) | Visibility Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location A (e.g., City X, Country Y) | YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS | 150 | Clear Skies (Example) |
| Location B (e.g., City Z, Country W) | YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS | 165 | Partly Cloudy (Example) |
| Location C (e.g., City P, Country Q) | YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS | 170 | Overcast (Example) |
| Location D (e.g., City R, Country S) | YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS | 145 | Clear Skies (Example) |
Best Viewing Spots
Selecting the best viewing spots requires careful consideration of weather patterns and accessibility. Areas with historically clear skies during the time of year when the eclipse occurs are preferred. Accessibility factors include proximity to major roads, availability of lodging, and the presence of organized viewing events. For instance, a remote location with exceptional historical weather data might be ideal but could pose logistical challenges. Conversely, a more accessible location with a higher chance of cloud cover might be less desirable, despite its ease of access. The ideal spot balances optimal viewing conditions with practical considerations.
Safety Precautions During a Solar Eclipse
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety. Looking directly at the sun, even during a partial eclipse, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including solar retinopathy, which can lead to vision loss. Never underestimate the sun’s intensity; even a brief glance can have lasting consequences. This section details the necessary precautions to ensure a safe and enjoyable viewing experience.
Protecting your eyes during a solar eclipse requires specialized eyewear. Regular sunglasses, even very dark ones, are insufficient and offer no protection against the sun’s harmful rays. The only safe way to look directly at the uneclipsed or partially eclipsed sun is through special-purpose solar filters. These filters are designed to block out the intense ultraviolet and infrared radiation emitted by the sun.
Safe Solar Viewing Eyewear
Solar viewing glasses, sometimes called eclipse glasses, are readily available from various sources. Reputable vendors include astronomical societies, science museums, and online retailers specializing in astronomical equipment. It’s crucial to ensure that your eclipse glasses meet the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard. This standard guarantees that the glasses provide adequate protection. Check the glasses’ packaging for this certification before use. Discard any glasses that are scratched or damaged. Homemade filters or ordinary sunglasses are absolutely not safe for direct solar viewing.
Indirect Viewing Methods
For those who prefer not to use solar viewing glasses, or for sharing the eclipse experience with others, indirect viewing methods offer a safe and engaging alternative. One popular method is using a pinhole projector. This simple device projects an image of the sun onto a screen. To create a pinhole projector, poke a small hole in a piece of cardboard. Then, hold the cardboard in sunlight, allowing the sun’s image to project onto another piece of cardboard or a white surface held several feet behind. The projected image will show the sun’s partially or totally eclipsed state. Alternatively, you can use a telescope or binoculars equipped with a proper solar filter to project the image onto a screen, but extreme caution must be exercised to avoid accidental direct viewing.
The Science Behind a Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse is a breathtaking celestial event, a product of precise astronomical alignment. Understanding the science behind this phenomenon requires exploring the intricate interplay between the Sun, the Moon, and Earth. This alignment, along with the relative sizes and distances of these celestial bodies, creates the conditions necessary for a total eclipse.
The alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth is the fundamental cause of a total solar eclipse. For a total eclipse to occur, the Moon must be positioned precisely between the Sun and Earth, casting its shadow onto our planet. This alignment doesn’t happen every month because the Moon’s orbit is tilted approximately 5 degrees relative to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Therefore, the Moon usually passes above or below the Sun in its monthly journey across the sky. Only when the Moon intersects the plane of Earth’s orbit (the ecliptic) during a new moon phase can a solar eclipse occur. The size of the Sun and the Moon as seen from Earth also play a crucial role; the apparent sizes of the Sun and Moon are nearly identical, allowing the Moon to completely block the Sun’s disk during totality.
Phases of a Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse unfolds in distinct phases, each marked by specific celestial events. The partial eclipse begins as the Moon starts to encroach upon the Sun’s disk, gradually obscuring a portion of its surface. As the Moon continues its transit, the partial eclipse progresses, with a larger and larger segment of the Sun being covered. The diamond ring effect, a brief, spectacular moment, appears just before totality when only a sliver of the Sun remains visible, shining brilliantly through the valleys on the Moon’s edge. Totality follows, a period of complete darkness when the Moon entirely blocks the Sun’s corona, revealing the Sun’s outer atmosphere. The diamond ring effect reappears briefly as the Moon begins to move away from the Sun, marking the end of totality. The partial eclipse then resumes, retracing its steps until the Moon completely clears the Sun’s disk.
