Total Eclipse 2025
A total solar eclipse is a breathtaking celestial event, captivating observers for millennia. It occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light and casting a shadow on a specific region of our planet. This phenomenon, governed by precise celestial mechanics, provides a unique opportunity to study the Sun’s corona and offers a spectacular visual experience.
The Science Behind Total Solar Eclipses
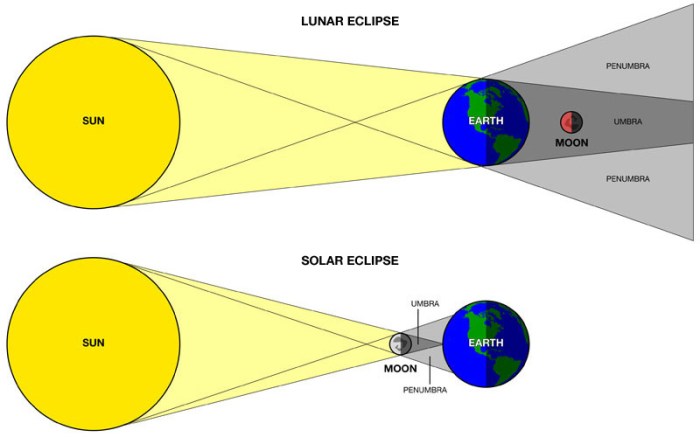
A total solar eclipse is a consequence of the Sun’s apparent size and the Moon’s orbital path around the Earth. While the Sun is vastly larger than the Moon, its greater distance from Earth makes its apparent angular size roughly equal to the Moon’s. This near-perfect alignment allows the Moon to entirely obscure the Sun’s disk during a total eclipse. The intricate dance of these celestial bodies, governed by gravitational forces and orbital mechanics, results in this extraordinary event. The umbra, the darkest part of the Moon’s shadow, is where totality occurs. The penumbra, the lighter outer shadow, experiences a partial eclipse.
Types of Solar Eclipses
Three main types of solar eclipses exist: partial, annular, and total. A partial solar eclipse happens when the Moon only partially covers the Sun’s disk, resulting in a crescent-shaped Sun. An annular eclipse occurs when the Moon is farther from Earth in its elliptical orbit, appearing smaller than the Sun. This leaves a bright ring of sunlight visible around the Moon’s silhouette. A total solar eclipse, as previously described, occurs when the Moon completely blocks the Sun’s disk, revealing the Sun’s corona, a pearly white halo of plasma.
Path of Totality for the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse
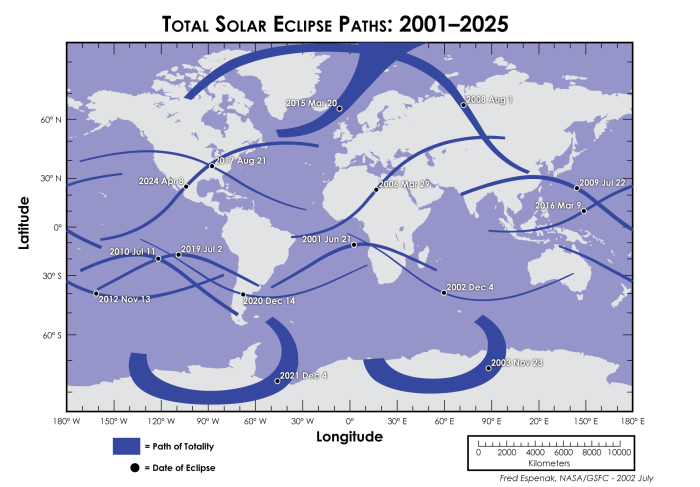
The 2025 total solar eclipse will traverse a specific path across the globe. Predicting the exact path requires complex calculations considering the Moon’s and Earth’s orbital movements. The path of totality, where the total eclipse will be visible, will follow a specific track across various geographical locations, varying in duration at different points along this path. The exact coordinates and duration of totality for each location along this path will be available closer to the date of the eclipse from various astronomical sources.
