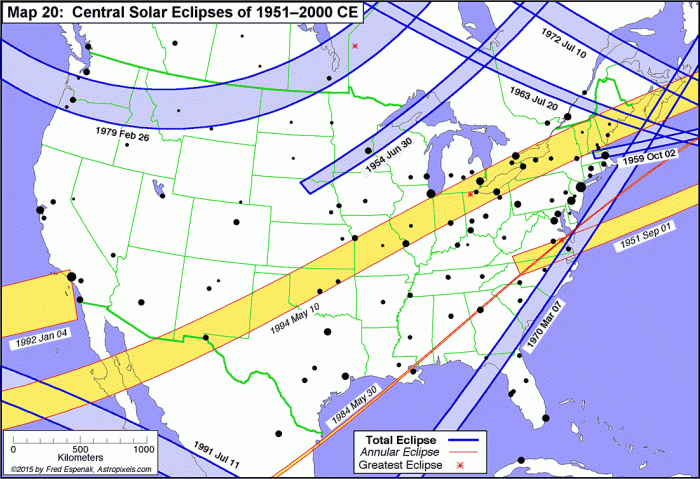
Next Total Solar Eclipse After 2025: Next Total Solar Eclipse Anywhere After 2025
Following the total solar eclipses of 2024 and earlier, several more opportunities to witness this spectacular celestial event will arise in the years beyond 2025. These eclipses, while sharing the fundamental process of the moon passing between the sun and Earth, offer unique viewing experiences due to variations in their paths and durations.
Global Overview of Total Solar Eclipses After 2025, Next Total Solar Eclipse Anywhere After 2025
Predicting the exact paths and durations of future total solar eclipses requires sophisticated astronomical calculations. However, using established models and data, we can provide a general overview of the upcoming events. The following list presents a selection of total solar eclipses occurring after 2025, noting that precise times and path details may be subject to minor refinements as calculations are further refined. The information provided here is based on current predictive models and should be considered an approximation.
Next Total Solar Eclipse Anywhere After 2025 – Note: Due to the limitations of this text-based format, a detailed world map illustrating the eclipse paths cannot be directly included. However, a mental image can be formed by considering that each eclipse will have a specific path of totality, a relatively narrow band across the Earth’s surface, where the total eclipse is visible. Outside this path, a partial eclipse will be observable.
Planning to witness a total solar eclipse? The next opportunity after 2025 will arrive later in the decade. But before then, you can check the specifics for the upcoming event with this helpful resource detailing the Total Eclipse 2025 In Houston Time , ensuring you’re well-prepared for this celestial spectacle. Following 2025, future eclipse viewing opportunities will be announced closer to the dates.
A table summarizing key characteristics of selected future total solar eclipses would be highly beneficial here. Unfortunately, I cannot create tables within this format. Instead, I will list the eclipses chronologically, providing approximate dates and brief descriptions.
Planning to witness the celestial spectacle of a total solar eclipse? While the next major event after 2025 is still some years away, you might be interested in the upcoming Total Solar Eclipse Nj 2025 , a significant event for the region. After New Jersey’s experience, anticipation for the next total solar eclipse anywhere will undoubtedly be high.
Mark your calendars!
For example, a total solar eclipse predicted for August 12, 2026, might have a path of totality traversing parts of North America, with a maximum duration of totality around 4 minutes. Another eclipse on December 26, 2028, could have a path cutting across South America and the South Atlantic, with potentially shorter totality durations. Each subsequent eclipse would follow a different trajectory, impacting the regions where totality is visible. The specific duration of totality will vary along the path of each eclipse, with the longest durations occurring near the center of the path. Accurate predictions require specialized software and astronomical data.
Planning to witness a total solar eclipse after 2025? While several locations will offer viewing opportunities, a significant event is the upcoming Toronto Total Eclipse in 2025. For detailed information on this spectacular celestial event, check out the comprehensive guide on the Toronto Total Eclipse 2025 website. Following the Toronto eclipse, future total solar eclipses will be visible from various parts of the globe, each offering a unique viewing experience.