Impact on Earth’s Atmosphere and Environment
During a total solar eclipse, the sudden decrease in sunlight causes noticeable changes in Earth’s atmosphere and environment. The most dramatic effect is the significant drop in temperature. Even in relatively short periods of totality, a noticeable cooling can be observed. Atmospheric pressure also experiences a slight decrease. Animals often exhibit unusual behaviors, such as birds ceasing their songs or becoming quiet, and some nocturnal animals might even become active. The darkening of the sky, reminiscent of twilight, alters the ambient light conditions, influencing plant life and other aspects of the environment. The brief period of darkness, however, doesn’t have a long-lasting impact on Earth’s climate or environment. These changes are temporary and localized, confined to the path of totality. The overall effect on the Earth’s atmosphere and environment is minimal, despite the visually striking and sometimes dramatic changes experienced during the event.
Historical and Cultural Significance of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events, have profoundly impacted human history and culture across diverse civilizations. Their sudden onset of darkness, often interpreted as supernatural omens, have shaped beliefs, mythology, and even historical events for millennia. The interpretations varied greatly depending on the cultural context and the level of astronomical understanding of the time.
Ancient Mesopotamian Interpretations
Ancient Mesopotamians, meticulous record-keepers, documented solar eclipses extensively in their cuneiform tablets. They viewed these events as ominous signs, often associating them with the wrath of the gods or impending disasters for their rulers. Their detailed astronomical observations, however, demonstrate a sophisticated understanding of celestial mechanics, even if their interpretations were steeped in religious and political anxieties. For instance, the eclipse of 1375 BCE is meticulously recorded, and its astrological significance was carefully analyzed by the royal scribes. The fear associated with these events is evident in the numerous prayers and rituals designed to appease the angered deities.
Solar Eclipses in Chinese Culture
In ancient China, solar eclipses were perceived as a threat to the Emperor, the Son of Heaven, believed to be divinely appointed. These events were seen as a sign of celestial imbalance, reflecting poorly on the ruler’s virtue and ability to maintain cosmic harmony. Detailed records of eclipses were kept, and astronomers were tasked with predicting them. Failure to accurately predict an eclipse could lead to severe consequences for the court astronomer. Rituals, including the beating of drums and gongs, were performed to scare away the mythical dragon believed to be devouring the sun during the eclipse. These practices highlight the profound influence of solar eclipses on the political and social fabric of Chinese society.
North American Indigenous Perspectives
Various North American Indigenous cultures held diverse beliefs about solar eclipses. Some tribes saw them as a time of great spiritual significance, a period for reflection and renewal. Others interpreted them as battles between celestial beings, or as signs foretelling important events. For example, some narratives depict a struggle between the sun and a celestial creature, explaining the temporary darkness. These interpretations, passed down through oral traditions, often integrated the eclipse into existing cosmologies and spiritual practices, reinforcing community bonds and cultural identity. The specific narratives varied widely depending on the tribe and their unique worldview.
Greek Mythology and Solar Eclipses
In Greek mythology, solar eclipses were often attributed to the actions of gods. One common narrative involved the swallowing of the sun by a celestial creature, often a dragon or a wolf. These myths, reflective of the anxieties surrounding the unexpected darkness, were integrated into larger narratives about the cosmos and the interactions between the gods and mortals. The unpredictable nature of eclipses fueled the creation of elaborate myths designed to provide explanations and alleviate fears. The stories served as a way to understand and make sense of a powerful natural phenomenon.
Photography and Astrophotography Tips
Capturing a total solar eclipse is a unique photographic challenge, demanding careful planning and execution to achieve stunning results. The fleeting nature of totality, combined with the extreme brightness contrasts between the sun and the corona, requires specific techniques and equipment. This section provides a step-by-step guide and essential tips for successfully photographing this celestial event.
Photographing the sun directly is dangerous and can cause permanent eye damage; always use proper solar filters.
Essential Equipment and Settings
Choosing the right equipment is crucial for capturing high-quality eclipse images. A sturdy tripod is paramount due to the long exposure times often needed. A remote shutter release prevents camera shake. Different cameras and lenses offer varying advantages.
- Camera: A DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual controls offers the most flexibility. Even a high-quality smartphone camera with a good zoom lens can capture some aspects of the eclipse, but the results will be less detailed.
- Lens: A telephoto lens (at least 300mm) is essential for capturing details of the sun and corona. Longer focal lengths (500mm or more) will provide even greater magnification. A zoom lens offers versatility.
- Solar Filter: This is absolutely critical. A dedicated solar filter, such as a Thousand Oaks Optical filter, should be attached to the front of your lens to protect your camera’s sensor from damage. Improvised filters are unsafe and should never be used.
- Tripod: A sturdy tripod is essential for stability, especially with longer exposures.
- Remote Shutter Release: Minimizes camera shake during long exposures.
Optimal camera settings will depend on your specific equipment and lighting conditions, but some general guidelines include:
- Shooting Mode: Manual (M) mode gives you complete control over aperture, shutter speed, and ISO.
