Upcoming Total Solar Eclipses After 2025
Following the 2024 and 2025 total solar eclipses, several more opportunities to witness this spectacular celestial event will arise. These eclipses, while geographically dispersed, offer unique viewing experiences depending on factors such as the duration of totality, accessibility of the eclipse path, and predicted weather conditions.
Chronological List of Total Solar Eclipses After 2025
The following list details the next several total solar eclipses, providing the date, time (UTC), and a general description of the eclipse path. Precise timings and path details can vary slightly depending on the source and level of accuracy required. These dates are based on current astronomical predictions.
- August 12, 2026: The path of totality will traverse parts of the North Atlantic Ocean and Spain. A relatively short duration of totality is anticipated.
- August 2, 2027: This eclipse’s path of totality will cross North America, beginning in the northern regions and extending into the eastern parts of the continent. A longer duration of totality is expected.
- July 22, 2028: The path of totality will traverse parts of Australia and the South Pacific Ocean. Accessibility may be a factor for many observers.
- July 12, 2029: This eclipse will traverse across the Northern Hemisphere, passing through parts of Europe, Asia and the North Atlantic.
- July 2, 2030: This eclipse’s path of totality will cross the Southern Hemisphere, passing over parts of the Pacific Ocean, and South America.
Map Illustrating the Path of Totality for the First Three Eclipses
Imagine three maps, each representing a different total solar eclipse.
Map 1 (August 12, 2026): This map would show a relatively narrow band of totality beginning in the North Atlantic Ocean, curving slightly to the east and then crossing over the northern part of Spain. The path would be relatively short and concentrated over a smaller geographic area. The ocean portion might be depicted in blue, while Spain would be shown in detail, highlighting the regions where totality will be visible.
Map 2 (August 2, 2027): This map would depict a broader band of totality traversing North America. It would begin in the northern regions, perhaps near Canada or Alaska, and then progress southeastward, passing through several states or provinces before exiting the continent. The map would clearly illustrate the path’s progression across the landmass, possibly using color-coding to represent different durations of totality along the path.
Map 3 (July 22, 2028): This map would primarily focus on the southern hemisphere. The path of totality would begin in the South Pacific Ocean, before reaching Australia, where it would cross over a section of the continent before ending again over the ocean. The map would clearly mark the Australian regions included in the path of totality.
Comparison of Viewing Opportunities
The viewing opportunities for these eclipses differ significantly. The 2026 eclipse, while offering a view over Spain, might have limited duration of totality and potential for cloud cover. The 2027 eclipse, crossing North America, offers potentially longer durations of totality and easier accessibility for many observers, although weather conditions could still vary across the path. The 2028 eclipse presents a more challenging viewing opportunity due to its location over the Pacific Ocean and Australia, potentially requiring more travel and potentially facing different weather patterns. The accessibility and weather conditions will be key factors determining the best viewing locations for each eclipse. The duration of totality, another crucial factor, is expected to be longer for the 2027 eclipse compared to the 2026 eclipse, making it potentially more desirable for serious eclipse watchers.
Predicting and Observing Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events, occur when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow on our planet. Understanding the mechanics behind these events, along with the necessary safety precautions and appreciating their historical significance, enhances our appreciation of these rare and spectacular occurrences.
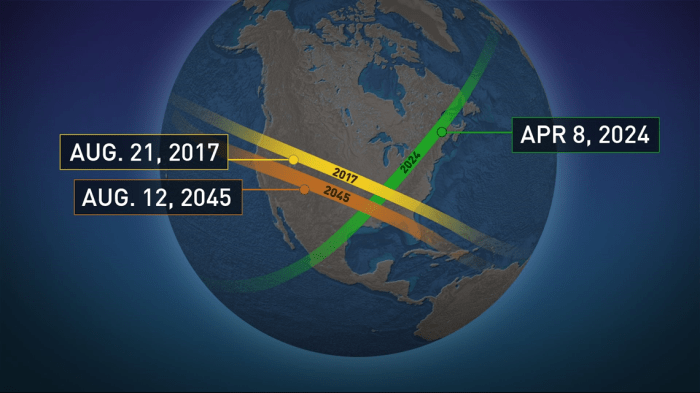
The precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth is the fundamental cause of a total solar eclipse. The Moon’s orbit is not perfectly circular, and its distance from Earth varies. Only when the Moon is at or near its perigee (closest point to Earth) and aligned perfectly with the Sun can it completely obscure the Sun’s disk, creating totality. The size and shape of the Moon’s shadow, known as the umbra, determine the path of totality – the narrow strip of land where the total eclipse is visible. Calculations based on celestial mechanics, including the precise positions and movements of the Sun and Moon, allow astronomers to predict the time, duration, and path of future eclipses with remarkable accuracy. For example, the precise prediction of the August 21, 2017, total solar eclipse across the United States allowed millions to witness this breathtaking event.