Comparison of Totality Durations
The duration of totality for a total solar eclipse is a key factor determining the viewing experience. It is influenced by the relative distances of the sun and moon from the Earth and the moon’s position in its orbit. Generally, eclipses near the moon’s perigee (closest point to Earth) have longer durations of totality. The precise duration varies along the path of the eclipse, reaching its maximum at the point of greatest eclipse. While precise predictions for future eclipses beyond a few years are challenging due to the complex orbital mechanics involved, historical data and current models allow for estimations. For instance, some future eclipses might offer totality durations exceeding 7 minutes in certain locations, while others may be significantly shorter.
Unique Astronomical Characteristics of Future Eclipses
Each total solar eclipse possesses unique characteristics influenced by the positions of the sun and moon. The sun’s position relative to the ecliptic (the plane of Earth’s orbit) affects the eclipse’s path and visibility. Similarly, the moon’s apparent size in the sky, determined by its distance from Earth, influences the duration of totality. Factors such as the sun’s activity level (sunspots, solar flares) also play a role, although these are less predictable in the long term. Precise details regarding the sun’s position and the moon’s apparent size for each specific eclipse require detailed astronomical calculations, and these would vary for each eclipse along its path.
Viewing the Eclipse
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a truly awe-inspiring experience. Careful planning and preparation are crucial to ensure a safe and memorable viewing. This section details optimal viewing locations, essential safety precautions, and strategies for maximizing your eclipse viewing experience, regardless of weather conditions.
Best Locations for Viewing Total Solar Eclipses After 2025
Predicting the precise best locations years in advance requires considering evolving weather data and accessibility changes. However, we can identify regions historically favorable for eclipse viewing based on their weather patterns and infrastructure. The following table offers a preliminary overview; specific locations within these regions will depend on the precise path of totality for each future eclipse. Remember to consult updated eclipse maps closer to the event date for precise path details.
| Region | Advantages | Disadvantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America (various locations depending on eclipse path) | Relatively good infrastructure, established tourism infrastructure in some areas. | Potential for cloud cover in certain regions. | Research specific locations along the path of totality for optimal weather forecasts closer to the eclipse date. |
| South America (various locations depending on eclipse path) | Clear skies in many regions, potentially less crowded than North America. | Infrastructure may be less developed in some areas. | Thorough research is needed to ensure access to suitable viewing locations and accommodations. |
| Africa (various locations depending on eclipse path) | Clear skies in many desert regions. | Infrastructure can vary significantly across the continent. | Consider logistical challenges and potential for remote locations. |
| Australia (various locations depending on eclipse path) | Established tourism infrastructure in many areas. | Potential for cloud cover in some regions. | Similar to North America, research specific locations for optimal weather conditions. |
Safe Eclipse Viewing Practices
Protecting your eyesight is paramount during a solar eclipse. Never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection, even during partial phases. Serious eye damage, including blindness, can result from unprotected viewing.
Impact of Weather Conditions on Eclipse Viewing
Cloud cover significantly impacts eclipse viewing. Even a thin layer of clouds can obscure the sun and diminish the experience. Atmospheric clarity, referring to the absence of haze or dust, also affects the visibility and vibrancy of the eclipse. Checking weather forecasts in the days leading up to the eclipse is crucial. Consider having backup locations in mind in case of unexpected cloud cover.
Eclipse Viewing Equipment
Several types of equipment can enhance eclipse viewing. ISO 12312-2 certified solar viewing glasses are essential for safe direct viewing of the partial phases. These glasses are inexpensive and readily available from reputable astronomy suppliers. For indirect viewing, pinhole projectors create a projected image of the sun, eliminating the need for direct viewing. More sophisticated options include solar telescopes, which allow for magnified viewing of the sun’s surface features during partial phases, but require careful handling and specialized filters. Remember that only properly filtered equipment should be used for direct solar observation.
The Science Behind Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses are awe-inspiring celestial events resulting from a precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. Understanding the mechanics behind this phenomenon requires exploring the interplay of orbital dynamics, celestial sizes, and the resulting shadow cast upon our planet.
The Astronomical Mechanics of a Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light from reaching a specific area on Earth’s surface. This alignment is only possible because the apparent size of the Moon in the sky is roughly the same as the Sun’s, a remarkable coincidence. The Moon’s orbit is not perfectly circular, however, so the apparent size of the Moon varies slightly throughout the year. This means that total solar eclipses aren’t guaranteed every time the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth. In fact, the Moon’s slightly elliptical orbit means total solar eclipses are relatively rare occurrences at any given location on Earth.
