Next Total Solar Eclipse After 2025
The next total solar eclipse after 2025 will occur on August 12, 2026. This eclipse will be a significant celestial event, traversing a path across several continents and offering a spectacular view for millions. Understanding its path, duration, and astronomical context allows for better appreciation of this rare phenomenon.
Path of Totality and Geographical Locations
The path of totality for the August 12, 2026, total solar eclipse will begin in the North Atlantic Ocean, crossing over Iceland and then traversing a swathe of northeastern North America, passing through Canada, and eventually exiting over the Atlantic. Key geographical locations within the path of totality include Reykjavik, Iceland; various locations in Northern Canada, particularly in Newfoundland and Labrador; and potentially some smaller islands in the North Atlantic. The eclipse’s path will be relatively narrow, meaning the total eclipse will only be visible from a limited area. The precise locations and duration of totality will vary depending on the specific point along the path.
Eclipse Timeline
Precise timings for the eclipse will vary depending on the specific location within the path of totality. However, a general timeline can be provided. The eclipse will begin in the early morning hours in Iceland, with totality occurring around mid-morning. As the moon’s shadow moves westward, the eclipse will progress across Canada, with the time of totality shifting later in the day. The eclipse will end in the late afternoon in the North Atlantic. More detailed timetables will be available closer to the date from astronomical sources. For instance, in Reykjavik, Iceland, the partial eclipse might begin around 10:00 AM local time, with totality beginning about an hour later. In contrast, a location in Newfoundland, Canada, might experience the start of the partial phase around 1:00 PM local time and totality a couple of hours later. The exact timings require precise astronomical calculations specific to a given location’s latitude and longitude.
Duration of Totality
The duration of totality for the August 12, 2026, eclipse will vary depending on the location along the path. In general, the maximum duration of totality will likely be around 4 minutes, although this can be slightly shorter or longer at different points along the path. This duration is relatively typical for total solar eclipses. Compared to some historically longer eclipses (such as the 7 minutes 8 seconds totality of the July 22, 2009, eclipse), this eclipse will be shorter. However, it is still a significant event, and longer than many other total solar eclipses. Future eclipses will also vary in duration of totality.
Astronomical Significance
The August 12, 2026, total solar eclipse holds no unique astronomical significance compared to other total solar eclipses. Its position relative to other celestial events is not exceptionally noteworthy. The significance lies primarily in its accessibility to populated areas and the resulting opportunity for widespread observation and scientific study. The eclipse will provide a valuable opportunity for researchers to study the Sun’s corona and other solar phenomena, which are only visible during totality.
Eclipse Visibility by Country and Maximum Eclipse Time
| Country | Time of Maximum Eclipse (Approximate) | Duration of Totality (Approximate) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iceland | Mid-morning | ~4 minutes (varies by location) | Visible across most of the country |
| Canada (Newfoundland and Labrador) | Afternoon | ~4 minutes (varies by location) | Visible in parts of these provinces |
| United States | N/A | N/A | Not visible in the contiguous US |
| Other North Atlantic Islands | Afternoon | Variable | Visibility depends on specific island location. |
Observing the Eclipse Safely
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety. Looking directly at the sun, even during a partial eclipse, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including solar retinopathy, which can lead to vision loss. Understanding and employing safe viewing practices is paramount to enjoying this celestial event without risking your eyesight.
Potential Dangers of Unsafe Solar Viewing
Directly viewing the sun without proper eye protection can lead to severe and irreversible damage to the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. The sun’s intense radiation, particularly ultraviolet and infrared light, can burn the retina, causing blurry vision, blind spots, and in severe cases, complete vision loss. This damage often occurs without immediate pain, making it even more dangerous. Even brief glances at the uneclipsed sun can cause harm, and the cumulative effect of multiple unsafe views during a partial eclipse can be devastating. Remember, the sun’s brightness remains dangerous even when partially obscured by the moon.
Safe Solar Viewing Glasses and Filters
Several types of specialized eyewear provide adequate protection for safe solar viewing. ISO 12312-2 certified solar viewing glasses are crucial; these glasses use a special filter that blocks out 99.999% of the sun’s harmful rays. Improperly made filters, such as homemade ones or regular sunglasses, are absolutely inadequate and dangerous. Another safe option is a solar filter designed for telescopes or binoculars. These filters must be placed over the front of the optics, never in the eyepiece. Always check that any filter you use is specifically designed for solar observation and carries the necessary safety certifications.