Safety Precautions for Observing Solar Eclipses
Directly viewing the Sun, even during a partial eclipse, can cause severe and permanent eye damage, including blindness. Never look at the Sun without proper eye protection. ISO 12312-2 certified solar viewing glasses are essential. These glasses are specifically designed to filter out harmful ultraviolet and infrared radiation. Improvised methods, such as using sunglasses or exposed film, are insufficient and extremely dangerous. During totality, when the Sun is completely obscured by the Moon, it is safe to remove the glasses and observe the eclipse directly, but only for the brief duration of totality. Remember to put your glasses back on immediately as the Sun begins to reappear. The partial phases before and after totality still require eye protection.
Historical Significance of Solar Eclipses
Throughout history, solar eclipses have held profound cultural and religious significance across diverse civilizations. Many cultures viewed eclipses as ominous signs, often associating them with divine wrath or impending doom. For instance, ancient Chinese texts describe eclipses as a dragon devouring the Sun, while some Native American tribes interpreted them as a celestial battle. In contrast, some cultures saw eclipses as significant, even auspicious events. The Vikings, for example, believed that the eclipse represented a battle between celestial wolves. The meticulous records of eclipses kept by ancient astronomers, such as those in Babylon and Greece, provide invaluable data for understanding the historical progression of astronomical knowledge and refining our ability to predict future eclipses. The study of historical eclipse accounts allows for a deeper understanding of past cultures and their interpretations of the cosmos.
Scientific Significance of Total Solar Eclipses
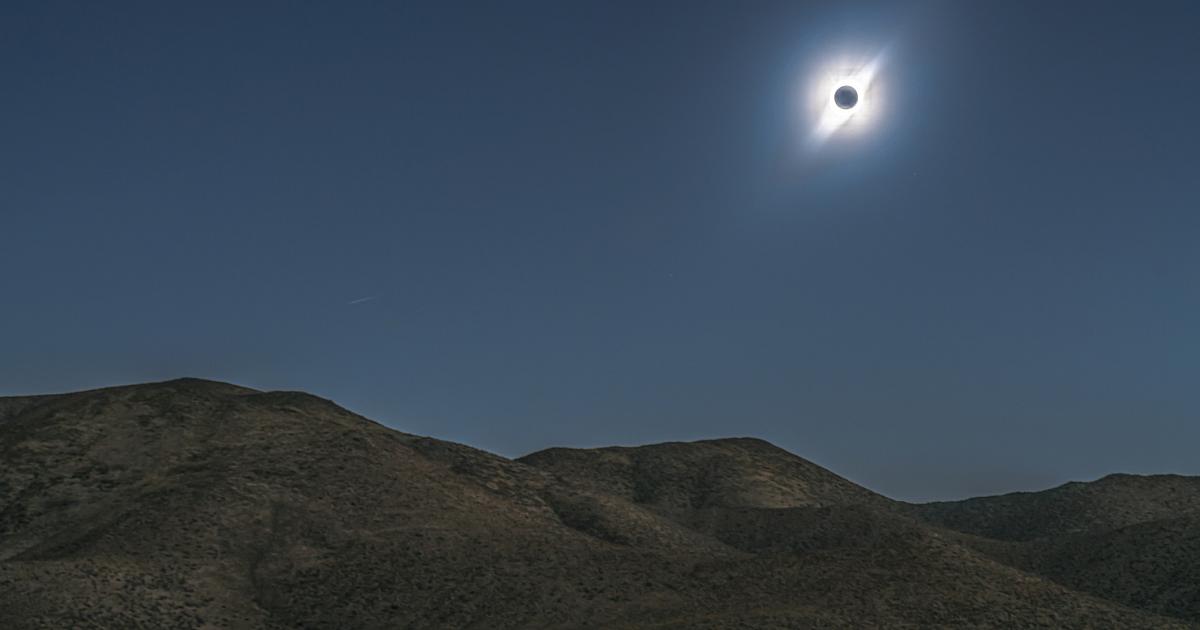

Total solar eclipses, while awe-inspiring spectacles, offer scientists a unique opportunity to conduct research otherwise impossible. The brief period of totality, when the sun’s corona is visible, allows for observations and data collection that significantly advance our understanding of the sun and its impact on Earth. These events provide a natural laboratory, allowing scientists to study phenomena that are usually obscured by the sun’s overwhelming brightness.