Stages of a Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse unfolds in distinct stages, each marked by a changing relationship between the Sun, Moon, and Earth. The first contact marks the beginning, when the Moon’s edge first appears to graze the Sun’s edge. As the Moon continues its transit, more and more of the Sun is obscured, leading to the partial eclipse phase. The partial eclipse progresses until totality is reached—the moment when the Sun is entirely hidden behind the Moon. During totality, the Sun’s corona, its outer atmosphere, becomes visible, a breathtaking sight that lasts for a few minutes, depending on the eclipse’s geometry. As the Moon moves away, the process reverses, culminating in the final contact when the Moon completely leaves the Sun’s disk.
Effects on Earth’s Atmosphere and Environment
The dramatic shift in light levels during a total solar eclipse causes noticeable changes in Earth’s atmosphere and environment. The most immediate effect is a significant drop in temperature, sometimes by several degrees Celsius. Animals often react to the sudden darkness and the change in ambient temperature, altering their behavior. The decrease in sunlight also affects plants, which respond to the change in light intensity. The brief period of darkness allows astronomers to observe the Sun’s corona and other celestial phenomena that are usually obscured by the Sun’s intense brightness.
Comparison with Partial and Annular Eclipses
While a total solar eclipse involves the complete blocking of the Sun’s disk by the Moon, partial and annular eclipses differ significantly. In a partial eclipse, only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon. This results in a less dramatic dimming of the sunlight. An annular eclipse occurs when the Moon is at its farthest point from Earth in its orbit, making its apparent size smaller than the Sun’s. In this case, the Moon appears as a dark disk against the brighter Sun, creating a “ring of fire” effect. The lack of complete blockage means that the environmental changes during an annular eclipse are less pronounced than those observed during a total solar eclipse. The corona is not visible during either partial or annular eclipses.
Cultural and Historical Significance of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events, have profoundly impacted human cultures and beliefs throughout history. Their sudden darkness and dramatic visual impact have inspired a rich tapestry of myths, legends, and religious interpretations, shaping societal responses and influencing scientific understanding. From ancient civilizations to modern times, the cultural significance of solar eclipses remains a compelling area of study.
Ancient Interpretations of Solar Eclipses
Many ancient cultures viewed solar eclipses as ominous signs, often associating them with supernatural forces or divine displeasure. The Babylonians, for example, meticulously recorded eclipses, viewing them as portents of significant events, both positive and negative, affecting the king and the kingdom. Their detailed astronomical records offer invaluable insights into their worldview and understanding of the cosmos. Similarly, in ancient China, eclipses were interpreted as a dragon devouring the sun, a celestial battle that required ritualistic interventions to appease the celestial dragon and restore balance. These rituals, often involving loud noises and the beating of drums, aimed to scare the dragon away and bring back the sun’s light. These diverse interpretations highlight the deeply embedded connection between celestial events and the social and political fabric of these societies.
Solar Eclipses in Mythology and Religion
Numerous myths and legends from around the globe weave solar eclipses into their narratives. In Norse mythology, the eclipse was attributed to the wolf Sköll chasing and devouring the sun. In some Native American traditions, the eclipse was viewed as a time of spiritual renewal and reflection. These narratives, often passed down through generations, reflect the deep-seated fear and wonder inspired by the eclipse phenomenon, highlighting its profound impact on religious beliefs and spiritual practices. For example, the Vikings saw the eclipse as a battle between the sun and a celestial wolf, reflecting their culture’s emphasis on struggle and conflict. The myths associated with solar eclipses are not simply stories; they reveal the ways different cultures understood the world and their place within it.
Timeline of Significant Historical Solar Eclipses
A chronological examination of historically significant solar eclipses reveals their influence on various societies. The eclipse of 585 BC, accurately predicted by Thales of Miletus, reportedly halted a war between the Lydians and Medes, demonstrating the early understanding of celestial mechanics and their potential impact on human affairs. The eclipse of 1133 AD, observed and documented by various European chroniclers, is significant for the detailed records that provide insights into the societal reactions to the event. These historical records, coupled with contemporary accounts, help illuminate how different cultures perceived and reacted to solar eclipses. The meticulous documentation of these events provides invaluable data for both historical and scientific research.
