Path of Total Lunar Eclipse 2025
Prepare to witness a celestial spectacle! In 2025, a total lunar eclipse will grace the night sky, offering a breathtaking display of shadow play across the moon’s surface. This event, a significant occurrence in the astronomical calendar, provides a unique opportunity to observe the intricate mechanics of our solar system in action and appreciate the beauty of the cosmos.
Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth passes directly between the sun and the moon, casting its shadow upon the lunar surface. This alignment, known as syzygy, only happens during a full moon. The Earth’s shadow consists of two parts: the umbra, a dark, central region where the sun is completely blocked, and the penumbra, a lighter, outer region where only part of the sun is obscured. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the entire moon passes into the Earth’s umbra, resulting in a dramatic darkening, often taking on a reddish hue due to the scattering of sunlight through the Earth’s atmosphere – a phenomenon often referred to as a “blood moon.” The duration and visibility of the eclipse depend on the precise orbital positions of the Earth and moon.
Celestial Mechanics of Lunar Eclipses
A lunar eclipse is a predictable event governed by the precise movements of the Earth and the moon around the sun. The moon’s orbit around the Earth is not perfectly aligned with the Earth’s orbit around the sun; it’s tilted at an angle of about 5 degrees. This means that most full moons do not result in a lunar eclipse. A lunar eclipse only happens when the full moon occurs near the points where the moon’s orbit intersects the Earth’s orbital plane – these points are called nodes. The geometry of the sun, Earth, and moon must align almost perfectly for a total eclipse to occur. Slight variations in these positions affect the duration and type of eclipse visible from different locations on Earth. For example, a penumbral lunar eclipse, where only the penumbra falls on the moon, is less dramatic than a total lunar eclipse. Precise calculations, based on astronomical models, are used to predict the path and timing of lunar eclipses years in advance. The 2025 total lunar eclipse is a prime example of this predictable celestial dance.
The 2025 Total Lunar Eclipse Path
The specific path of the 2025 total lunar eclipse across the Earth will determine which regions experience totality and which see only partial phases. This path is calculated using sophisticated astronomical software and models that account for the Earth’s rotation, the moon’s orbit, and the sun’s position. Predicting the path allows astronomers and eclipse enthusiasts to plan viewing locations for optimal observation. The geographical location significantly impacts the visibility of the eclipse. Those within the path of totality will witness the moon completely immersed in the Earth’s umbra, while those in the penumbra will observe a partial eclipse. The exact timing of the eclipse phases will also vary depending on the observer’s longitude and latitude. The 2025 eclipse’s path will likely traverse several continents, making it a widely observable event for millions across the globe. Detailed maps showing the path of totality and the times of the eclipse phases will be readily available closer to the event.
Visibility and Timing of the Eclipse
The total lunar eclipse of 2025 will be a spectacular celestial event, but its visibility will depend heavily on geographical location and the time of day. Understanding the eclipse’s path and timing is crucial for those hoping to witness this phenomenon. This section details the geographical regions where the eclipse will be visible and provides precise timing information for key stages of the eclipse in various locations.
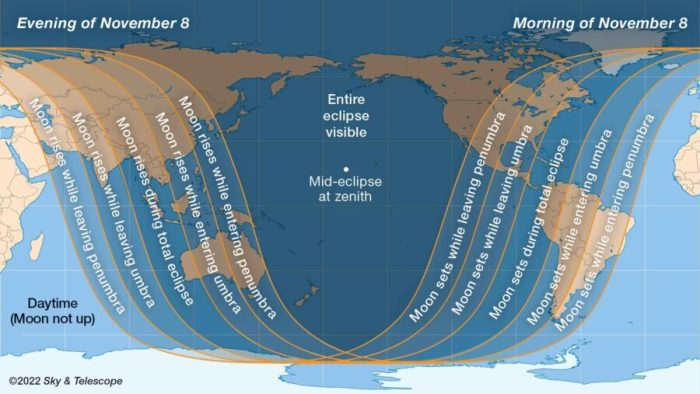
The total lunar eclipse will be visible across a significant portion of the globe. The best viewing will be in regions where the moon is above the horizon during the totality phase.
