Total Solar Eclipse 2025
The total solar eclipse of 2025 will be a significant astronomical event, offering a spectacular celestial display for observers in a specific geographic region. This event provides a unique opportunity to witness the sun’s corona and experience the dramatic changes in light and temperature during totality. Understanding the mechanics behind this phenomenon and the differences between various types of eclipses enhances appreciation for this rare occurrence.
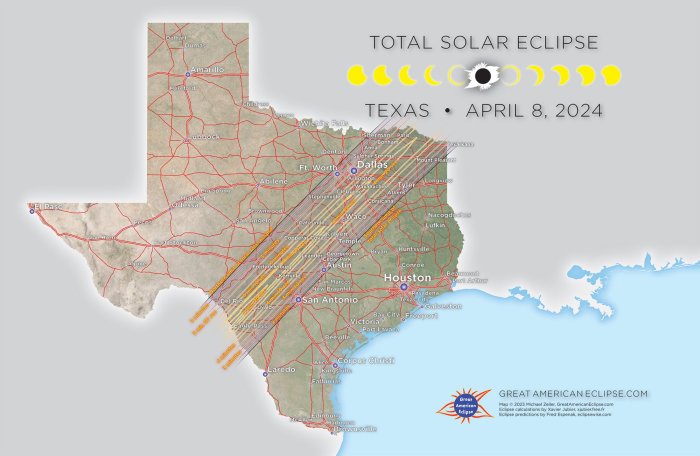
Total Eclipse Solar 2025 – The total solar eclipse of August 12, 2025, will be visible across a path traversing North America, beginning over the Pacific Ocean and crossing portions of the United States and Canada. The precise timing will vary depending on the location, with totality lasting a few minutes at the eclipse’s path of totality’s center. Specific times for each location along the path can be found on numerous astronomy websites and eclipse prediction tools. The event will start early in the morning on the West Coast of North America and move eastward, with the later stages of the eclipse being visible in the eastern parts of Canada.
The Total Solar Eclipse of 2025 promises a spectacular celestial event across North America. For those seeking optimal viewing locations, consider planning your trip to Texarkana, which falls directly within the path of totality; check out the details at Texarkana Total Eclipse 2025 to begin your preparations. Remember to secure your viewing spot early for the Total Solar Eclipse 2025, a truly unforgettable experience.
Total Solar Eclipse Phenomena
A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes directly between the sun and the Earth, completely blocking the sun’s disk from our perspective. This precise alignment is necessary for totality to occur. The Earth, moon, and sun must be in a nearly perfect syzygy – a straight line. The moon’s umbral shadow, the darkest part of its shadow, then falls upon a specific region of the Earth’s surface. Observers within this umbral shadow experience the total eclipse, witnessing the sun’s corona – the outermost part of its atmosphere – a breathtaking sight normally invisible due to the sun’s intense brightness. The duration of totality depends on the relative positions of the sun, moon, and Earth, and typically lasts only a few minutes.
Types of Solar Eclipses
There are three main types of solar eclipses: partial, annular, and total. A partial solar eclipse occurs when only a portion of the sun is obscured by the moon. This happens when the sun, moon, and Earth are not perfectly aligned. The amount of the sun’s disk covered varies depending on the observer’s location. An annular eclipse occurs when the moon is at or near its furthest point from Earth in its orbit (apogee). Because of this increased distance, the moon appears smaller than the sun, and thus doesn’t completely cover it. Instead, a bright ring of the sun remains visible around the moon’s silhouette, creating a “ring of fire” effect. A total solar eclipse, as previously described, happens when the moon completely covers the sun’s disk, resulting in the dramatic darkening and visibility of the sun’s corona. The difference between these types lies solely in the relative positions and sizes of the sun and moon as seen from Earth. The 2025 event is a total solar eclipse due to the specific alignment of the celestial bodies at that time.
Path of Totality: Total Eclipse Solar 2025
The 2025 total solar eclipse will traverse a significant portion of North America, offering a spectacular celestial event for observers along its path. Understanding the path of totality is crucial for planning optimal viewing experiences. This section details the path, durations of totality, and prime viewing locations.