Modern Cultural Significance of Solar Eclipses
Today, solar eclipses retain their cultural significance, although interpretations have shifted. While the fear and superstition associated with eclipses in ancient times have largely subsided, the event continues to capture public imagination and interest. Modern scientific understanding of solar eclipses has not diminished their appeal; instead, it has enhanced their allure, transforming them into events that attract both scientists and enthusiasts alike. The widespread media coverage and public excitement surrounding recent total solar eclipses are testament to the enduring cultural fascination with this celestial spectacle. The events attract massive numbers of spectators and have spurred significant scientific research and advancements. The collective experience of witnessing a total solar eclipse further strengthens its modern cultural impact.
Photography and Astrophotography of Solar Eclipses
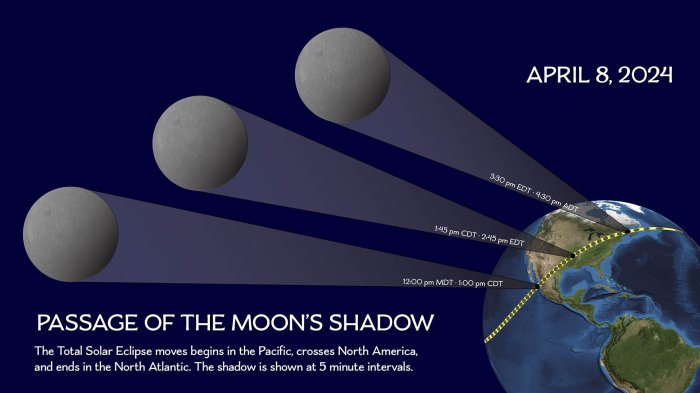
Capturing the breathtaking spectacle of a total solar eclipse requires careful planning and the right equipment. Whether you’re a seasoned astrophotographer or a novice with a smartphone, understanding the unique challenges and opportunities presented by this celestial event is crucial for achieving stunning results. This section will guide you through the process, from selecting your gear to mastering the techniques needed to capture the drama of a total solar eclipse.
Essential Equipment and Settings for Astrophotography of a Total Solar Eclipse
The equipment needed varies depending on the type of images you want to capture. For wide-field shots showcasing the eclipse within the landscape, a DSLR or mirrorless camera with a wide-angle lens is sufficient. For detailed close-ups of the corona, a telescope with a suitable adapter for your camera is necessary. Regardless of your setup, a sturdy tripod is essential for sharp images. Precise focusing is critical, especially during totality. Live view on your camera will help achieve this. For astrophotography, remote triggering is also recommended to avoid camera shake.
- Camera: DSLR or mirrorless camera capable of manual settings (aperture, shutter speed, ISO).
- Lens: Wide-angle lens (14-24mm) for landscape shots; telephoto lens (100mm-600mm or longer, even a telescope) for close-ups of the sun’s corona.
- Tripod: Sturdy tripod essential to minimize camera shake.
- Remote Shutter Release: Prevents camera shake during long exposures.
- Solar Filter: Absolutely crucial for all stages *except* totality. Use only certified solar filters designed for astrophotography.
- Intervalometer (optional): For time-lapse photography.
Appropriate settings will depend on your equipment and the specific conditions, but a good starting point for capturing the partial phases is a relatively fast shutter speed (1/2000th to 1/4000th of a second) and a small aperture (f/8 to f/11) to avoid overexposure. During totality, you’ll need to significantly increase exposure time, possibly to several seconds, and open up your aperture. Experimentation is key. ISO should be kept relatively low to minimize noise.
Step-by-Step Guide for Capturing Stunning Photographs of a Total Solar Eclipse
1. Planning and Preparation: Research the eclipse path and choose a location with clear skies and minimal light pollution. Practice your technique beforehand with a similar setup.
2. Equipment Setup: Set up your camera and tripod well in advance of the eclipse. Ensure everything is securely fastened.
3. Partial Phases: Attach your solar filter before the partial phases begin. Take several shots at different shutter speeds and apertures to determine the optimal settings. Remember to use your remote shutter release to avoid vibrations.