Safe Eclipse Observation Using Projection Methods
Projection methods offer a safe and engaging way to observe the eclipse indirectly. A simple pinhole projector can be made by poking a small hole in a piece of cardboard. When sunlight passes through the hole and onto another surface, it projects an image of the sun. Alternatively, a more sophisticated projector can be made using two pieces of cardboard and a lens. The image projected onto the second piece of cardboard shows a clear image of the sun’s progress during the eclipse. These methods allow multiple people to view the eclipse safely and simultaneously, offering a shared viewing experience.
Importance of Adhering to Safety Guidelines During the Eclipse
Strict adherence to safety guidelines is non-negotiable when observing a solar eclipse. Never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection. Even during the brief moments of totality (when the moon completely covers the sun), it’s recommended to use eclipse glasses to avoid any accidental exposure to the sun’s corona. It’s crucial to supervise children closely and ensure they are using approved safety equipment at all times. The consequences of unsafe viewing can be devastating and lifelong. Remember, protecting your eyesight is paramount.
Safely Photographing the Eclipse
Photographing a solar eclipse requires specialized equipment and techniques to protect both your eyes and your camera. Use a solar filter specifically designed for cameras and lenses, attaching it to the front of your lens. Never attempt to photograph the eclipse through a telescope or binoculars without a properly fitted solar filter. Experiment with different exposure settings and shooting modes beforehand to get the best results. Remember that the sun’s brightness changes throughout the eclipse, so adjust your settings accordingly. A tripod is essential to ensure sharp, stable images.
The Science Behind Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events, are a result of the precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. Understanding the mechanics behind these events requires exploring the interplay of orbital dynamics and the relative sizes and distances of these three bodies. This intricate dance of celestial objects creates a spectacle that has captivated humanity for millennia.
Celestial Mechanics of Solar Eclipses
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, casting its shadow on our planet. This alignment isn’t a frequent occurrence because the Moon’s orbit is inclined at approximately 5 degrees relative to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Eclipses only happen when the Moon crosses the ecliptic plane – the plane of Earth’s orbit – during a new moon phase. The geometry of this alignment determines the type of eclipse experienced at a given location. The Moon’s umbral shadow, the darkest part of its shadow, creates a total eclipse. The penumbral shadow, the lighter outer part, results in a partial eclipse.
Types of Solar Eclipses
There are three main types of solar eclipses: total, partial, and annular. A total solar eclipse happens when the Moon completely blocks the Sun’s disk from view, revealing the Sun’s corona. A partial solar eclipse occurs when only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon; the Sun appears as a crescent. An annular eclipse, also known as a “ring of fire” eclipse, happens when the Moon is farthest from Earth in its orbit, appearing smaller than the Sun. In this case, the Moon doesn’t completely cover the Sun, leaving a bright ring visible around the Moon’s silhouette.
The Solar Corona
The corona is the Sun’s outermost atmosphere, normally invisible due to the overwhelming brightness of the Sun’s surface. Only during a total solar eclipse does the Moon’s blockage of the Sun’s bright disk allow us to observe this ethereal, pearly white halo. The corona’s intricate structure, consisting of plasma loops and streamers extending millions of kilometers into space, provides valuable insights into the Sun’s magnetic field and its dynamic processes. Studying the corona during a total eclipse has been crucial to our understanding of solar physics.
Historical and Cultural Significance of Solar Eclipses
Throughout history, solar eclipses have held immense cultural and religious significance across diverse societies. Many ancient cultures viewed eclipses as ominous signs, often associating them with divine wrath or supernatural events. Some cultures developed sophisticated methods for predicting eclipses, demonstrating advanced astronomical knowledge. For instance, ancient Babylonian astronomers meticulously recorded eclipse observations, leading to the development of predictive models. In many cultures, eclipses were incorporated into mythology and folklore, often featuring stories of celestial battles or the temporary disappearance of the Sun god. The impact of these events on societal beliefs and practices underscores their enduring influence on human history.