The path of totality is a relatively narrow band across the Earth’s surface where the moon completely blocks the sun’s disk. Outside this path, only a partial eclipse will be visible. The width of the path varies slightly depending on the location, generally ranging from dozens to a hundred miles.
Path of Totality Map, Total Eclipse Solar 2025
Imagine a map of North America. A curving band, starting in the Pacific Ocean, sweeps across parts of Oregon, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. Then it continues across the Gulf of Mexico and ends in the Atlantic Ocean. The band is not perfectly straight; it curves slightly, and its width varies. The darkest portion of the band represents the area experiencing the longest duration of totality. The area immediately surrounding this dark band experiences near-totality, with only a very small sliver of the sun visible. The further one moves from the central line, the less complete the eclipse becomes. The map would clearly illustrate this curving path, showcasing the states and regions directly impacted by the eclipse.
Duration of Totality at Various Locations
The duration of totality, the period when the sun is completely obscured, differs depending on the observer’s location within the path. Locations closer to the central line of the path will experience a longer period of totality than those closer to the edges.
| Location | State | Approximate Duration of Totality |
|---|---|---|
| Dallas, OR | Oregon | 4 minutes |
| Casper, WY | Wyoming | 4 minutes 20 seconds |
| Omaha, NE | Nebraska | 3 minutes 50 seconds |
| Little Rock, AR | Arkansas | 4 minutes 10 seconds |
| New Orleans, LA | Louisiana | 3 minutes 30 seconds |
*Note: These durations are approximate and can vary slightly based on the precise location within each city. More precise timings will be available closer to the eclipse date from specialized astronomical resources.
Optimal Viewing Locations and Times
Choosing an optimal viewing location involves considering factors like weather forecasts, accessibility, and the duration of totality. Locations along the central line, offering the longest duration of totality, are generally preferred. Specific times will vary depending on the location, but generally, the eclipse will occur in the mid-afternoon for most locations along the path.
For example, in Dallas, Oregon, the eclipse might reach totality around 2:30 PM local time, while in Little Rock, Arkansas, the peak might occur around 3:00 PM local time. It’s crucial to consult a detailed eclipse map and timing resource closer to the date to obtain precise times for specific locations. Weather conditions are also critical; clear skies are essential for optimal viewing. Therefore, choosing a location with a historically good weather forecast during that time of year is highly recommended.
Safety Precautions During a Solar Eclipse
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety. Looking directly at the sun, even during an eclipse, can cause serious and permanent damage to your eyes. The sun’s intense radiation can burn the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of your eye, leading to vision impairment or even blindness. Understanding and implementing proper safety measures is paramount to enjoying this celestial event without jeopardizing your eyesight.
Safe viewing methods are essential to protect your eyes from the sun’s harmful rays. Never look directly at the uneclipsed or partially eclipsed sun without proper eye protection. The sun’s brightness, even when partially obscured, is still intense enough to cause retinal damage. Improper eye protection, such as regular sunglasses or homemade filters, will not suffice.
Safe Viewing Methods and Recommended Eyewear
Safe solar viewing requires specialized eyewear that meets the ISO 12312-2 international safety standard. This standard ensures the eyewear filters out enough of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation. These filters significantly reduce the amount of light reaching your eyes to a safe level. Examples of safe eyewear include eclipse glasses or handheld solar viewers. These are usually made of black polymer that has been specially treated to block out harmful radiation. They should be clearly marked with the ISO 12312-2 safety standard. Never use homemade filters or ordinary sunglasses, as these offer insufficient protection and could still lead to eye damage.
Potential Long-Term Effects of Sun Gazing During an Eclipse
Looking directly at the sun during a solar eclipse, even for a short period, can result in solar retinopathy. This is a condition where the sun’s intense radiation damages the retina, leading to a range of vision problems. These problems can include blurred vision, distorted vision, a blind spot in the center of your vision, and in severe cases, permanent vision loss. The damage might not be immediately apparent, and symptoms can develop gradually over time. The effects can be subtle at first, making it crucial to take precautions and avoid direct viewing of the sun without proper protection. For example, someone might initially experience slight discomfort or a reduced ability to see clearly in low light conditions. Over time, however, the damage could worsen, resulting in significant and irreversible vision impairment. There is no cure for solar retinopathy; prevention is the only effective approach.
