Next Total Solar Eclipse in New York After 2025
Predicting the exact dates and paths of total solar eclipses visible from specific locations requires complex astronomical calculations. However, using established astronomical data and prediction models, we can project the next opportunities for New York State to experience this celestial event. It’s important to remember that these predictions are based on current models and may be subject to minor adjustments as our understanding of celestial mechanics improves.
Timeline of Total Solar Eclipses Visible from New York After 2025
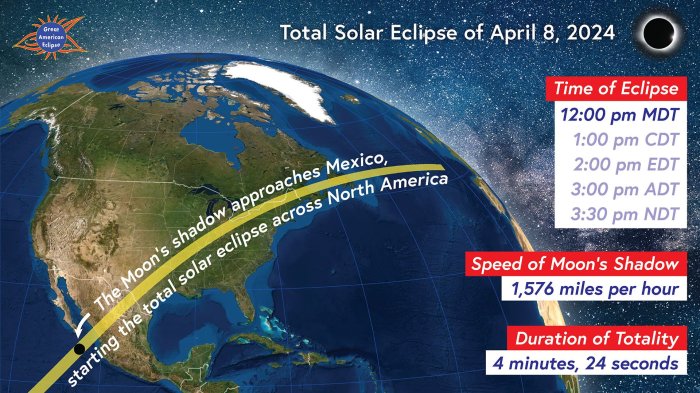
The next total solar eclipse visible from any part of New York State will occur significantly later than the April 8th, 2024 event. Pinpointing the exact date and path requires specialized astronomical software and detailed calculations. While precise dates and paths are not readily available for eclipses many decades into the future due to the complexity of long-term orbital predictions, we can make general statements based on established cycles. New York will likely not experience another total solar eclipse until well into the second half of the 21st century. The frequency of total solar eclipses over a given location is relatively infrequent.
Comparison of Future Eclipses with the 2024 Eclipse
The 2024 total solar eclipse provided a relatively long duration of totality for parts of New York State, offering an extended period to observe the phenomenon. Future total solar eclipses visible from the state will likely offer shorter durations of totality or will only be visible from a limited portion of the state, compared to the broader swath covered in 2024. The path of totality in 2024 traversed a significant portion of the state, allowing many residents easy access to the event. Future eclipses might be less accessible, requiring travel to specific regions within New York or even to neighboring states to experience the totality. The differences in visibility and duration are primarily due to the constantly shifting positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun in their respective orbits.
Visual Representation of Eclipse Paths
A visual representation would depict a series of maps, each representing a future total solar eclipse visible from New York. Each map would show the path of totality as a relatively narrow band traversing the state, potentially varying in width and location depending on the eclipse. The maps would illustrate the limited area within the state where totality is observable. For example, a map for a hypothetical eclipse in the year 2077 might show a narrow band crossing only the western portion of the state, while another map for an eclipse in 2099 might illustrate a path cutting through the central or eastern parts. The differences in the paths would reflect the moon’s varying orbital position relative to the Earth and Sun over time. The maps would clearly highlight the differences in path coverage compared to the extensive path of the 2024 eclipse.
Observing the Eclipse Safely
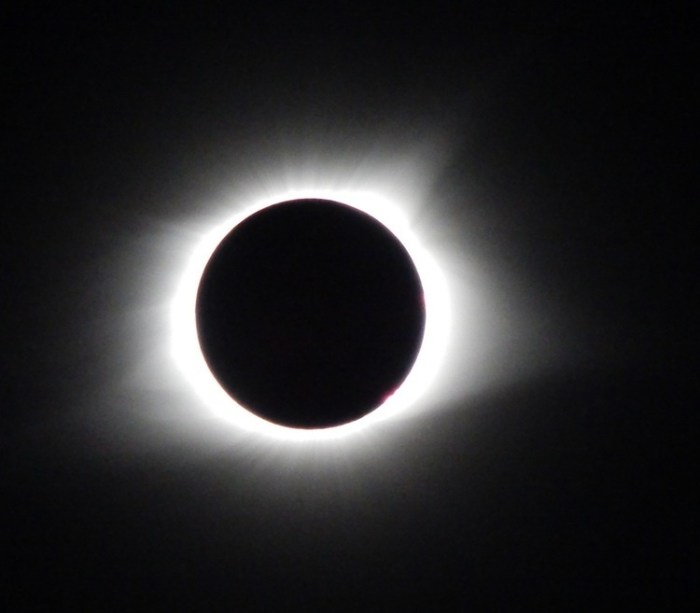

Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety. Looking directly at the sun, even for a short period, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including solar retinopathy, which can lead to vision loss. Never underestimate the sun’s power; protective eyewear is absolutely essential.