Total solar eclipses provide a crucial window for studying the sun’s corona, the outermost part of its atmosphere. This region, typically invisible due to the sun’s intense light, is a dynamic and complex environment where temperatures reach millions of degrees Celsius. Observations during totality allow scientists to study coronal mass ejections (CMEs), powerful bursts of plasma that can disrupt Earth’s magnetic field and cause geomagnetic storms. Studying CMEs during eclipses helps us better understand space weather and its potential impact on our technological infrastructure.
Coronal Mass Ejection Studies, The Next Total Solar Eclipse After 2025
During a total solar eclipse, the sun’s corona becomes visible, allowing for detailed observations of its structure and dynamics. Scientists utilize specialized instruments like coronagraphs to image and spectroscopically analyze the corona, studying its temperature, density, and magnetic field strength. This data helps in understanding the processes that lead to CMEs and predicting their occurrence. For example, the 2017 total solar eclipse across the United States provided valuable data on a CME that occurred just days before, enabling researchers to refine models predicting the impact of such events on Earth. The high-resolution images captured during the eclipse revealed intricate details of the CME’s structure, providing crucial insights into its evolution and propagation. These observations were complemented by data from space-based telescopes, providing a comprehensive view of the event.
Observations of the Sun’s Gravitational Field
Total solar eclipses also provide opportunities to study the sun’s gravitational field. During totality, the apparent bending of starlight around the sun, predicted by Einstein’s theory of general relativity, can be observed. This phenomenon, known as gravitational lensing, confirms Einstein’s theory and provides insights into the distribution of mass within the sun. Precise measurements of the starlight bending during past eclipses have consistently supported Einstein’s predictions, furthering our understanding of gravity on a cosmic scale.
Comparison with Other Astronomical Observation Methods
While other astronomical observation methods, such as space-based telescopes and radio telescopes, provide valuable data about the sun, total solar eclipses offer a unique perspective. Space-based telescopes, such as SOHO and SDO, provide continuous monitoring of the sun, but they cannot observe the corona with the same level of detail as during a total eclipse. Radio telescopes provide information about the sun’s radio emissions, but they do not offer the same visual detail as optical observations during an eclipse. Therefore, total solar eclipses complement other astronomical observation methods, providing a crucial piece of the puzzle in our understanding of the sun.
Data Collected During a Total Solar Eclipse
The data collected during a total solar eclipse is diverse and contributes significantly to our understanding of the sun. This includes high-resolution images of the corona, spectroscopic data revealing the chemical composition and temperature of the corona, measurements of the sun’s gravitational field, and observations of the sun’s inner corona and chromosphere. This data allows scientists to study the sun’s magnetic field, its energy transport mechanisms, and the dynamics of the solar atmosphere. The analysis of this data helps improve models of solar activity, enabling better predictions of space weather and its potential effects on Earth. Furthermore, eclipse observations contribute to our understanding of the sun’s evolution and its influence on the planets within our solar system.
Planning a Trip to Witness a Total Solar Eclipse
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a truly unforgettable experience. However, planning such a trip requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure a safe and enjoyable journey. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to help you organize your eclipse-viewing adventure.
Step-by-Step Eclipse Trip Planning
Planning a trip to see a total solar eclipse involves several key stages. First, you need to identify the date and path of totality for the eclipse you wish to see. Numerous websites and resources provide accurate predictions. Next, research potential viewing locations along the path of totality, considering factors like weather forecasts, accessibility, and accommodation availability. Booking flights and accommodation well in advance is crucial, especially for popular eclipse destinations, as prices tend to surge closer to the event. Finally, create a detailed itinerary that includes travel arrangements, accommodation details, and a plan for viewing the eclipse itself, ensuring you arrive at your viewing location with ample time to set up and prepare.