Geographical Visibility
A map depicting the visibility zones would show a large swathe of the Earth’s surface shaded to indicate areas with varying degrees of visibility. The darkest shading would represent regions experiencing the total eclipse, while lighter shading would denote areas seeing a partial eclipse. Areas outside the shaded regions would not see any part of the eclipse. For example, North and South America would have excellent viewing opportunities, along with parts of Europe, Africa, and Asia. The Pacific Ocean region would also offer prime viewing locations. The precise boundaries of these zones would require a detailed cartographic representation, but the general pattern is that the entire eclipse will be visible from a broad region spanning across several continents.
Eclipse Timing (UTC and Local Times)
Precise timing of the eclipse phases will vary depending on location. However, we can provide example times for major cities to illustrate the variations. For example, let’s consider the times for New York City, London, and Tokyo. Each city will experience slightly different times for the penumbral, partial, and total phases of the eclipse, and these times will be further offset from the Universal Coordinated Time (UTC). The penumbral phase, the initial stage where the Earth’s penumbra begins to fall on the Moon, might start at 18:00 UTC in New York City, translating to 14:00 local time. The partial phase, where the Earth’s umbra begins to cover the Moon, could begin at 19:30 UTC (15:30 local time). Totality, the most spectacular phase when the Moon is fully within the Earth’s umbra, might start at 21:00 UTC (17:00 local time). The exact times for London and Tokyo would differ, accounting for their respective time zones. The difference in timing highlights the importance of checking local times based on the observer’s specific location. Precise calculations for various locations would require sophisticated astronomical software or online eclipse calculators.
Time Zone Variations
The time of visibility is intrinsically linked to the observer’s location and the corresponding time zone. As the Earth rotates, different regions will experience the eclipse at different times. The further east a location is, the later the eclipse will be observed. Conversely, locations further west will see the eclipse earlier. For instance, a city on the west coast of North America will witness the eclipse hours before a city on the east coast. This variation is a direct consequence of the Earth’s rotation and the changing position of the Moon relative to the observer. This variation must be accounted for when planning eclipse viewing events.
The Science Behind Lunar Eclipses: Path Of Total Lunar Eclipse 2025
Lunar eclipses, captivating celestial events, occur when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the lunar surface. This seemingly simple alignment reveals a complex interplay of light, shadow, and celestial mechanics. Understanding the geometry of the Earth’s shadow and the different ways it can obscure the Moon is key to grasping the various types of lunar eclipses we observe.
The Earth’s shadow isn’t uniform; it’s composed of two distinct parts: the umbra and the penumbra. The umbra is the darkest, central part of the shadow where the Sun is completely blocked by the Earth. The penumbra, on the other hand, is a lighter, outer region where only a portion of the Sun is obscured. The size and shape of both the umbra and penumbra depend on the relative positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon.
Earth’s Shadow Components: Umbra and Penumbra
The umbra’s cone-like shape extends into space, and its size varies depending on the Earth-Sun distance. During a lunar eclipse, the Moon’s passage through the umbra or penumbra determines the type of eclipse observed. If the Moon passes entirely within the umbra, a total lunar eclipse occurs. If only a portion of the Moon enters the umbra, we see a partial lunar eclipse. Finally, if the Moon only passes through the penumbra, the eclipse is classified as a penumbral lunar eclipse. The difference in shading across these regions is significant; the umbra exhibits a dramatic darkening, while the penumbra shows a more subtle dimming. The precise path of the Moon through the Earth’s shadow dictates the duration and intensity of the eclipse.