The sun’s intense radiation can severely damage the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This damage can occur even before you feel any discomfort. Unlike other burns, solar retinopathy often doesn’t produce immediate pain, making it especially dangerous. Permanent vision impairment or even blindness can result from unprotected viewing.
Safe Solar Viewing Glasses and Filters
Safe solar viewing requires specialized eyewear or filters that meet specific safety standards. Improperly made filters or regular sunglasses, even dark ones, offer insufficient protection and are dangerous to use. Acceptable filters must meet the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard. This standard ensures the filters block out harmful levels of ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR), and visible light.
The most common type of safe solar viewer is eclipse glasses. These are inexpensive and widely available from reputable astronomical societies and online retailers. They typically feature a special polymer film that effectively blocks harmful solar radiation. Another option is a solar filter for telescopes or binoculars, which must be placed over the front of the optics, never in the eyepiece. These filters are generally more expensive but necessary for magnified viewing. Improper use of solar filters can lead to equipment damage and serious eye injury. Always check for the ISO 12312-2 certification mark before using any solar viewing device.
Safe Eclipse Viewing Procedures
Before the eclipse begins, inspect your solar viewing glasses or filter carefully for any scratches or damage. Discard any damaged equipment immediately.
1. Preparation: Choose a safe viewing location, ideally one with a clear view of the sky and minimal obstructions. Bring a comfortable chair or blanket to sit on.
2. Putting on the Glasses: Carefully put on your ISO 12312-2 certified eclipse glasses, ensuring they completely cover your eyes. Avoid touching the lenses; handle them by the edges.
3. Observing the Eclipse: Once you’re wearing your glasses, you can begin to observe the eclipse. Start viewing only when the partial eclipse phase begins, and never look directly at the sun without your glasses. During the total eclipse (if you are in the path of totality), you can safely remove your glasses to view the sun’s corona. However, immediately put your glasses back on as soon as the totality ends and the sun begins to reappear.
4. Supervision: Children should always be supervised by an adult when viewing the eclipse. Ensure that they understand the importance of wearing their eclipse glasses at all times except during the brief period of totality.
5. Post-Observation: After the eclipse is over, carefully remove and store your solar viewing glasses for future use (provided they are undamaged).
The Science Behind Solar Eclipses
A solar eclipse, a captivating celestial event, occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow on our planet. This seemingly simple alignment is the result of a remarkable cosmic coincidence: the Sun’s apparent size in the sky is almost identical to the Moon’s, despite the vast difference in their actual sizes and distances from Earth. This near-perfect match allows for the dramatic spectacle of a total solar eclipse.
The precise mechanics involve the Sun, Moon, and Earth all being in a nearly straight line. The Moon’s orbit around the Earth is not perfectly aligned with the Earth’s orbit around the Sun; this slight inclination means eclipses don’t happen every month. Instead, they occur only when the Moon’s orbit intersects the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, at points called nodes. If the alignment is perfect, a total solar eclipse is visible from a narrow path on Earth’s surface.
Types of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses are categorized based on the Moon’s apparent size relative to the Sun during the eclipse. This apparent size depends on the Moon’s distance from Earth. A closer Moon appears larger, while a more distant Moon appears smaller.
