Next Total Solar Eclipse in North America After 2025
The next total solar eclipse gracing North America will occur on August 12, 2045. This celestial event, a breathtaking spectacle of nature, happens when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light for a brief period. Understanding the mechanics behind this phenomenon and the historical context of past eclipses in the region provides a richer appreciation for the upcoming event.
Celestial Mechanics of Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses are a consequence of the precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. The Moon’s orbit around the Earth is slightly elliptical, meaning its distance from Earth varies. A total eclipse only occurs when the Moon is at or near its perigee (closest point to Earth), appearing large enough in the sky to completely cover the Sun’s disk. The shadow cast by the Moon, known as the umbra, is the region where totality is visible. Outside of the umbra lies the penumbra, where a partial eclipse is observed. The precise geometry of this alignment dictates the path of totality and the duration of the eclipse at any given location. Slight variations in the Moon’s orbit and the Earth’s tilt affect the path and duration of each eclipse, making each one unique.
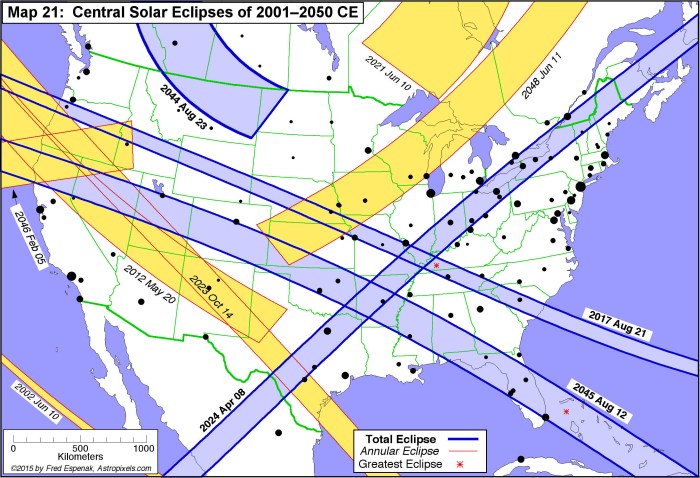
Significant Past Total Solar Eclipses in North America
North America has witnessed numerous total solar eclipses throughout history. Some notable examples include the eclipse of July 29, 2017, which traversed a path across the United States, and the eclipse of August 21, 2017, which was widely observed across the country and generated significant public interest. These events not only captivated millions but also provided invaluable opportunities for scientific research and observation. Earlier significant eclipses occurred in 1918, 1979, and 1991, each offering unique observational paths across the continent. Historical records of these eclipses offer valuable data for understanding the long-term patterns and predictability of these celestial events.
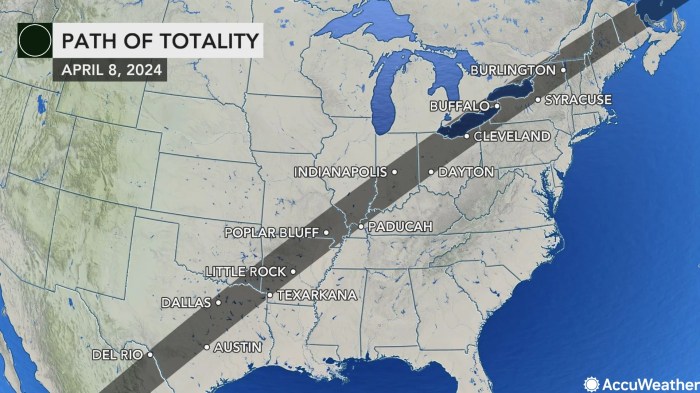
Path of Totality for the August 12, 2045, Total Solar Eclipse
The total solar eclipse of August 12, 2045, will trace a path across parts of North America. While precise details are still being refined, the path of totality is projected to begin over the Pacific Ocean, crossing into North America somewhere in the western United States. It will then sweep across parts of the central and eastern US before exiting over the Atlantic Ocean. The width of the path of totality will vary along its trajectory, potentially ranging from a few kilometers to over a hundred kilometers wide in certain areas. The duration of totality will also vary, potentially lasting anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes, depending on the observer’s location along the path. Imagine a map showing a diagonal band across the US, starting in the West and moving East, gradually widening and then narrowing. The darker, central part of this band represents the area of totality, where the Sun will be completely obscured by the Moon. Locations closer to the center of this band will experience a longer period of totality than locations near the edges. Detailed predictions, including precise timings and durations of totality for specific locations, will become available closer to the date of the eclipse. The path will likely impact significant population centers and offer a considerable opportunity for public viewing.