Types of Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses are categorized based on the Moon’s interaction with the Earth’s shadow. Total lunar eclipses, where the entire Moon enters the Earth’s umbra, offer the most spectacular visual display. Partial lunar eclipses, conversely, show only a portion of the Moon immersed in the umbra, creating a partially shadowed appearance. Penumbral lunar eclipses are the subtlest, with the Moon passing solely through the Earth’s penumbra, resulting in a barely perceptible dimming. The visibility and intensity of these eclipses are influenced by the Moon’s orbital path and the alignment with the Earth’s shadow. For instance, a total lunar eclipse during perigee (when the Moon is closest to Earth) can appear slightly larger and brighter than one during apogee (when it’s farthest).
The “Blood Moon” Phenomenon, Path Of Total Lunar Eclipse 2025
During a total lunar eclipse, a captivating phenomenon known as the “blood moon” can occur. This reddish hue isn’t caused by the Moon itself changing color, but rather by the scattering of sunlight in Earth’s atmosphere. As sunlight passes through Earth’s atmosphere, shorter wavelengths of light (like blue and green) are scattered more effectively, while longer wavelengths (like red and orange) are bent and refracted towards the Moon. This filtered sunlight illuminates the Moon, giving it the characteristic reddish or copper-colored appearance associated with the “blood moon.” The intensity of the red color can vary depending on atmospheric conditions, with clearer skies generally producing a more vibrant red. The 2025 total lunar eclipse, for example, depending on atmospheric conditions, might present a spectacular “blood moon” spectacle.
Observing the Eclipse Safely
Unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses are completely safe to view with the naked eye. There’s no risk of eye damage because you’re not looking directly at the sun. However, using optical aids can enhance your viewing experience significantly, revealing the subtle details of the Earth’s shadow on the moon’s surface.
Observing a lunar eclipse is a visually rewarding experience, and employing certain techniques can maximize its impact. The key is to find a location with minimal light pollution and unobstructed views of the night sky. This allows for a much clearer and more detailed observation of the eclipse’s progression.
Binoculars and Telescopes for Enhanced Viewing
Binoculars and telescopes offer magnified views, revealing the intricate textures and subtle color changes on the lunar surface during the eclipse. A pair of standard 7×50 binoculars provides a good balance of magnification and field of view, making them ideal for eclipse viewing. Larger binoculars or telescopes will provide even greater detail, allowing you to observe the progression of the Earth’s shadow across the moon’s surface with remarkable clarity. Remember to use a sturdy tripod to stabilize your equipment, especially with higher magnifications. This will prevent blurry images caused by hand-shaking.
Optimal Viewing Conditions
The most crucial factor for optimal viewing is clear skies. Clouds will completely obscure the eclipse. Therefore, checking weather forecasts before the eclipse is essential. Light pollution significantly impacts visibility. The brighter the surrounding environment, the fainter the eclipsed moon will appear. Ideally, find a location away from city lights, such as a rural area or a dark-sky park, for the best possible viewing experience. For instance, the difference between observing from a brightly lit city center and a dark, rural location is night and day; the eclipsed moon will be far more vibrant and detailed in the latter.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Lunar eclipses, with their dramatic transformation of the night sky, have held profound cultural and historical significance across diverse societies for millennia. Their unpredictable nature and the celestial mechanics behind them have inspired awe, fear, and a rich tapestry of myths, legends, and rituals designed to understand and even control these celestial events. The interpretations varied widely, reflecting the unique cosmologies and belief systems of different cultures.
Many ancient cultures viewed lunar eclipses as ominous signs, often associating them with supernatural forces or divine displeasure. These events were frequently interpreted as portents of war, famine, or other calamities. Detailed records of these interpretations, often woven into historical narratives and religious texts, provide invaluable insights into the worldview of past civilizations.
Myths and Legends Associated with Lunar Eclipses
Various cultures developed elaborate myths to explain the phenomenon of lunar eclipses. In some Native American traditions, for example, a celestial creature was believed to devour the moon during an eclipse. Rituals were performed to scare away the creature and ensure the moon’s safe return. In other cultures, eclipses were interpreted as a struggle between celestial deities, with the eclipse representing a temporary victory of one over the other. These narratives often served as cautionary tales, reinforcing social norms and explaining the natural world through a supernatural lens. For instance, the ancient Greeks believed that eclipses were caused by the Earth’s shadow falling on the moon, but many cultures developed their own explanations rooted in mythology and religious beliefs. The stories themselves reveal much about the values and beliefs of the societies that created them.