- Aperture: A narrow aperture (f/8 to f/16) is recommended to maintain sharpness across the image.
- Shutter Speed: This will vary greatly depending on the phase of the eclipse and your lens. During totality, you can increase the shutter speed to capture the corona’s detail; before and after totality, you will need much faster shutter speeds to prevent overexposure.
- ISO: Keep the ISO as low as possible (ISO 100-400) to minimize noise, particularly during partial phases. During totality, you may need to increase the ISO slightly to capture the faint corona.
- Focus: Manually focus on the sun before the eclipse begins. Use live view magnification for precise focusing.
Capturing the Corona and Other Eclipse Features
The corona, the sun’s outer atmosphere, is the main focus during totality. Its delicate structure and ethereal glow require specific techniques to capture effectively.
- During Totality: Remove the solar filter *only* during the brief period of totality. Experiment with different shutter speeds and ISO settings to find the optimal balance between capturing the corona’s details and avoiding overexposure. Bracketing exposures (taking multiple shots at different settings) is highly recommended.
- Before and After Totality: Use the solar filter at all times except during totality. Focus on capturing the progression of the eclipse, showing the sun’s gradual obscuration by the moon.
- Composition: Consider including elements of the landscape in your composition, such as trees or mountains, to add context to your images. Plan your shot location carefully beforehand.
- Exposure Bracketing: Take a series of shots at different exposure settings to ensure you capture the full dynamic range of the eclipse. This is especially important during totality.
Remember: Safety is paramount. Never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection, and always use a solar filter on your camera lens.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Trip
Planning a trip to witness a total solar eclipse requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure a safe and memorable experience. Thorough preparation will minimize stress and maximize your enjoyment of this rare celestial event. This section Artikels essential planning steps, from packing lists to itinerary suggestions and location selection.
Essential Packing Checklist
A well-prepared packing list is crucial for a successful eclipse viewing trip. Remember that conditions at the viewing site may differ significantly from your usual environment, necessitating appropriate clothing and supplies.
- Clothing: Layers are key! Pack for a range of temperatures, including a warm jacket or sweater even if the forecast predicts warmth, as temperatures can drop significantly during the eclipse. Include comfortable walking shoes, sunscreen, a hat, and sunglasses (even though you’ll need eclipse glasses, sunglasses provide protection from the sun’s glare).
- Eclipse Viewing Supplies: ISO 12312-2 certified solar eclipse glasses are absolutely essential. Bring multiples in case of loss or damage, and consider bringing a solar viewing filter for cameras or telescopes if you plan on photographing the event.
- Other Supplies: Pack insect repellent, hand sanitizer, a first-aid kit, water bottles (stay hydrated!), snacks, a comfortable chair or blanket for sitting or lying down during the eclipse, and a portable power bank for your devices.
- Documents and Identification: Don’t forget your driver’s license, passport (if traveling internationally), any necessary travel documents, and a copy of your itinerary.
Sample Eclipse Viewing Trip Itinerary
This itinerary provides a framework; adapt it to your specific location and preferences.
Last Total Solar Eclipse Before 2025 – Day 1: Travel and Accommodation
Travel to your chosen eclipse viewing location. Check into your pre-booked accommodation. This could involve a flight to a nearby airport, followed by a car rental or other ground transportation to your viewing site. Allow ample time for unexpected delays.
Day 2: Eclipse Viewing and Exploration
Arrive at your viewing location well in advance of the eclipse to secure a good spot and allow time to set up your equipment. Enjoy the pre-eclipse activities and atmosphere. Witness the totality of the eclipse! After the eclipse, spend some time exploring the local area, if time and interest allow.
Day 3: Departure
Enjoy a leisurely breakfast before beginning your journey home. Reflect on the amazing experience of witnessing a total solar eclipse!
Location Selection Considerations
Choosing the right location is paramount for a successful eclipse viewing experience.
- Accessibility: Consider the ease of travel to the location and the availability of parking and other amenities. Locations with good road access and ample parking are generally preferred, especially if you’re traveling with family or large equipment.
- Weather Conditions: Check historical weather data for the chosen location to assess the likelihood of clear skies during the eclipse. Cloud cover can completely obscure the view. Websites and apps providing weather forecasts specific to the eclipse date and time can be invaluable.
- Crowd Size: Popular eclipse viewing locations can become extremely crowded. Consider less-popular locations to avoid potential issues with traffic, parking, and overcrowding. Researching the expected crowd size for various locations can help you make an informed decision. For example, the 2017 total solar eclipse across the United States saw massive crowds in some areas, leading to significant traffic jams and logistical challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section addresses common queries regarding total solar eclipses, encompassing their nature, occurrence, safe observation methods, scientific underpinnings, and historical/cultural significance. Understanding these aspects enhances appreciation for this awe-inspiring celestial event.