Viewing the Eclipse: Next Total Solar Eclipse In North America After 2025
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a truly awe-inspiring experience, but careful planning and preparation are crucial for a safe and memorable event. This section details optimal viewing locations, essential safety precautions, and practical tips for your eclipse-viewing trip.
Best Viewing Locations
Choosing a location along the path of totality with clear skies and minimal light pollution is paramount for optimal viewing. The path of totality for the next North American total solar eclipse will vary depending on the specific eclipse. However, the following table provides examples of ideal locations based on historical data and typical weather patterns, highlighting factors such as estimated viewing duration and accessibility. Remember to check updated forecasts closer to the event date.
| Location | State | Estimated Viewing Duration (Approximate) | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Location 1 (e.g., a National Park) | Example State (e.g., Oregon) | 2 minutes 30 seconds | Good; ample parking and facilities available. |
| Example Location 2 (e.g., a small town) | Example State (e.g., Nebraska) | 2 minutes 15 seconds | Moderate; limited parking, potential for crowds. |
| Example Location 3 (e.g., a rural area) | Example State (e.g., Texas) | 2 minutes | Good; easy access from major highways, but limited amenities. |
Eclipse Viewing Safety Precautions
Looking directly at the sun, even during a partial eclipse, can cause serious and permanent eye damage. Never look at the uneclipsed or partially eclipsed sun without proper eye protection. The intense solar radiation can damage the retina, leading to vision impairment or blindness.
Safe viewing methods include using certified ISO 12312-2 eclipse glasses, which are specifically designed to filter out harmful solar radiation. These glasses are readily available from reputable astronomy suppliers and science museums. Alternatively, you can use a pinhole projector, which creates a projected image of the sun onto a surface. This method is safe and easy to construct using simple materials like cardboard.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Trip
Planning ahead is essential for a smooth and enjoyable eclipse-viewing trip. Accommodation options range from camping in designated areas to booking hotel rooms well in advance, especially if the eclipse is occurring in a popular destination. Transportation should be considered carefully, as roads can become congested during the event. Consider using public transportation or carpooling if possible. Finally, be prepared for large crowds, especially in popular viewing locations. Arriving early and having a backup plan for accommodation and transportation is recommended.
Scientific Significance of Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses, while awe-inspiring spectacles, offer invaluable opportunities for scientific advancement. The brief period of totality, when the moon completely obscures the sun’s disk, allows researchers to study aspects of the sun and its immediate environment that are otherwise impossible to observe. This unique phenomenon provides a window into processes crucial to understanding our star and its influence on the solar system.
The most significant scientific contribution of total solar eclipses lies in the study of the sun’s corona. The corona, the sun’s outermost atmosphere, is incredibly faint and is usually overwhelmed by the sun’s bright surface. Only during a total eclipse does the corona become visible to the naked eye, allowing for detailed observation and data collection. This data is crucial for understanding the sun’s magnetic field, solar wind generation, and the dynamics of coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which can have significant impacts on Earth.
Coronal Observations and Solar Physics
Observations of the corona during total solar eclipses have revealed its intricate structure, including streamers, plumes, and coronal holes. Spectroscopic analysis of the coronal light allows scientists to determine the temperature, density, and chemical composition of different regions of the corona. These data are essential for testing and refining theoretical models of coronal heating, a long-standing problem in solar physics. For instance, the unexpected high temperatures of the corona, millions of degrees hotter than the sun’s surface, are still an area of active research, and eclipse observations play a crucial role in understanding this phenomenon. Furthermore, the study of coronal mass ejections, massive bursts of plasma from the sun, is significantly enhanced by eclipse observations, allowing for tracking of their initial stages and helping to predict space weather events that can disrupt satellite communications and power grids on Earth.