Historical and Cultural Significance of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events, have held profound significance across diverse cultures throughout history. Their sudden onset of darkness, often accompanied by unusual atmospheric conditions, inspired a wide range of interpretations, from divine omens to natural phenomena requiring explanation. These interpretations reveal much about the beliefs, anxieties, and scientific understanding of past societies.
The impact of solar eclipses on various cultures is evident in their rich tapestry of myths, rituals, and artistic expressions. Early societies, lacking the scientific knowledge to explain the event, often attributed eclipses to supernatural forces, interpreting them as signs from the gods, portents of impending doom, or actions of mythical creatures. This resulted in the development of elaborate rituals and ceremonies aimed at appeasing deities or warding off perceived threats. Modern science, however, provides a clear understanding of eclipses as predictable astronomical events, governed by the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. This contrast highlights the evolution of human understanding from myth and superstition to scientific explanation.
Ancient Mesopotamian Interpretations
Ancient Mesopotamians, meticulous record-keepers, documented solar eclipses with remarkable accuracy, dating back to the early second millennium BCE. Their cuneiform tablets detail observations of eclipses, often associating them with events affecting the king or the state. For instance, an eclipse might be interpreted as a sign of divine displeasure, foreshadowing war, famine, or the death of a ruler. Their detailed astronomical observations, however, also indicate a developing understanding of the cyclical nature of these events, suggesting a blend of mythological interpretation and nascent scientific observation. The meticulous recording of these events, regardless of their interpretation, provides valuable insights into their astronomical knowledge.
Chinese Mythology and Eclipses
In ancient China, solar eclipses were seen as a celestial dragon devouring the sun. This belief led to the development of elaborate rituals aimed at scaring away the dragon, often involving the beating of drums and gongs to create a cacophony of sound intended to drive the mythical creature away. These rituals highlight the cultural significance of eclipses and the attempts to control or influence events perceived as beyond human control. The detailed records of eclipses kept by Chinese astronomers, however, demonstrate a parallel development of astronomical knowledge, albeit intertwined with mythological explanations. Their observations contributed significantly to the early development of astronomy.
Modern Scientific Understanding vs. Historical Beliefs
The modern scientific understanding of solar eclipses, based on Newtonian physics and Kepler’s laws, offers a completely different perspective compared to historical interpretations. We now understand that eclipses are predictable events resulting from the alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth, with the Moon casting a shadow on the Earth. This understanding eliminates the need for supernatural explanations and allows for accurate predictions of eclipse occurrences. The contrast between historical beliefs, rooted in mythology and superstition, and the current scientific understanding underscores the remarkable progress in our comprehension of the universe. The shift from fear and ritualistic responses to precise prediction and scientific observation represents a significant advancement in human knowledge.
Photography and Astrophotography of the 2025 Eclipse
Capturing the breathtaking spectacle of a total solar eclipse requires careful planning and the right equipment. Whether you’re a seasoned astrophotographer or a keen amateur, achieving high-quality images of this rare celestial event demands a strategic approach encompassing both the technical aspects of photography and an understanding of the eclipse itself. This section will Artikel the necessary tools and techniques to successfully photograph the 2025 eclipse.
The equipment needed will vary depending on your desired level of detail and the type of images you aim to capture. For capturing the overall experience, a simple DSLR camera with a decent zoom lens might suffice. However, for detailed shots of the corona and other features, more specialized equipment is necessary.
Essential Equipment for Eclipse Photography
A successful eclipse photograph requires more than just a camera. The following equipment is recommended for capturing high-quality images:
- Camera Body: A DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual controls is essential for precise exposure adjustments. Cameras with live view functionality are highly beneficial for precise focusing, especially when using a telescope.
- Lenses: A telephoto lens with a focal length of at least 400mm is recommended for capturing details of the sun during partial phases. For extreme close-ups of the corona during totality, lenses with focal lengths of 800mm or more, or a telescope with a suitable adapter, are preferable. Consider using a teleconverter to extend the reach of your existing lens.
- Mount: A sturdy tripod is absolutely crucial to avoid blurry images, especially with longer exposures. A motorized equatorial mount, while more expensive, will significantly improve tracking of the sun during partial phases, minimizing trailing.