A total solar eclipse happens when the Moon completely blocks the Sun’s disk, revealing the Sun’s corona, a stunning halo of plasma extending millions of kilometers into space. During totality, the sky darkens dramatically, and the temperature drops noticeably. The experience is profoundly awe-inspiring. For example, the total solar eclipse of August 21, 2017, which crossed the continental United States, provided a spectacular display for millions of observers.
A partial solar eclipse occurs when only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon. The extent of the partial eclipse varies depending on the observer’s location; those further from the path of totality see a smaller fraction of the Sun blocked. A partial eclipse is less dramatic than a total eclipse, but still a noteworthy celestial event.
An annular eclipse happens when the Moon is farther from Earth in its orbit, making it appear smaller than the Sun. In this case, the Moon doesn’t completely cover the Sun, leaving a bright ring of sunlight visible around the Moon’s silhouette. This ring, known as the “ring of fire,” is a striking sight. The annular eclipse of June 10, 2021, was visible across parts of Canada, Greenland, and Russia.
Historical Significance of Solar Eclipses
Throughout history, solar eclipses have held profound cultural and religious significance across various civilizations. Many ancient cultures interpreted eclipses as ominous signs, often associating them with divine anger or impending doom. Some cultures developed sophisticated methods for predicting eclipses, demonstrating a remarkable understanding of celestial mechanics, long before modern astronomy.
For instance, ancient Chinese astronomers meticulously recorded eclipses for centuries, developing complex predictive models. Similarly, Babylonian astronomers left behind detailed records of eclipses, which helped modern scientists understand the Moon’s orbital patterns. In some cultures, eclipses were seen as moments of transition or spiritual renewal. The myths and legends surrounding solar eclipses offer a fascinating glimpse into the ways different cultures perceived and understood the cosmos. These historical accounts provide invaluable insights into the development of astronomical knowledge and the relationship between humanity and the celestial realm.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Experience: Next Total Solar Eclipse New York After 2025
Planning your trip to witness a total solar eclipse in New York requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure a memorable and safe experience. This includes choosing an optimal viewing location, securing suitable accommodation, and potentially participating in organized eclipse-related events. The ideal location will depend on the specific path of totality for the eclipse and the predicted weather conditions.
Optimal Viewing Locations in New York State
The path of totality for a total solar eclipse will vary depending on the specific date of the eclipse. To determine the optimal viewing location, one must consult eclipse prediction resources and find areas within the path of totality that have a high probability of clear skies on the eclipse day. Historical weather data for the specific region should be analyzed. Accessibility to the location is also crucial, considering factors like road conditions, parking availability, and potential crowds. For example, a location offering a wide-open view with minimal light pollution, easily accessible by car and with ample parking, would be ideal. Another consideration would be the proximity to accommodations and other amenities.
Accommodation Options and Travel Arrangements
Securing accommodation well in advance is essential, particularly if the eclipse falls on a popular travel period. Options range from hotels and motels in larger towns near the eclipse path to camping sites offering more rustic experiences. Airbnb and other vacation rental platforms also offer diverse choices. Travel arrangements should consider potential traffic congestion on eclipse day. Public transport options, if available, should be explored. Planning alternate routes and allowing ample travel time is crucial to avoid delays and reach the viewing location comfortably before the eclipse begins. For instance, booking accommodations months in advance, especially if the eclipse coincides with other major events, is recommended. Similarly, reserving rental cars or planning carpools well in advance can mitigate potential transportation challenges.
Community Events and Festivals
Many communities along the path of totality often organize eclipse-related events and festivals. These events might include viewing parties with astronomers providing expert commentary, educational workshops, and related entertainment. Checking local tourism websites and community calendars in the months leading up to the eclipse will provide information on any planned events. These festivals can enhance the eclipse viewing experience by providing a sense of community and access to additional resources and information. For example, some communities might organize stargazing events in the days leading up to the eclipse, offering opportunities to learn about astronomy and prepare for the main event.
Photography and Videography of the Eclipse
Capturing a total solar eclipse on camera is a rewarding challenge, demanding careful planning and the right equipment. The fleeting nature of totality, coupled with the extreme brightness variations between the partial phases and the corona, requires a strategic approach to ensure you capture the awe-inspiring spectacle effectively. This section Artikels the essential equipment and techniques for successfully photographing and videographing this rare celestial event.