Phases of a Total Solar Eclipse
The following table illustrates the phases of a total solar eclipse:
| Phase | Description | Visual Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| First Contact | The Moon begins to encroach upon the Sun’s disk. | A small, dark notch appears on the Sun’s edge. |
| Partial Eclipse | The Moon progressively covers more of the Sun. | The Sun appears as a crescent. |
| Totality | The Moon completely blocks the Sun’s disk. | The Sun’s corona becomes visible; the sky darkens dramatically. |
| Third Contact | The Moon begins to move away from the Sun’s disk. | The Sun reappears as a small crescent. |
| Partial Eclipse (Ending) | The Moon continues to move away, revealing more of the Sun. | The crescent gradually becomes larger. |
| Fourth Contact | The Moon completely clears the Sun’s disk. | The eclipse ends. |
Impact on Different Regions
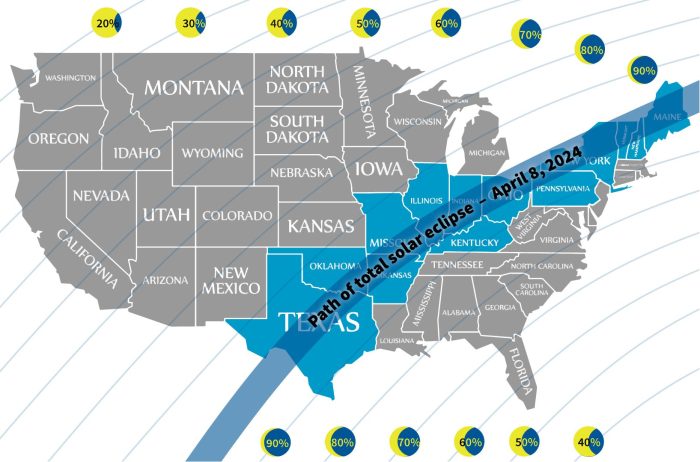
The total solar eclipse of 2024, and future eclipses, will have varying impacts across the globe, affecting economies, wildlife, and cultural perceptions in unique ways. The path of totality, the area where the sun is completely obscured by the moon, dictates the regions experiencing the most significant effects. These effects are not solely limited to the path of totality; the surrounding regions also experience a noticeable increase in tourism and related activities.
Regions Experiencing Greatest Impact
The regions experiencing the greatest impact from the 2024 total solar eclipse are those directly in the path of totality. This path, in 2024, traverses parts of North America, Mexico, and Central America. These areas will see a surge in tourism as eclipse chasers and astronomy enthusiasts converge, creating a concentrated economic boost in a relatively short period. The duration of totality, which varies along the path, also influences the magnitude of the impact; locations experiencing longer periods of totality are expected to draw larger crowds and experience greater economic benefits. Past eclipses have shown that areas with well-planned infrastructure and promotional campaigns reap the most rewards. For example, the 2017 eclipse across the United States saw significant economic gains in towns and cities along the path of totality, with many reporting substantial increases in hotel bookings, restaurant sales, and overall tourism revenue.
Predicted Economic Effects in Regions Experiencing Totality
The economic effects in regions experiencing totality are primarily positive, though they can be unevenly distributed. Increased tourism leads to higher revenues for hotels, restaurants, and local businesses. The influx of visitors creates temporary job opportunities, from hospitality and transportation to merchandise sales. However, careful planning is crucial; inadequate infrastructure can lead to logistical challenges and even negative impacts. For example, if a region lacks sufficient accommodation or transportation capacity, the influx of visitors could overwhelm local resources and create issues such as traffic congestion, strain on public services, and even price gouging. Conversely, regions that anticipate and prepare for the influx of tourists through infrastructure improvements, marketing, and community engagement generally experience substantial positive economic benefits. The 2017 US eclipse provided numerous examples of successful and unsuccessful economic management strategies during a total solar eclipse.
Effects on Wildlife and Animal Behavior During the Eclipse
During a total solar eclipse, the sudden drop in light and temperature can trigger noticeable changes in wildlife behavior. Animals that are active during the day may become quieter or seek shelter, while nocturnal animals may exhibit unusual activity. Birds may stop singing and return to their nests, while some mammals may display altered patterns of movement and foraging. The precise effects vary depending on the species and the environment. Studies have documented a range of responses, from subtle shifts in activity to more pronounced behavioral changes. These observations highlight the intricate relationship between animals and their environment and how even temporary changes in light and temperature can influence their behavior. Scientific studies on past eclipses have provided valuable data on these effects, offering insights into the ecological impacts of such celestial events.