4. Totality: Remove the solar filter *only* during the total phase. The corona is extremely faint, requiring longer exposures and potentially higher ISO settings. Experiment with exposure times to capture the details of the corona.
5. Post-Totality: Reattach your solar filter immediately after totality ends. Continue shooting the partial phases as they recede.
6. Post-Processing: Use photo editing software to enhance the images, adjusting brightness, contrast, and sharpness.
Different Photographic Techniques for Capturing the Different Stages of a Total Solar Eclipse
During the partial phases, the primary goal is to capture the sun’s progression across the moon. A telephoto lens is recommended to show the sun’s partial obscuration in detail. For wide-field shots, a wide-angle lens will showcase the sun’s position relative to the landscape. During totality, the focus shifts to capturing the corona’s intricate structure. Longer exposures with a telephoto lens are needed to reveal its delicate details. Time-lapse photography is ideal for showcasing the entire eclipse sequence.
Examples of Breathtaking Eclipse Photographs and the Techniques Used
Imagine a photograph showing the sun almost completely eclipsed, a sliver of light peeking from behind the moon. This could be achieved using a high-powered telephoto lens, perhaps 400mm or more, with a fast shutter speed to freeze the moment and a small aperture to maintain sharpness. The image would highlight the precise geometry of the event. Another image might capture the landscape bathed in the eerie twilight of totality, with the sun’s corona visible as a bright halo. This would be a wide-angle shot, possibly taken with a 16mm or 24mm lens at a longer exposure, showcasing the dramatic contrast between the darkened landscape and the bright corona. A third image could depict a detailed close-up of the corona’s streamers and filaments, requiring a very long exposure using a telescope or a very long telephoto lens, possibly several seconds, at a wide open aperture. Each image represents a different technique tailored to capture the specific nuances of the eclipse at different phases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section addresses some common questions about the next total solar eclipse occurring after 2025. Understanding these points will help you plan your viewing experience and ensure your safety.
The Next Total Solar Eclipse After 2025
The next total solar eclipse after 2025 will occur on August 12, 2026. This eclipse will be visible across a path that stretches from the North Atlantic Ocean, across Iceland, and into northern parts of Europe and Asia.
Duration of Totality for the August 12, 2026 Eclipse
The duration of totality for the August 12, 2026 eclipse will vary depending on the viewing location along the path of totality. The maximum duration of totality will be approximately 2 minutes and 18 seconds. The length of totality is affected by the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth; specifically, the Moon’s distance from the Earth plays a significant role. A closer Moon leads to a longer eclipse.
Best Places to View the August 12, 2026 Eclipse
Several locations offer excellent opportunities to view the eclipse, balancing weather probabilities and accessibility. Iceland presents a compelling option due to its position directly within the path of totality, offering a high probability of clear skies. Parts of northern Spain and northern Norway also offer good viewing prospects, with relatively good infrastructure and accessibility. However, weather conditions should always be checked closer to the date. Specific locations within these regions, away from significant light pollution, will enhance the viewing experience.
Safe Solar Eclipse Viewing Practices
Looking directly at the sun, even during a partial eclipse, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. It is crucial to never look at the sun without proper eye protection. Certified solar viewing glasses, which meet the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard, are essential for safe viewing. These glasses are not regular sunglasses; they are specifically designed to block harmful solar radiation. Alternatively, indirect viewing methods, such as pinhole projection, can be used to safely observe the eclipse. Never use homemade filters or improperly designed equipment, as these can be dangerous.
Planning to witness the next total solar eclipse after 2025? While you anticipate that celestial event, don’t overlook the upcoming spectacle: the Total Solar Eclipse 2025 In Mexico , offering a fantastic viewing opportunity. After Mexico’s eclipse, the search for the next total solar eclipse begins anew, with various locations around the globe vying for the title of best viewing spot.
Planning to witness a total solar eclipse? The next opportunity after 2025 is still a few years away, but before then, you can check out the exciting path of totality for the 2025 event, specifically in Texas, by visiting this resource: 2025 Total Solar Eclipse Path Texas. Knowing the 2025 path helps you prepare for future celestial events and understand the fascinating phenomenon of solar eclipses.