Historical Records and Observations
Precise astronomical records of lunar eclipses date back thousands of years. Babylonian astronomers, for example, meticulously documented eclipses, creating detailed chronologies that allowed them to predict future events with remarkable accuracy. These records, inscribed on clay tablets, provide invaluable data for modern astronomers studying the Earth-Moon system and its long-term evolution. Similarly, ancient Chinese astronomers also maintained detailed records of eclipses, which were often incorporated into their complex astrological systems. The accuracy and longevity of these historical records demonstrate the early human fascination with celestial events and the development of sophisticated astronomical observation techniques. The study of these historical records continues to enhance our understanding of both the past and the celestial mechanics at play.
Photography Tips for the Lunar Eclipse
Capturing a lunar eclipse photographically offers a unique challenge and reward. The subtle shifts in color and brightness during the eclipse require careful planning and precise camera settings to produce stunning images. This guide provides essential tips for successfully photographing this celestial event.
The key to successful lunar eclipse photography lies in understanding your camera’s capabilities and adjusting settings to compensate for the low light conditions. Properly exposing for the darkened moon while retaining detail in the surrounding sky requires a balance of aperture, shutter speed, and ISO settings. Experimentation is key, but understanding the basics will significantly improve your chances of capturing breathtaking shots.
Camera Settings and Techniques
Achieving sharp, well-exposed images of a lunar eclipse requires careful consideration of your camera settings. A tripod is absolutely essential to prevent camera shake, especially during long exposures. Begin by setting your camera to manual mode (M) to have complete control over aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. A telephoto lens is highly recommended to magnify the moon and capture its details. For example, a lens with a focal length of 200mm or longer will provide excellent results. A higher focal length lens will allow for even more detail, though you may need to increase the ISO setting to compensate for the dimmer light.
Capturing the Different Stages of the Eclipse
The eclipse progresses through several distinct phases: penumbral, partial, total, and again partial and penumbral. Each phase offers unique photographic opportunities. During the penumbral phase, the change in brightness is subtle, requiring careful exposure adjustments. The partial phase shows a gradual darkening of the moon, offering dynamic compositional possibilities. The total phase, when the moon is fully in Earth’s umbra, presents the most dramatic visual effect – a deep red or copper hue. This phase is often the most photographed, but careful exposure is still crucial to avoid over- or under-exposure. Finally, as the moon emerges from the umbra, the partial and penumbral phases repeat in reverse order, offering further photographic chances.
Composing Compelling Images of the Eclipse
Composition plays a crucial role in creating compelling eclipse photographs. Simply capturing the moon is not enough; you need to consider the surrounding environment. Including elements like landscapes, buildings, or trees can add context and depth to your image. For example, a silhouette of a tree against the eclipsed moon can create a dramatic and memorable shot. Another approach involves capturing the moon’s progression throughout the eclipse in a series of images, showing the gradual change in its appearance. This requires careful planning and consistent exposure settings to maintain a visual coherence across the series. Remember that a clear, unobstructed view of the horizon is crucial for capturing the best shots.
Future Lunar Eclipses
Planning to witness the celestial spectacle of a lunar eclipse again? The 2025 total lunar eclipse was a memorable event, but rest assured, more breathtaking lunar eclipses are on the horizon. Predicting these events allows enthusiasts to prepare and anticipate these fascinating astronomical occurrences. This section details several upcoming total lunar eclipses, providing information on their visibility and key characteristics.
Predicting the exact dates and visibility of future lunar eclipses requires precise astronomical calculations. These calculations consider the relative positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon, accounting for the orbital variations of these celestial bodies. While slight variations in predictions might occur due to the complexity of orbital mechanics, the provided dates represent the best current estimates based on established scientific models. Comparing these future eclipses with the 2025 event allows us to appreciate the unique characteristics of each eclipse and the variations in their visibility across the globe.