Essential Items Checklist for Eclipse Viewing
Proper preparation is vital for a safe and comfortable eclipse viewing experience. A well-packed bag containing the necessary items will minimize stress and allow you to fully enjoy the event.
- Eye Protection: ISO 12312-2 certified eclipse glasses are absolutely essential. These glasses are specifically designed to filter out harmful solar radiation and prevent eye damage. Do not use homemade filters or regular sunglasses; they will not provide adequate protection.
- Camera Equipment (Optional): If you plan to photograph or video the eclipse, ensure your equipment is suitable. A tripod is highly recommended for stability. Consider using a solar filter for your camera lens to protect it from damage.
- Comfortable Clothing: Pack layers of clothing appropriate for the weather conditions at your chosen viewing location. Temperatures can fluctuate significantly during the eclipse.
- Sunscreen and Hat: Even on a cloudy day, the sun’s rays can be intense. Protect your skin with sunscreen and wear a hat to shield your face.
- Snacks and Water: Staying hydrated and energized is important, especially if you’re spending a considerable amount of time outdoors.
- Portable Chair or Blanket: Choose comfortable seating to enjoy the eclipse comfortably for an extended period.
- First-Aid Kit: A basic first-aid kit can be helpful for minor injuries or ailments.
Finding Optimal Viewing Locations
Selecting the right viewing location is critical for maximizing your eclipse experience. Consider these strategies:
- Weather Forecasts: Check weather forecasts for the entire path of totality several days before the eclipse. Aim for a location with the highest probability of clear skies.
- Accessibility and Crowds: Research the accessibility of potential viewing locations. Consider factors like parking, public transportation, and potential crowds. Some locations may require advance reservations or permits.
- Elevation and Obstructions: Higher elevations often offer clearer views with fewer obstructions. Avoid locations with significant trees, buildings, or hills that could block your view of the sun.
- Local Information: Consult local tourism websites and eclipse-related resources for information on recommended viewing spots and potential events or gatherings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): The Next Total Solar Eclipse After 2025
This section addresses common queries regarding total solar eclipses, covering their frequency, the differences between partial and total eclipses, reliable information sources, and the crucial topic of safe viewing practices. Understanding these aspects ensures a safe and informative experience for anyone interested in witnessing this spectacular celestial event.
Total Solar Eclipse Frequency
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events at any given location on Earth. While a total solar eclipse occurs somewhere on Earth approximately every 18 months, any specific location will only experience a total solar eclipse once every 375 years, on average. This rarity underscores the importance of planning ahead if you wish to witness one. The frequency is influenced by the relative positions of the sun, moon, and Earth, and slight variations in these positions lead to this uneven distribution of visibility across the globe.
Partial Versus Total Solar Eclipses
The key difference between a partial and total solar eclipse lies in the extent to which the moon obscures the sun. During a partial solar eclipse, only a portion of the sun is blocked by the moon, resulting in a crescent-shaped sun. A total solar eclipse, however, occurs when the moon completely covers the sun’s disk, briefly plunging the area within the path of totality into darkness. Scientifically, the difference is significant. During totality, the sun’s corona, the outer atmosphere, becomes visible, allowing for unique observations and research opportunities not possible during a partial eclipse. The dramatic drop in ambient light and the observable changes in temperature are also far more pronounced during a total eclipse.
Reliable Sources for Eclipse Information
Several reputable organizations provide accurate and up-to-date information about upcoming solar eclipses. NASA’s website is an excellent starting point, offering detailed predictions, maps showing the path of totality, and safety guidelines. Other reliable sources include the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and various national observatories and space agencies around the world. Many astronomy clubs and societies also publish eclipse information and often organize viewing events. It’s crucial to rely on these trusted sources to avoid misinformation.