Cultural Responses to Solar Eclipses in Different Regions
Cultural responses to solar eclipses vary widely across the globe, reflecting diverse beliefs and traditions. In some cultures, eclipses are viewed as ominous events, associated with supernatural forces or negative omens. Others regard them as sacred or auspicious occasions, marking significant moments in time. These diverse interpretations often shape how communities prepare for and react to an eclipse, influencing rituals, ceremonies, and overall social behavior. The differences highlight the diverse ways humans interact with and interpret natural phenomena. For instance, some cultures have elaborate rituals to ward off evil spirits believed to be associated with eclipses, while others celebrate them as festivals.
Planned Eclipse Viewing Events and Festivals Around the World
Many regions are planning viewing events and festivals to coincide with the next total solar eclipse. These events offer opportunities for education, community engagement, and celebration.
- Numerous astronomy clubs and organizations are hosting viewing parties along the path of totality, providing telescopes, educational resources, and a communal atmosphere for witnessing the event.
- Several cities and towns are organizing festivals incorporating local culture and cuisine, alongside eclipse-themed activities.
- National parks and other natural areas are offering special viewing opportunities, combining the awe of the eclipse with the beauty of the surrounding landscape.
- Many educational institutions are planning outreach programs to engage the public and provide information about the science behind solar eclipses.
- Several online platforms are streaming live coverage of the eclipse, making it accessible to a global audience.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Trip
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a once-in-a-lifetime experience, and careful planning is key to maximizing your enjoyment. This section will guide you through the process of selecting the perfect viewing location, arranging travel and accommodation, and optimizing your eclipse viewing experience. We’ll also explore ways to incorporate other travel activities into your trip, and provide a sample itinerary to inspire your own planning.
Choosing the Optimal Viewing Location
The path of totality, the area where the sun is completely obscured by the moon, is relatively narrow. Therefore, selecting a location within this path is crucial. Factors to consider include weather forecasts (clear skies are essential!), accessibility (consider proximity to airports and accommodation), and crowd levels (popular locations can become very crowded). Websites and apps dedicated to eclipse predictions provide detailed maps of the path of totality, enabling you to pinpoint potential viewing spots. Researching historical weather data for the chosen region can significantly increase your chances of clear skies. For example, examining past weather patterns in a region known for clear skies in April (if the eclipse occurs in April) offers valuable insight.
Logistical Aspects of Planning an Eclipse Trip
Planning your trip involves several key logistical steps. First, you need to book flights and accommodation well in advance, especially if traveling to a popular eclipse viewing destination. Prices tend to surge as the eclipse date approaches. Consider transportation within the viewing area; renting a car may offer greater flexibility in reaching optimal viewing spots. Pre-booking accommodations, securing rental cars, and purchasing flight tickets well in advance is highly recommended to avoid potential issues and price increases. For example, booking flights six months in advance can often secure better rates than booking a few weeks prior to departure.
Maximizing Your Eclipse Viewing Experience
To make the most of your eclipse viewing, consider the following tips. Bring eclipse glasses that meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard. These glasses are crucial for protecting your eyes from the sun’s harmful rays. Arrive at your viewing location well before the eclipse begins to allow ample time to set up and prepare. Bring comfortable seating, sunscreen, and insect repellent. Consider bringing binoculars or a telescope with a solar filter for a closer look (though remember that even with these tools, you still need proper eye protection). Finally, take time to soak in the atmosphere and share the experience with fellow eclipse enthusiasts.
Combining Eclipse Viewing with Other Travel Activities
Many eclipse viewing locations offer opportunities for additional travel experiences. For instance, you might combine your eclipse trip with a visit to national parks, historical sites, or other attractions in the region. Researching local points of interest near your chosen viewing location can significantly enhance your overall travel experience. For example, if the eclipse is visible near a popular national park, you could spend a few days exploring the park before and after the eclipse.
Sample Eclipse Viewing Trip Itinerary
- Day 1: Arrive in [City near eclipse path], check into hotel, explore the local area.
- Day 2: Visit a local attraction (e.g., museum, historical site), prepare eclipse viewing equipment.
- Day 3: Travel to the chosen eclipse viewing location, set up viewing area, enjoy the total solar eclipse!
- Day 4: Participate in post-eclipse activities (e.g., stargazing, meet fellow eclipse watchers), depart from [City near eclipse path].