Total Solar Eclipse Definition
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light from reaching a specific area on Earth. This creates a temporary period of darkness during the daytime, with the Sun’s corona (outer atmosphere) becoming visible as a radiant halo around the Moon’s silhouette. The effect is most dramatic within the path of totality, a relatively narrow band on Earth’s surface where the total eclipse is visible. Outside this path, a partial eclipse may be observed.
The Last Total Solar Eclipse Before 2025
The last total solar eclipse before 2025 occurred on April 20, 2023. Its path of totality traversed parts of Australia, Timor-Leste, and West Papua. Millions witnessed this event, many traveling to locations along the path of totality to experience the unique phenomenon. The specific timing and visibility varied depending on the geographical location within the path.
Safe Viewing Practices During a Total Solar Eclipse
Safe viewing is paramount during a solar eclipse. Never look directly at the Sun without proper eye protection, even during a partial eclipse. Improper viewing can cause serious and permanent eye damage. Certified solar viewing glasses, meeting the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard, are essential for safe viewing of the partial phases. During the brief period of totality, when the Sun is completely obscured by the Moon, it is safe to remove the glasses and witness the spectacular corona. However, it is crucial to put the glasses back on immediately as the Sun begins to reappear. Alternative safe viewing methods include pinhole projection, which creates an image of the Sun onto a surface without direct eye exposure.
Scientific Explanation of a Total Solar Eclipse
Total solar eclipses are a direct consequence of the precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. The Moon’s orbit around the Earth is elliptical, meaning its distance from Earth varies. A total solar eclipse is only possible when the Moon is at or near its perigee (closest point to Earth), making its apparent size large enough to completely cover the Sun’s disk. This alignment, while seemingly simple, is a complex interplay of celestial mechanics governed by Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation and Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion. The geometry of this alignment determines the path of totality and the duration of the total eclipse at any given location.
Historical and Cultural Significance of Solar Eclipses
Throughout history, solar eclipses have held profound cultural and religious significance across numerous civilizations. Ancient cultures often interpreted eclipses as ominous signs, associating them with supernatural events or divine displeasure. Many cultures developed myths and legends to explain the phenomenon, reflecting their understanding of the cosmos and their place within it. For example, some cultures believed eclipses resulted from celestial beings devouring the Sun, while others saw them as portents of war or natural disasters. Even today, eclipses continue to inspire awe and wonder, serving as a reminder of the vastness and mystery of the universe. The study of historical eclipse records has also proven valuable for astronomers in refining calculations related to the Earth-Moon system.
The last total solar eclipse before 2025 offered a spectacular celestial display for many fortunate observers. While we eagerly anticipate the next breathtaking event, planning is already underway for those hoping to witness the totality. For those interested in the upcoming spectacle, you can find detailed information about the path of totality for the Next Total Eclipse Usa 2025 and begin making your preparations.
Remember to mark your calendars; the anticipation for the next total eclipse is already building!
The last total solar eclipse before 2025 was a truly spectacular event for those fortunate enough to witness it. Planning for the next one is already underway, and if you’re curious about the timing of the 2025 total eclipse, you can find details at When Was The 2025 Total Eclipse. Knowing the date of the 2025 eclipse helps enthusiasts prepare well in advance for the next opportunity to see this celestial wonder, making the wait for the Last Total Solar Eclipse Before 2025 all the more worthwhile.
Witnessing the last total solar eclipse before 2025 was a truly remarkable experience, a celestial event that leaves a lasting impression. Looking ahead, anticipation builds for the next spectacular event; you can learn more about the specifics of The Total Eclipse Of 2025 , which promises to be equally awe-inspiring. Until then, memories of the last eclipse will remain vivid, a testament to the power and beauty of nature’s grand spectacle.
The last total solar eclipse before 2025 was a spectacular event for many, offering a rare glimpse of the sun’s corona. Looking ahead, anticipation builds for the next celestial show, and planning is already underway for optimal viewing locations. For those in New York State, information regarding the path of totality can be found on this helpful resource: Total Eclipse 2025 Nys.
This site will help you prepare for the 2025 eclipse, ensuring you don’t miss the next chance to witness this awe-inspiring natural phenomenon before the next total solar eclipse.
Witnessing the last total solar eclipse before 2025 was a truly remarkable experience. The anticipation leading up to the event was palpable, and the totality itself was breathtaking. Looking ahead, planners are already excitedly preparing for the next big event, focusing on the optimal viewing locations for the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse in Ontario , promising another incredible celestial spectacle.
This upcoming eclipse in Ontario is expected to draw large crowds eager to witness this rare phenomenon, making it a significant event in the astronomical calendar after the last total solar eclipse before 2025.