Risks of Viewing a Solar Eclipse
Looking directly at the sun during a solar eclipse, even a partial one, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including solar retinopathy, which can lead to vision impairment or even blindness. Never look at the sun without proper eye protection designed specifically for solar viewing. Improvised methods like sunglasses or exposed film are insufficient and dangerous. Safe viewing practices include using certified solar eclipse glasses that meet the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard. Alternatively, indirect viewing methods, such as projecting the sun’s image onto a screen using a pinhole projector, are also safe and effective. Protecting your eyes is paramount; irreversible damage can occur in seconds.
Illustrative Examples of Past Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses, breathtaking celestial events, have captivated humanity for millennia. Their unique characteristics, from the path of totality to the duration of darkness, have inspired awe and wonder, leaving lasting impacts on the cultures and communities that witnessed them. Examining specific historical eclipses reveals not only the scientific significance but also the profound human experience interwoven with these astronomical phenomena.
The 1919 eclipse provided crucial evidence supporting Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
The 1919 Eclipse and the Confirmation of General Relativity
The total solar eclipse of May 29, 1919, holds a unique place in the history of science. Its path of totality traversed the Atlantic Ocean and parts of South America and Africa, with key observations conducted from the island of Príncipe off the coast of West Africa and Sobral, Brazil. The eclipse’s relatively long duration of totality, around six minutes in some locations, allowed astronomers, led by Arthur Eddington, to photographically measure the apparent displacement of stars near the sun. This was a critical test of Einstein’s recently proposed theory of general relativity, which predicted that the sun’s gravity would bend the light from these distant stars. The results from the 1919 eclipse strongly supported Einstein’s theory, catapulting him to international fame and marking a pivotal moment in the history of physics. The visual experience of the eclipse itself was described in many accounts as profoundly awe-inspiring, with the sudden onset of darkness, the visibility of the corona, and the overall dramatic shift in the atmosphere creating an unforgettable spectacle. The scientific outcome, however, irrevocably changed the understanding of gravity and the universe itself.
The Great American Eclipse of 2017 and its Societal Impact
The total solar eclipse of August 21, 2017, which swept across the contiguous United States, had a significant societal impact. The path of totality, a roughly 70-mile-wide swathe stretching from Oregon to South Carolina, saw an unprecedented influx of tourists and eclipse chasers. This resulted in a significant economic boost for many communities along the path, with hotels, restaurants, and local businesses experiencing a surge in revenue. The event also fostered a sense of national unity and shared experience, bringing people together from diverse backgrounds to witness this spectacular natural phenomenon. Many communities organized viewing parties and public events, further enhancing the social cohesion and collective memory associated with the eclipse. The media coverage was extensive, creating a nationwide buzz and heightening public interest in astronomy and science. This widespread interest translated into increased funding for STEM education and outreach programs, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of this single, remarkable event. The experience of totality was described by many as a life-changing moment, generating a profound sense of wonder and appreciation for the cosmos.
Planning ahead for the next total solar eclipse after 2025? It’s wise to start researching potential viewing locations now. A great resource to help you visualize the path of totality for the 2025 eclipse is the Total Solar Eclipse Map 2025 , which provides detailed information. Using this map can assist in your preparations for the upcoming celestial event, ensuring you’re in the best position to witness this incredible phenomenon.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse after 2025? It’s a great idea to start researching now! To better understand the scale and planning involved, consider reviewing the path of totality for the 2025 eclipse, which you can find detailed on this helpful resource: Path Of Total Solar Eclipse 2025. Understanding the 2025 path will give you a good foundation for predicting and preparing for future celestial events.
Planning to witness the celestial spectacle of a total solar eclipse? The next one after 2025 is still a few years away, but before you look ahead, it’s worth checking out the details of the upcoming event: Total Solar Eclipse 2025. Understanding the 2025 eclipse helps prepare you for future viewing opportunities and the unique aspects of each celestial event.
Therefore, let’s focus on that first before considering subsequent eclipses.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse after 2025? It’s a good idea to start researching now! Understanding the paths of previous eclipses is crucial, and a great resource for this is the detailed map of the Total Solar Eclipse Path 2025 , which helps illustrate the scale and impact of these events. This will give you a better understanding of what to expect for future celestial events.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse after 2025? It’s a good idea to start researching now! Understanding the paths of previous eclipses is crucial, and a great resource for this is the detailed map of the Total Solar Eclipse Path 2025 , which helps illustrate the scale and impact of these events. This will give you a better understanding of what to expect for future celestial events.