- Solar Filters: Crucially important for protecting your equipment and your eyesight, these filters must be placed in front of your lens (or telescope) at all times except during the brief period of totality. Avoid using homemade filters; only use reputable brands specifically designed for solar observation. These filters significantly reduce the intensity of the sun’s light, allowing for safe viewing and photography.
- Remote Shutter Release: This prevents camera shake during long exposures, ensuring sharper images. A wired remote is generally preferred to avoid potential interference.
- Extra Batteries and Memory Cards: Be prepared for potential power drain and ensure you have sufficient storage capacity.
Camera and Telescope Setup for Optimal Results
Proper setup is vital for successful eclipse photography. Precise focusing and stable positioning are paramount.
- Camera Positioning: Set up your equipment well in advance, ensuring a clear view of the eclipse path. Use a sturdy tripod to eliminate camera shake. Level the tripod carefully for optimal stability.
- Focusing: Manual focusing is crucial, particularly with telephoto lenses. Focus on a distant object before the eclipse begins to establish a baseline. Fine-tuning may be needed during the partial phases.
- Telescope Setup (if applicable): If using a telescope, ensure it is properly aligned and polar aligned (if using an equatorial mount). Securely attach the camera to the telescope using a suitable T-adapter. Pay close attention to collimation, which is the precise alignment of the telescope’s optical components.
- Exposure Settings: Experiment with different exposure settings during the partial phases to determine optimal values. These will vary greatly depending on the lens, filter, and ambient light conditions. During totality, the exposure settings will need to be adjusted significantly to capture the faint details of the corona. Use manual mode (M) to have complete control over your camera settings.
Capturing the Corona and Other Details During Totality
The brief period of totality is the most critical time for capturing the corona. The exposure settings during this phase differ dramatically from those used during partial phases.
- Exposure Bracketing: Take multiple shots with varying exposure times to ensure you capture the subtle details of the corona. Start with shorter exposures to avoid overexposing the brighter inner corona, then gradually increase the exposure time to capture the fainter outer regions. This technique ensures that at least one shot will capture the full dynamic range of the corona.
- ISO Settings: During totality, increase the ISO to a higher setting (depending on your camera’s capabilities and noise performance), but be mindful of potential image noise. This will allow for faster shutter speeds, minimizing the risk of blurry images.
- Aperture: Use a relatively wide aperture (low f-number) to maximize light gathering, especially for capturing the faint details of the corona. However, be aware of the impact on depth of field.
- Composition: Consider the overall composition of your image. Include landmarks or foreground elements to provide context and scale to your eclipse photographs. Pre-visualize your shot and plan your composition accordingly.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Experience
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a truly unforgettable experience, but careful planning is crucial to ensure a smooth and safe journey. This section Artikels a step-by-step guide to help you prepare for the 2025 total solar eclipse, maximizing your chances of witnessing this celestial event. Consider this your roadmap to an awe-inspiring experience.
Step-by-Step Eclipse Trip Planning Guide
Planning a trip to view the 2025 total solar eclipse involves several key steps. First, identify your preferred viewing location within the path of totality. This requires researching the eclipse’s path and considering factors like accessibility, accommodation availability, and weather forecasts. Next, book your travel arrangements well in advance, securing flights, rental cars, or other transportation. Remember that popular locations will fill up quickly. Then, reserve your accommodation, choosing options that suit your budget and preferences. Finally, create a detailed itinerary, factoring in travel time, eclipse viewing time, and any planned pre- or post-eclipse activities. For example, you might schedule a visit to local attractions or plan a celebratory dinner after the eclipse. Thorough preparation will minimize stress and maximize enjoyment.
Essential Items Checklist for Eclipse Viewing
A well-prepared eclipse viewing kit is essential for a safe and enjoyable experience. This checklist includes critical items for comfort and safety.
- Accommodation: Book lodging well in advance, considering proximity to the path of totality and your budget.
- Transportation: Arrange transportation to and from your viewing location, accounting for potential traffic congestion.
- Solar Eclipse Glasses: These are absolutely crucial. Ensure they meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard. Do not use homemade filters or sunglasses.
- Camera Equipment (Optional): If you plan to photograph the eclipse, bring a suitable camera, lens, and tripod. Practice beforehand.