Celestial Mechanics During a Total Solar Eclipse: A Simplified Diagram
Imagine a simplified diagram with three celestial bodies: the Sun (a large circle representing the star), the Earth (a smaller circle representing our planet), and the Moon (an even smaller circle representing the natural satellite). The Sun is positioned to the left, the Earth in the center, and the Moon directly between the Sun and Earth. The Moon’s shadow, depicted as a cone extending from the Moon towards the Earth, shows the umbra (dark inner cone) and penumbra (lighter outer cone). The umbra represents the area of totality on Earth, while the penumbra experiences a partial eclipse. The diagram clearly illustrates the alignment required for a total solar eclipse to occur. The labels “Sun,” “Earth,” and “Moon” are clearly marked next to their respective circles. The size relationships reflect the apparent sizes as viewed from Earth.
Visualizing the 2025 Total Eclipse: Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram
Understanding the geometry of a total solar eclipse is crucial for appreciating the phenomenon. A well-constructed diagram provides a clear and concise representation of the alignment of the sun, moon, and Earth, highlighting the crucial elements involved in creating the eclipse. This section details the creation of such a diagram and explores visual comparisons between partial and total eclipses.
Diagram of the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse
A comprehensive diagram should depict the Earth, the sun (significantly larger in scale), and the moon positioned between them. The moon’s umbra, the cone-shaped shadow where totality occurs, should be clearly shown intersecting the Earth’s surface along the path of totality. The penumbra, the lighter outer shadow, should also be illustrated, representing the area experiencing a partial eclipse. The path of totality, a curved line across the Earth’s surface, should be highlighted to show the region experiencing the total eclipse. Accurate scaling, while challenging, is desirable to convey the relative sizes and distances involved. The sun should be represented with rays or a textured surface to indicate its light source. Color-coding could further enhance the diagram; for instance, the umbra could be shaded darker than the penumbra, and the path of totality could be a distinct color. Clear labels identifying the sun, moon, Earth, umbra, penumbra, and path of totality are essential for comprehension.
Step-by-Step Diagram Construction
Constructing a similar diagram requires simple drawing tools. Begin by drawing a circle representing the Earth. Next, draw a much larger circle representing the sun, off to one side. Then, draw a smaller circle representing the moon, positioned between the Earth and the sun, carefully aligning it to create the eclipse. Draw the umbra as a cone extending from the moon to the Earth. Extend the penumbra as a wider cone around the umbra. Finally, trace the path of totality as a curved line across the Earth’s surface where the umbra touches. Add labels to identify each component. Use shading and color to differentiate the umbra, penumbra, and path of totality for visual clarity. Consider using a compass and ruler for greater accuracy in the circles and path.
Comparison of Partial and Total Eclipses
A comparison diagram effectively illustrates the difference between partial and total solar eclipses. Side-by-side depictions are ideal. On one side, show the sun partially obscured by the moon, with a crescent shape visible. This represents a partial eclipse. The other side should depict the sun completely covered by the moon, revealing only the corona, the sun’s outer atmosphere. This illustrates a total eclipse. The diagrams should use similar scaling and perspectives for effective comparison. Labels clearly distinguishing “Partial Eclipse” and “Total Eclipse” should be included. The contrast in brightness between the two scenarios should be visually apparent, emphasizing the dramatic difference in the sun’s appearance. For example, the partial eclipse image might show a noticeably brighter crescent of the sun, whereas the total eclipse image could be significantly darker, highlighting the corona’s relatively faint light.
Predicting and Observing the 2025 Total Eclipse
Predicting and observing the 2024 total solar eclipse requires careful planning and preparation. Accurate predictions allow enthusiasts to position themselves for optimal viewing, while understanding the eclipse phases and safety precautions ensures a safe and memorable experience. This section will detail the timeline of events for a specific location, crucial safety measures, the phases of the eclipse, and unique atmospheric phenomena visible during totality.
Dallas, TX Eclipse Timeline
The path of totality for the April 8, 2025, total solar eclipse will pass near Dallas, Texas. While not directly in the path, the city will experience a near-total eclipse, with a significant portion of the sun obscured. The exact timing will vary slightly depending on the precise location within Dallas, but a representative timeline could be as follows:
Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram – The partial eclipse begins approximately an hour before totality. The sun will appear progressively more crescent-shaped as the moon moves in front of it. Totality, the period when the sun is completely obscured, will last for several minutes. Following totality, the partial eclipse will continue for approximately another hour, with the sun gradually returning to its full disk. Precise times for the beginning and end of the partial and total phases should be consulted closer to the date using a reputable eclipse prediction website or app. These sites utilize sophisticated astronomical calculations to provide accurate predictions based on location.