Comparison with Other Solar Observation Methods
While total solar eclipses provide unique opportunities, they are limited by their infrequent occurrence and short duration. Modern solar observatories, such as the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Parker Solar Probe, offer continuous monitoring of the sun and provide a wealth of data on solar activity. However, these instruments often lack the spatial resolution and sensitivity needed to observe certain features of the corona in the same detail as during a total solar eclipse. Therefore, eclipse observations complement data from space-based observatories, providing crucial information that enhances our understanding of solar phenomena. For example, coronagraphs on spacecraft can create artificial eclipses, but they cannot fully replicate the unique viewing conditions provided by a natural total solar eclipse. This means that data from eclipses can provide independent verification and calibration for data obtained through other methods. The combination of data from different sources provides a more complete and accurate picture of the sun’s dynamic behavior.
Cultural and Historical Perspectives on Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events, have held profound cultural and historical significance across diverse societies throughout human history. Their dramatic appearance, transforming midday into twilight, has inspired a wide range of interpretations, from divine omens to natural phenomena requiring scientific explanation. The reactions to these events, both fear and fascination, shaped cultural narratives and contributed to the development of astronomical understanding.
The impact of solar eclipses on various cultures is extensive and varied. Many ancient civilizations viewed eclipses as supernatural occurrences, often associating them with divine displeasure, impending doom, or the actions of mythical beings. These interpretations influenced religious rituals, social structures, and even political decisions. For example, some cultures performed rituals to appease deities believed to be causing the eclipse, while others saw it as a time for reflection or societal purification. The interpretations were not static; they evolved alongside cultural and scientific advancements.
Ancient Interpretations of Solar Eclipses
Ancient Mesopotamian records contain detailed accounts of solar eclipses, often interpreted as negative omens foreshadowing the death of kings or other calamities. These records provide valuable insights into their astronomical observations and attempts to predict these events, though their methods were largely based on cyclical patterns rather than a comprehensive understanding of celestial mechanics. In contrast, some cultures, like the ancient Chinese, developed sophisticated systems for predicting eclipses, attributing them to a celestial dragon devouring the sun. Their mythology intertwined with their astronomical knowledge, resulting in elaborate rituals designed to ward off the dragon and restore the sun’s light. The Inca civilization viewed eclipses as a sign that the sun god was angered, prompting them to perform sacrifices and make offerings to appease the deity. These diverse interpretations reflect the varied cosmological beliefs and practices of different cultures.
Historical Accounts and Scientific Advancements
The historical record is replete with accounts of total solar eclipses, influencing not only cultural beliefs but also scientific progress. The eclipse of 585 BC, famously described by Herodotus, is credited with halting a battle between the Medes and Lydians, highlighting the eclipse’s power to disrupt even major historical events. Later, Greek astronomers like Ptolemy made significant contributions to understanding the mechanics of eclipses, refining prediction methods and improving the accuracy of their calculations. The medieval period saw a blend of scientific and superstitious interpretations, with some scholars attempting to reconcile astronomical observations with religious doctrines. The scientific revolution brought a paradigm shift, with figures like Isaac Newton providing a comprehensive explanation of eclipses based on the laws of gravity and celestial mechanics. The ability to accurately predict eclipses became a testament to the advancements in scientific understanding.
Visual Comparison: Historical and Modern Depictions, Next Total Solar Eclipse In North America After 2025
A visual comparison of historical and modern depictions of solar eclipses would reveal a striking contrast. A historical illustration, perhaps a medieval manuscript depicting a dragon devouring the sun, would showcase symbolic and artistic representations reflecting the cultural interpretations of the time. The visual elements would emphasize the symbolic nature of the event, with vivid colors and fantastical creatures dominating the composition. In contrast, a modern scientific illustration would likely feature a precise diagram of the sun, moon, and Earth, showing the geometric alignment causing the eclipse. The visual elements would prioritize accuracy and scientific detail, utilizing precise measurements and astronomical data to create a realistic representation. The contrast highlights the evolution from mythological interpretations to scientifically-based explanations, demonstrating how understanding of the phenomenon has transformed over centuries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section addresses common queries regarding total solar eclipses, focusing on their nature, frequency, optimal viewing locations, and safe observation methods. Understanding these aspects ensures a safe and enriching experience for anyone witnessing this awe-inspiring celestial event.