Upcoming Total Lunar Eclipses
The following table lists some significant total lunar eclipses expected in the coming years. Note that the visibility zones are broad approximations and the exact experience will vary depending on location and weather conditions.
| Date | Visibility Zone (Approximate) | Eclipse Characteristics (Compared to 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| [Insert Date of Next Total Lunar Eclipse] | [Insert Approximate Visibility Zone, e.g., Americas, Pacific Ocean] | [e.g., Shorter duration than 2025 eclipse; potentially darker umbra; visible in a different region.] |
| [Insert Date of Following Total Lunar Eclipse] | [Insert Approximate Visibility Zone, e.g., Asia, Australia] | [e.g., Longer total eclipse phase compared to 2025; brighter umbra; visible from a different part of the world.] |
| [Insert Date of Another Total Lunar Eclipse] | [Insert Approximate Visibility Zone, e.g., Europe, Africa] | [e.g., Similar duration to 2025, but with a slightly different path across the Earth’s surface; different viewing angles compared to 2025.] |
Note: These dates and visibility zones are subject to minor adjustments as the prediction models are refined. Consult specialized astronomical resources for the most up-to-date information closer to the eclipse dates. Always check local weather forecasts for optimal viewing conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section addresses some of the most common questions about the total lunar eclipse of 2025. Understanding these points will help you prepare for and enjoy this celestial event. We’ve compiled answers based on scientific understanding and reliable astronomical predictions.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What causes a lunar eclipse? | A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. This alignment only happens during a full moon. The type of eclipse (partial, penumbral, or total) depends on how much of the Moon enters the Earth’s umbra (the darkest part of the shadow). |
| Where can I see the 2025 total lunar eclipse? | The visibility of the eclipse depends on its path across the Earth. Specific locations experiencing totality will be widely publicized closer to the date by astronomical organizations and news sources. Generally, the eclipse will be visible from a portion of the Americas, the Pacific Ocean, and parts of Asia, depending on the specific time and the phase of the eclipse. Consult online eclipse prediction tools for precise visibility maps closer to the event. For example, timeanddate.com provides detailed eclipse visibility maps. |
| What equipment do I need to view it? | To safely view a lunar eclipse, you don’t need any special equipment. Unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses are safe to observe with the naked eye. However, binoculars or a telescope will enhance the viewing experience, allowing you to see more detail on the Moon’s surface and the progression of the Earth’s shadow. |
| How long will the total lunar eclipse last? | The duration of totality – the period when the Moon is completely within the Earth’s umbra – varies for each eclipse. For the 2025 total lunar eclipse, the exact duration of totality will be determined closer to the event by astronomical calculations, but it will likely last for a period ranging from several minutes to potentially over an hour. |
| Will the Moon disappear completely during the eclipse? | No, the Moon will not disappear completely. Even during totality, sunlight refracted through the Earth’s atmosphere will cast a reddish hue onto the Moon, creating what is often called a “blood moon.” The intensity of this red color can vary depending on atmospheric conditions. |
| Are there any safety precautions I should take while viewing the eclipse? | Unlike solar eclipses, viewing a lunar eclipse is safe without any special eye protection. However, be mindful of your surroundings, especially if observing the eclipse outdoors at night. Ensure you are in a safe and well-lit area if you are not observing from a home setting. |
Illustrative Content
A series of detailed images can greatly enhance our understanding of a total lunar eclipse. These visuals can effectively communicate the complex interplay of the Sun, Earth, and Moon, illustrating the geometry of the event and the resulting phenomena. We will describe three key images to provide a comprehensive visual representation of the eclipse.