Next Total Solar Eclipse New York After 2025 – Successfully photographing a total solar eclipse requires a combination of specialized equipment and careful planning. Understanding the unique challenges posed by the extreme brightness differences between the partial phases and totality is crucial for obtaining high-quality images and videos.
Essential Equipment for Eclipse Photography and Videography
A successful eclipse capture relies on having the correct gear. Choosing the right camera, lenses, and filters is paramount. Improper equipment can lead to ruined images or even damage to your camera’s sensor.
The core components for capturing stunning eclipse imagery include a DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual controls, a sturdy tripod, solar filters for all phases except totality, and lenses offering a range of focal lengths. Consider investing in a telephoto lens (at least 300mm) to capture detailed images of the sun’s corona during totality, and a wide-angle lens to capture the surrounding landscape. A remote shutter release is also highly recommended to minimize camera shake. For videography, a camera capable of shooting high-definition video at a suitable frame rate is necessary. A good external microphone can also greatly improve the quality of your video recording.
Capturing the Different Phases of the Eclipse
The eclipse unfolds in stages, each requiring a different photographic approach. From the subtle initial encroachment of the moon to the dramatic corona of totality, careful adjustments to camera settings are vital.
During the partial phases, a solar filter is absolutely essential to protect your eyes and camera equipment. Start with a relatively fast shutter speed and a narrow aperture (high f-stop number) to avoid overexposure. As the eclipse progresses, you may need to adjust your settings to compensate for the decreasing light. During totality, the solar filter can be removed, allowing you to capture the stunning detail of the sun’s corona. Experiment with different shutter speeds and apertures to find the optimal settings for your equipment and lighting conditions. For videography, maintain consistent settings throughout the partial phases and use a tripod to prevent camera shake. During totality, adjust your settings to capture the corona’s brilliance without overexposure.
Creating a Time-Lapse Video of the Eclipse
A time-lapse video condenses the hours-long eclipse into a captivating short film. Careful planning and execution are key to creating a smooth and visually appealing time-lapse.
To create a time-lapse, you’ll need to shoot a sequence of still images at regular intervals. The interval depends on your desired final video length and the eclipse’s duration. Most cameras offer intervalometer functionality built-in, or you can use an external intervalometer for more precise control. Once you have your sequence of images, you can use video editing software like Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, or even free options like DaVinci Resolve to stitch the images together into a time-lapse. Experiment with different frame rates and transitions to achieve the desired effect. Remember to keep your camera perfectly still on a tripod throughout the entire process to avoid jerky movements in your time-lapse.
Impact of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, while awe-inspiring celestial events, offer invaluable opportunities for scientific advancement. These events provide unique windows into the Sun’s atmosphere and corona, allowing researchers to gather data otherwise impossible to obtain. The temporary obscuring of the Sun’s bright face reveals details about its structure and processes that are crucial to our understanding of stellar evolution and the dynamics of our solar system.
The fleeting nature of totality makes efficient data collection paramount. This necessitates careful planning, sophisticated instrumentation, and collaborative efforts from scientists across diverse disciplines. The scientific significance of solar eclipses extends beyond simply observing the Sun; they serve as a natural laboratory for testing and refining our understanding of fundamental physical laws.
Studies of the Sun’s Corona
The Sun’s corona, its outermost atmosphere, is millions of degrees hotter than its surface. This temperature disparity remains a significant mystery in solar physics. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon blocks the Sun’s blindingly bright photosphere, allowing direct observation of the corona. Spectroscopic analysis of the coronal light reveals its composition and temperature, providing crucial data to model the mechanisms driving coronal heating. For example, the 1991 eclipse expedition to Hawaii provided significant data on coronal mass ejections (CMEs), powerful bursts of plasma that can disrupt Earth’s magnetic field. These observations contributed significantly to improved space weather forecasting models.