Understanding the path of totality is crucial when interpreting a Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram. Precise timing is essential for optimal viewing, and to determine this for your location, you’ll want to check the specifics; for Colorado, consult this resource: Total Eclipse 2025 Time Colorado. This information, combined with a detailed diagram, will allow you to fully appreciate the eclipse’s progression across the sky.
Essential Safety Precautions for Viewing a Solar Eclipse
Directly viewing the sun, even during a partial eclipse, can cause serious and permanent eye damage. It is crucial to use proper eye protection at all times except during the brief period of totality. Improper eye protection, such as sunglasses or homemade filters, will not suffice. The only safe way to look directly at the uneclipsed or partially eclipsed sun is through special-purpose solar filters, such as “eclipse glasses” or handheld solar viewers. These filters are specifically designed to reduce the sun’s intensity to safe levels. Always check that your eclipse glasses meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard. Never look at the sun through a camera, telescope, binoculars, or other optical device without a properly attached solar filter. Even during totality, when the sun’s corona is visible, it is generally advisable to use eclipse glasses to protect your eyes from the bright light.
Phases of a Total Solar Eclipse and Visual Characteristics, Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram
A total solar eclipse unfolds in distinct phases. The partial eclipse phase begins as the moon starts to transit the sun’s disk, creating a gradually increasing crescent shape. As the moon continues its transit, the sky darkens noticeably. As totality approaches, a phenomenon known as “shadow bands” might be visible – fleeting, wavy shadows that appear on the ground. During totality, the sun’s corona, its outer atmosphere, becomes visible as a radiant halo around the completely obscured solar disk. The sky darkens dramatically, resembling twilight. Stars and planets may become visible. After totality, the process reverses, with the sun gradually emerging from behind the moon, culminating in the end of the partial eclipse.
Unique Atmospheric Effects During Totality
The dramatic drop in ambient light during totality leads to several unique atmospheric effects. The temperature may noticeably decrease. Animals may exhibit unusual behavior, such as birds becoming quiet or going to roost. The sudden darkening of the sky can create a dramatic and awe-inspiring effect, transforming the landscape and creating a unique ambiance. The visibility of the corona and the possibility of seeing shadow bands are specific to totality and add to the overall visual spectacle.
The Historical and Cultural Significance of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events where the Moon obscures the Sun, have held profound cultural and historical significance across diverse societies throughout human history. Their dramatic and unpredictable nature has led to a wide range of interpretations, from omens of doom to celebrations of cosmic renewal. Understanding these varied perspectives offers a fascinating glimpse into the beliefs and worldviews of past civilizations.
The impact of solar eclipses on different cultures is multifaceted, shaped by their unique cosmological beliefs and societal structures. Many ancient cultures viewed eclipses as supernatural events, often associating them with divine intervention or the actions of powerful celestial beings. These interpretations frequently influenced their religious practices, social structures, and political decisions. Conversely, the development of scientific understanding has provided a more rational explanation for the phenomenon, though the inherent wonder and spectacle of a total solar eclipse continue to captivate modern audiences.
Interpretations of Solar Eclipses Across Cultures
Ancient civilizations often lacked the scientific understanding to explain eclipses, resulting in diverse interpretations reflecting their unique cosmological beliefs. For example, some cultures viewed eclipses as a celestial battle between the Sun and the Moon, or as a temporary swallowing of the Sun by a mythical creature. In other societies, they were seen as harbingers of significant events, both positive and negative, influencing the actions of rulers and shaping the course of history. The Babylonian astronomers, for instance, meticulously recorded eclipses, demonstrating a keen interest in understanding their cyclical nature, even without a complete scientific explanation. Their records provide valuable insights into the historical frequency of eclipses and their impact on Babylonian society. In contrast, some indigenous cultures developed sophisticated methods for predicting eclipses, demonstrating a deep understanding of celestial mechanics.
Cultural Reactions and Explanations of Solar Eclipses
Cultural reactions to solar eclipses varied significantly. Some cultures responded with fear and ritualistic practices designed to appease angry deities or ward off evil spirits. Loud noises, prayers, and sacrificial offerings were common responses aimed at restoring cosmic balance. Other cultures viewed eclipses as auspicious occasions, marking significant events or signaling changes in leadership. The Vikings, for example, associated eclipses with the actions of celestial wolves chasing the Sun. These contrasting reactions highlight the profound impact of cultural beliefs on the interpretation and experience of these celestial events. The Inca civilization, known for its advanced astronomical knowledge, interpreted solar eclipses as a sign of displeasure from their gods, leading to rituals to appease them.