Earth, Moon, and Sun Alignment During a Total Lunar Eclipse
This image depicts the Sun, Earth, and Moon perfectly aligned, with the Earth positioned between the Sun and the Moon. The Earth casts its umbra (the darkest part of its shadow) onto the Moon, completely obscuring the direct sunlight. The relative sizes and distances are accurately represented: the Sun, significantly larger than the Earth, is shown at a considerable distance. The Earth is depicted at a scale appropriate to its size relative to the Moon, which is shown orbiting the Earth. The Earth’s umbra is clearly visible, extending from the Earth and encompassing the Moon. The image might also show the penumbra (the lighter, outer part of the Earth’s shadow), partially shading the Moon before and after totality. The curvature of the Earth and the Moon is clearly visible, emphasizing their spherical nature. The image could also include labels indicating the Sun, Earth, Moon, umbra, and penumbra for clarity.
Progression of the Eclipse from Penumbral to Total Phases
This image is a sequence of four or more panels, showing the Moon’s passage through the Earth’s shadow. The first panel depicts the initial penumbral phase, where a subtle shading appears on the Moon’s surface. The second panel shows the partial phase, with a portion of the Moon entering the umbra, creating a noticeable dark shadow. The third panel showcases the total phase, with the Moon fully immersed in the Earth’s umbra, exhibiting the characteristic reddish hue of a “blood moon.” The final panel depicts the Moon beginning to emerge from the umbra, marking the start of the partial phase again, gradually transitioning back to the penumbral phase and eventually the end of the eclipse. Each panel should clearly show the changing position of the Moon relative to the Earth’s shadow, highlighting the progression of the eclipse. Time stamps corresponding to each phase could also be included to enhance understanding.
The “Blood Moon” Effect During Totality
This image focuses solely on the Moon during totality. The Moon is depicted as a deep reddish-brown color, the characteristic “blood moon” effect. This color is not due to the absence of light, but rather the result of the scattering of sunlight by the Earth’s atmosphere. The image could highlight the subtle variations in the shade of red across the lunar surface, which can be caused by dust particles and atmospheric conditions. The image could also illustrate the contrast between the dark, reddish Moon and the surrounding night sky. The texture of the lunar surface might be visible, even though dimly lit. The image could also include an inset showing a close-up view of a specific lunar feature to highlight the details that are still visible despite the Earth’s shadow.
The Path of Total Lunar Eclipse 2025 will offer a spectacular celestial display, unlike the solar eclipse. However, if you’re interested in a different type of eclipse in 2025, you might want to check out the path of the total solar eclipse, specifically the Path Of 2025 Total Eclipse In Texas , for optimal viewing locations.
Returning to the lunar eclipse, remember to find a location with clear night skies for the best viewing experience.
The path of the 2025 total lunar eclipse will be visible across a wide swathe of the globe. However, for those interested in witnessing a *solar* eclipse that year, a fantastic viewing location is Tulsa, Oklahoma; check out the details on this at Total Eclipse 2025 Tulsa to plan your trip. Returning to the lunar eclipse, its visibility will depend greatly on weather conditions and the specific location of the observer.
Predicting the path of the Total Lunar Eclipse 2025 requires careful astronomical calculations. However, understanding the specifics of a solar eclipse, like the one visible in North Carolina, is equally important. For detailed information on the visibility of the Total Eclipse 2025 in Winston Salem, check out this excellent resource: Total Eclipse 2025 Winston Salem Nc.
Returning to lunar eclipses, accurate prediction of their paths helps astronomers and enthusiasts prepare for optimal viewing conditions worldwide.
Predicting the path of the 2025 Total Lunar Eclipse involves complex astronomical calculations. Interestingly, 2025 also offers a spectacular solar eclipse, as evidenced by this resource on the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse Rochester Ny , which will be a significant event for North American observers. Returning to the lunar eclipse, its path across the globe will be determined by the alignment of the sun, Earth, and moon.
Predicting the path of the 2025 Total Lunar Eclipse involves complex astronomical calculations. Interestingly, 2025 also offers a spectacular solar eclipse, as evidenced by this resource on the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse Rochester Ny , which will be a significant event for North American observers. Returning to the lunar eclipse, its path across the globe will be determined by the alignment of the sun, Earth, and moon.