Observations of the Sun’s Chromosphere
The chromosphere, a relatively thin layer between the photosphere and the corona, is also visible during a total solar eclipse. Observations of the chromosphere during eclipses have revealed intricate details about its structure and dynamics, including spicules – jet-like features that extend thousands of kilometers into the corona. High-resolution imaging and spectroscopic data collected during eclipses have helped refine models of chromospheric heating and the mechanisms that drive solar flares. The 2017 total solar eclipse, visible across the United States, yielded a wealth of data on chromospheric dynamics, improving our understanding of the Sun’s energy release processes.
Testing Theories of General Relativity
Einstein’s theory of General Relativity predicts that the gravity of massive objects bends the path of light. Solar eclipses provide a rare opportunity to test this prediction. During a total eclipse, the Sun’s gravity bends the light from distant stars, causing them to appear slightly displaced. Measurements of this effect, first successfully performed by Arthur Eddington during a 1919 eclipse, provided strong evidence supporting Einstein’s theory. Subsequent eclipse expeditions have continued to refine these measurements, providing further validation of General Relativity and advancing our understanding of gravitation.
Future Research Opportunities
Future research using solar eclipses will likely focus on improving the spatial and temporal resolution of observations. Advanced imaging techniques and sophisticated instrumentation, deployed during future eclipses, will allow for more detailed studies of the Sun’s dynamic atmosphere. The development of sophisticated computer models, incorporating data from multiple eclipse expeditions, will also play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of solar processes. For instance, coordinated observations from multiple locations during a total solar eclipse, combined with space-based observations, could provide unprecedented insights into the three-dimensional structure and dynamics of CMEs. The potential for scientific discovery related to solar eclipses remains immense, promising to unravel further mysteries of our Sun and its influence on our solar system.
Frequently Asked Questions about Future Solar Eclipses in New York
Planning to witness the awe-inspiring spectacle of a total solar eclipse in New York? Understanding the frequency, ideal viewing locations, and necessary safety precautions is crucial for a memorable and safe experience. This section addresses common queries regarding future solar eclipses in the state.
The Next Total Solar Eclipse Visible from New York, Next Total Solar Eclipse New York After 2025
The next total solar eclipse visible from New York will occur on August 12, 2045. This eclipse will traverse a path across a portion of the state, offering a breathtaking view of the sun’s corona to those within the path of totality. The duration of totality will vary depending on the specific location within New York, but observers can expect several minutes of darkness during the peak of the eclipse.
Frequency of Total Solar Eclipses in New York
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events. While partial solar eclipses are more frequent, total solar eclipses, where the moon completely blocks the sun’s disk, are less common. Several factors influence their visibility in a specific location, including the moon’s orbit, the Earth’s tilt, and the relative positions of the sun, moon, and Earth. New York, like many other locations, experiences total solar eclipses infrequently; the intervals between them can span several decades.
Ideal Locations for Viewing a Total Solar Eclipse in New York
Selecting the optimal viewing location for a total solar eclipse is essential to maximize the experience. For the 2045 eclipse, areas within the path of totality in New York will offer the best viewing opportunities. Specific locations will need to be determined closer to the date, considering factors such as weather forecasts and accessibility. However, areas with open skies, minimal light pollution, and convenient access will likely prove most popular. Potential locations could include state parks or other areas with clear views of the horizon.
Safety Precautions During a Solar Eclipse
Protecting your eyesight during a solar eclipse is paramount. Never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection, even during the partial phases of the eclipse. The sun’s rays, even partially obscured, can cause severe and permanent eye damage. Safe solar viewing glasses, meeting the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard, are essential. These glasses significantly reduce the sun’s intensity, allowing safe viewing.
Equipment Needed for Safe Eclipse Viewing
Safe solar viewing glasses are the most crucial piece of equipment. Beyond this, binoculars or telescopes equipped with appropriate solar filters can enhance the viewing experience, allowing for closer observation of the sun’s corona and other details during totality. However, it’s crucial to ensure any optical equipment used is specifically designed for solar viewing and has the appropriate safety filters to prevent eye damage. A comfortable chair or blanket can also make for a more enjoyable viewing experience.