Significant Historical Events Coinciding with Solar Eclipses
Several historical events have coincided with total solar eclipses, leading to their incorporation into narratives and mythology. The precise correlation between an eclipse and a historical event is often debated due to the lack of precise dating in some historical records. However, anecdotal evidence suggests that some significant battles or political upheavals coincided with eclipses, leading to their interpretation as omens or harbingers of change. The eclipse of 585 BC, recorded by Herodotus, is often cited as having halted a battle between the Medes and the Lydians, showcasing the impact these events could have on human affairs. While the causal link may be debated, the event remains a compelling example of the historical intertwining of solar eclipses and human events.
Timeline of Major Historical and Cultural References to Solar Eclipses
While precise dating for many early eclipse observations is uncertain, a general timeline can illustrate the enduring human fascination with these events:
Ancient Mesopotamia (2000 BC): Early recorded observations and predictions of eclipses.
Ancient China (14th Century BC): Detailed records of eclipses, often interpreted as omens related to the emperor’s conduct.
Ancient Greece (6th Century BC): Philosophers like Thales of Miletus attempted to explain eclipses scientifically.
Medieval Europe (11th-15th Centuries): Eclipses were often interpreted as divine warnings or signs of impending doom.
Scientific Revolution (17th-18th Centuries): Improved understanding of celestial mechanics led to more accurate predictions of eclipses.
Modern Era (20th-21st Centuries): Eclipses are studied scientifically and viewed as opportunities for astronomical research and public engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions about the 2025 Total Eclipse
The 2025 total solar eclipse promises to be a spectacular celestial event, and many people have questions about how best to experience it safely and understand what they will see. This section addresses some of the most common queries.
Safe Solar Eclipse Viewing
Viewing a solar eclipse without proper eye protection can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. Never look directly at the sun, even during a partial eclipse, without certified solar viewing glasses or other safe methods. Improper filters, such as sunglasses or homemade devices, offer inadequate protection and can be dangerous. Safe viewing methods include using ISO 12312-2 certified solar viewing glasses, which are readily available online and from astronomy retailers. Alternatively, you can use a pinhole projector to indirectly view the sun’s image projected onto a screen. This method involves creating a small hole in a piece of cardboard to project the sun’s image onto another surface. Remember, the only safe time to look directly at the sun during a total eclipse is during the brief period of totality, when the moon completely blocks the sun’s disk. Even then, it’s advisable to have your eclipse glasses handy in case of unexpected cloud cover.
Visibility of the 2025 Total Solar Eclipse
The path of totality for the 2025 total solar eclipse will traverse a significant portion of North America, starting in the Pacific Ocean and crossing parts of California, Nevada, Utah, Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, and several other states before exiting the continent. The eclipse will then continue across the Atlantic Ocean. A detailed map would show a relatively narrow band representing the path of totality, where the sun will be completely obscured by the moon. Areas outside this band will experience a partial eclipse, with the sun only partially covered. The exact timing of the eclipse will vary depending on the location within the path of totality. For instance, the duration of totality might be longer in central locations within the path and shorter near the edges. Think of it as a ribbon across the Earth, with totality being the most intense within the center of that ribbon.
Duration of Totality
The duration of totality during the 2025 total solar eclipse will vary depending on the observer’s location within the path of totality. The maximum duration will occur near the center of the path, possibly lasting around 4 minutes and 27 seconds. However, observers closer to the edges of the path will experience a significantly shorter period of totality, perhaps only a few seconds. This variation is due to the geometry of the sun, moon, and Earth during the eclipse. For example, a person situated near the edges of the path of totality will only witness the moon partially covering the sun for a shorter period before it moves out of the direct alignment.
Unique Phenomena Visible During Totality
During the brief period of totality, several unique celestial phenomena become visible. The sun’s corona, its outer atmosphere, will be spectacularly visible as a pearly white halo surrounding the moon. This is normally obscured by the sun’s bright surface. Solar prominences, massive eruptions of plasma from the sun’s surface, might also be visible as bright red or pink jets extending outward from the sun’s edge. Finally, shadow bands, rapidly moving bands of light and dark, may be visible just before and after totality. These are caused by atmospheric disturbances and appear as wavy patterns on the ground. Observing these phenomena is one of the most compelling reasons to witness a total solar eclipse.