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Next Total Solar Eclipse After 2025 World
This section addresses common queries regarding total solar eclipses, encompassing their nature, frequency, viewing safety, and photography techniques. Understanding these aspects ensures a safe and enriching experience for eclipse enthusiasts.
Total Solar Eclipses Explained
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light from reaching a specific area on Earth’s surface. This creates a temporary period of darkness during the daytime, revealing the Sun’s corona – its outer atmosphere – which is usually invisible to the naked eye. The apparent size of the Moon and Sun are nearly identical from Earth’s perspective, making total solar eclipses possible. This alignment is a rare and spectacular astronomical event.
Frequency and Predictability of Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses are not frequent occurrences. On average, a total solar eclipse occurs somewhere on Earth about every 18 months. However, any given location on Earth only experiences a total solar eclipse roughly once every 375 years. While the timing and path of total solar eclipses can be accurately predicted years in advance using sophisticated astronomical calculations, the precise duration and visibility at a specific location depend on various factors. For example, the eclipse of August 21, 2017, was visible across a large swathe of the United States, while others may only be visible from remote or sparsely populated areas.
Locations of the Next Total Solar Eclipse, Next Total Solar Eclipse After 2025 World
The next total solar eclipse will be visible from various locations, primarily across parts of North America and the South Pacific, but specific visibility will depend on the date and exact path of totality. Consult detailed eclipse maps published by NASA or other reputable astronomical organizations to determine precise visibility zones for the next event. These maps show the path of totality – the narrow band where the Sun is completely obscured – as well as the surrounding areas where a partial eclipse can be observed.
Safe Solar Eclipse Viewing
Never look directly at the Sun during a solar eclipse without proper eye protection. Doing so can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. The only safe time to look directly at the Sun during a total eclipse is during the brief period of totality, when the Sun’s disk is completely covered by the Moon. For all other times, including partial phases, use certified ISO 12312-2 rated solar viewing glasses or a certified solar filter for telescopes and cameras. Improvised methods like sunglasses or smoked glass are not sufficient and are dangerous.
Photographing a Solar Eclipse
Capturing a solar eclipse photographically requires specialized equipment and techniques. A DSLR or mirrorless camera with a telephoto lens (at least 300mm) is recommended, along with a solar filter to protect both the camera’s sensor and the lens. Consider using a sturdy tripod to prevent camera shake, and explore manual exposure settings to control the image’s brightness and sharpness. For capturing the corona during totality, you may need to adjust your settings to a faster shutter speed and higher ISO, depending on the ambient light conditions. Practice beforehand to ensure you are comfortable with your equipment and settings before the actual eclipse.
Next Total Solar Eclipse After 2025 World – Planning for the next total solar eclipse after 2025 requires looking ahead several years. Before considering those future events, however, it’s worth noting the significant upcoming event in the United States: the Total Eclipse Cincinnati 2025, which you can learn more about at Total Eclipse Cincinnati 2025. After this exciting event, the hunt for the next celestial spectacle begins, promising another captivating display of nature’s wonder.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse after 2025 requires advance preparation, considering the path of totality. To illustrate regional interest, consider this question: To find out which Ohio cities will experience the 2024 eclipse, check this useful resource: What Cities In Ohio Will See The Total Eclipse In 2025. This will help you understand the scale of the event and prepare for future celestial events worldwide.
Planning to witness the next total solar eclipse after 2025? While you’re strategizing, it’s worth noting that the 2025 eclipse will be visible in parts of North America, and to find out the precise timing for New York City, check this helpful resource: Total Eclipse 2025 Time Nyc. After 2025, however, future total solar eclipses will grace different parts of the globe, offering unique viewing opportunities for eclipse enthusiasts worldwide.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse after 2025 requires looking ahead, but first, let’s finalize our plans for the upcoming one. To help you prepare for the celestial event in April 2025, you might find this resource helpful: Where To See The Total Eclipse In April 2025. After experiencing the April 2025 eclipse, we can then fully focus on the subsequent celestial events further down the line.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse after 2025 requires some foresight. Before looking ahead, however, it’s useful to understand the duration of the upcoming event; you can find details on exactly how long totality will last in 2025 by checking out this helpful resource: How Long Will The 2025 Total Eclipse Last. Knowing this helps in preparing for future eclipse viewing expeditions, as durations vary significantly impacting viewing strategies.