Total Solar Eclipse Definition
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light from reaching a specific area on Earth’s surface. This creates a temporary period of darkness during the daytime, revealing the Sun’s corona – its outer atmosphere – which is usually invisible due to the Sun’s overwhelming brightness. The path of totality, where the total eclipse is visible, is a relatively narrow band across the Earth’s surface. Outside this path, a partial eclipse may be observed, where only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon.
Frequency of Total Solar Eclipses in North America
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events at any given location. While a partial solar eclipse may be visible from a given location several times per decade, total solar eclipses are much less frequent. North America experiences a total solar eclipse approximately every few decades, with the exact frequency varying due to the complex interplay of the Sun, Moon, and Earth’s orbits. For example, the total solar eclipse of August 21, 2017, was a significant event, and the next one after 2025 will be a considerable wait for many North American locations. Predictability is high, with astronomers capable of calculating eclipse paths years, even centuries, in advance.
Optimal Viewing Locations for the Next Total Solar Eclipse in North America After 2025
Determining the best location to view a total solar eclipse involves several factors. Clear skies are paramount; a cloudy day will obscure the view. The path of totality’s width is also important, with wider paths offering more viewing time. Accessibility and infrastructure – availability of transportation, lodging, and amenities – are also crucial considerations for viewers. Specific locations within the path of totality will vary depending on the eclipse’s path, which needs to be determined closer to the event by NASA and other astronomical organizations. However, historically, areas with relatively low light pollution and predictable weather patterns in the path of totality have proven to be popular choices.
Safe Viewing Equipment for Total Solar Eclipses
Never look directly at the Sun during a partial solar eclipse or any other time without proper eye protection. Doing so can cause severe and permanent eye damage, including blindness. During the totality phase of a total solar eclipse, when the Sun is completely blocked by the Moon, it is safe to view the eclipse without eye protection. However, the moment before and after totality, eye protection is crucial. Safe viewing methods include using certified solar eclipse glasses or viewers that meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard. These glasses are specifically designed to filter out harmful solar radiation. Alternatively, indirect viewing methods such as pinhole projectors can be used to safely project the Sun’s image onto a screen. Improper methods such as sunglasses, smoked glass, or exposed film are dangerous and should never be used.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse in North America after 2025? While that’s still a ways off, the excitement is already building for the 2025 event. For those in Texas, you can learn more about the path of totality by checking out this helpful resource on the Total Solar Eclipse 2025 Path Texas. This will help you determine if you’re in the optimal viewing area for the 2025 eclipse before considering future events.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse in North America after 2025? While that’s still a few years away, consider the upcoming event in 2025. For those in the Northeast, detailed information on the path of totality and viewing opportunities in Massachusetts can be found here: Total Eclipse 2025 Massachusetts. After this exciting event, the wait for the next North American total eclipse will continue, but this one promises to be a spectacular sight.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse in North America after 2025 requires looking ahead several years. However, before then, North Americans have a fantastic opportunity to witness totality in 2025, with Illinois being a prime viewing location; you can find more details on this event at Total Eclipse In Illinois 2025. After experiencing the 2025 eclipse, the anticipation for the next North American total eclipse will surely build.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse in North America after 2025? While that’s still some time away, it’s worth noting that a significant event is happening sooner: the 2025 total solar eclipse will be visible across parts of the United States, including Illinois, as detailed on this helpful resource: Total Solar Eclipse 2025 Illinois. After witnessing this spectacle, you can begin to eagerly anticipate the next North American eclipse.
The next total solar eclipse gracing North America after 2025 is a highly anticipated celestial event. Planning ahead is key, and to help you prepare, consider checking out this helpful resource on finding the Best Place To Watch Total Eclipse 2025 for optimal viewing conditions. Securing your spot early will ensure you don’t miss this incredible astronomical spectacle; the next North American eclipse after that one is still several years away.