Diagram Formats and Presentation
Presenting eclipse data effectively requires a variety of visual aids to cater to different learning styles and preferences. Clear and concise diagrams are crucial for understanding the complex timings and geographical aspects of a total solar eclipse. This section explores several methods for presenting information about the 2025 total solar eclipse.
Responsive HTML Table for Eclipse Data
A responsive HTML table offers a structured way to display eclipse data. The table below demonstrates how time, location, event, and a description can be organized for easy readability across various devices. This format allows users to quickly compare information at different locations and times during the eclipse. The use of CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) would be necessary to achieve the “responsive” aspect, ensuring the table adapts to different screen sizes.
| Time (UTC) | Location (Approximate) | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14:00 | North Pacific Ocean | First Contact | The Moon begins to partially obscure the Sun. |
| 15:30 | Near Baja California, Mexico | Totality Begins | The Sun is completely covered by the Moon, revealing the corona. |
| 15:35 | Central Mexico | Maximum Eclipse | The point of greatest duration of totality. |
| 15:40 | Gulf of Mexico | Totality Ends | The Moon begins to uncover the Sun. |
| 17:00 | Atlantic Ocean | Last Contact | The Moon completes its transit across the Sun. |
Infographic Depicting Eclipse Stages
A visually appealing infographic simplifies the complex process of a total solar eclipse. This infographic would utilize a circular layout, mirroring the Sun. Each segment would represent a key stage of the eclipse, starting with the first contact and ending with the last contact. Each segment would contain a brief description and a simple icon representing the stage. For example, the “Totality” segment could feature an image of the solar corona. A color gradient could be used to transition between stages, adding a visually dynamic element. The central area of the circle could display a stylized image of the Sun and Moon during the maximum eclipse, and a time scale could be incorporated around the circumference for clarity. The overall design would use a clean, modern aesthetic with a limited color palette to avoid visual clutter. The font choice would be clear and easily readable, even at smaller sizes.
Flowchart for Eclipse Observation Planning
A flowchart provides a clear, step-by-step guide to planning for observing a total solar eclipse. The flowchart would begin with “Decide on a Viewing Location,” branching into considerations such as accessibility, weather predictions, and the duration of totality. Subsequent steps would include “Secure Accommodation and Transportation,” “Acquire Necessary Equipment (e.g., eclipse glasses, camera),” “Plan for Safety Precautions (e.g., eye protection, sun protection),” and “Check Weather Forecast.” Each step would lead to the next, with potential alternative paths represented by decision points (e.g., “Good Weather Forecast? Yes/No”). The final step would be “Enjoy the Eclipse!” The flowchart would use standardized flowchart symbols (rectangles for processes, diamonds for decisions) and clear, concise labels for each step. The visual representation makes the planning process easily understandable and actionable.
Understanding the path of totality for the Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram is crucial for planning viewing locations. To confirm the date and understand the significance of this celestial event, you should check out this informative article: The 2025 Solar Eclipse Will Be Total On April 8. This information will help you accurately interpret the Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram and choose the optimal spot to witness the eclipse.
Understanding the path of totality for the Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram is crucial for planning viewing locations. To determine the precise timing for optimal viewing in a specific area, such as New York City, you’ll want to consult a resource like this one: Total Eclipse 2025 Time In New York. This information, combined with the overall eclipse diagram, allows for precise predictions of visibility and duration at any given location.
Understanding the path of totality is crucial when interpreting a Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram. To fully appreciate the significance of this specific eclipse, it’s helpful to understand why this event is generating so much excitement; you can learn more by reading this article: Why 2025’s Total Solar Eclipse Will Be So Special. Armed with this knowledge, you can then better utilize a Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram to plan your viewing experience.
Understanding the path of totality is crucial when interpreting a Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram. To accurately determine the visibility from a specific location, you’ll need precise timing information, readily available by checking the exact time of the eclipse for your region; for those in California, a helpful resource is the Eclipse Total 2025 Hora California website. This data is then essential for correctly overlaying the path onto your Total Eclipse 2025 Diagram.