- Binoculars (Optional): Binoculars can enhance your viewing experience, but ensure they have appropriate solar filters.
- Comfortable Seating: Bring chairs or blankets for comfortable viewing, especially if you’ll be standing for a long period.
- Sunscreen, Hat, and Water: Protect yourself from the sun with sunscreen, a hat, and plenty of water, especially during warmer weather.
- Snacks and Drinks: Pack snacks and drinks to keep your energy levels up throughout the day.
- First-Aid Kit: A basic first-aid kit is always a good idea for any outdoor activity.
Reliable Sources for Weather Forecasts and Eclipse Information
Accurate weather forecasts and eclipse information are vital for successful eclipse viewing. Several reliable sources can provide this information.
- National Weather Service (or your country’s equivalent): Provides detailed weather forecasts for specific locations, crucial for planning around potential cloud cover.
- NASA: NASA’s website offers comprehensive information about eclipses, including maps of the path of totality and detailed timing information.
- Timeanddate.com: This website provides accurate eclipse information, including interactive maps and local times.
- Local astronomy clubs or organizations: These groups often organize eclipse viewing events and provide valuable local information.
The Science Behind the Eclipse
Solar eclipses, awe-inspiring celestial events, are a direct result of the precise interplay between the Sun, the Moon, and the Earth. Understanding the mechanics of this cosmic dance requires examining the orbital dynamics of our celestial neighbors and the geometry of their alignment.
The Moon orbits the Earth in an elliptical path, meaning its distance from our planet varies throughout its cycle. This variation in distance is crucial because a solar eclipse only occurs when the Moon is sufficiently close to Earth to appear large enough in the sky to completely or partially obscure the Sun. If the Moon were consistently farther away, it would never appear large enough to block the Sun’s light completely, resulting only in partial eclipses or none at all. The Moon’s orbital plane is also slightly tilted relative to the Earth’s orbital plane around the Sun (the ecliptic), which is why solar eclipses don’t happen every month. Alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth along the ecliptic is a necessary condition for a solar eclipse to occur.
Types of Solar Eclipses and Their Frequency
Solar eclipses are categorized based on the extent to which the Moon covers the Sun. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon completely blocks the Sun’s disk, revealing the Sun’s corona – its outer atmosphere. During a partial solar eclipse, only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon. An annular solar eclipse happens when the Moon is farther from Earth, appearing smaller in the sky, and leaving a ring of sunlight visible around the Moon’s silhouette. Hybrid eclipses are rare events that transition between annular and total eclipses along the path of totality, depending on the observer’s location. The frequency of each type varies; total solar eclipses are less frequent than partial eclipses, with annular eclipses falling somewhere in between. The precise frequency depends on the constantly changing orbital mechanics of the Moon and Earth. For example, while a total solar eclipse may occur at a particular location only once every few hundred years, partial eclipses are far more common.
Scientific Research Opportunities During Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses offer a unique opportunity for scientific research that is otherwise impossible. The brief period of totality allows scientists to study the Sun’s corona, a region normally obscured by the bright solar disk. Observations during these eclipses have significantly contributed to our understanding of the Sun’s magnetic field, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections – phenomena that can affect Earth’s space weather. Furthermore, the sudden dimming of sunlight during totality provides a natural laboratory for studying the Earth’s atmosphere and its response to rapid changes in solar radiation. For instance, scientists can examine the impact on atmospheric temperature, wind patterns, and even animal behavior. The data collected during total solar eclipses often lead to advancements in our understanding of solar physics and its connection to terrestrial processes. The 2017 total solar eclipse, for example, provided valuable data used to refine models of the Sun’s corona and its dynamics.
Impact on Wildlife and Nature
A total solar eclipse, a dramatic celestial event, isn’t just a spectacle for humans; it significantly impacts the natural world, triggering observable behavioral changes in animals and subtle shifts in plant life and ecosystems. The sudden and dramatic decrease in light and temperature can disrupt the usual rhythms of nature, revealing fascinating insights into the intricate relationships between organisms and their environment.
The effects of a total solar eclipse on wildlife are often dramatic and readily apparent. Animals, reliant on visual cues and the regular patterns of light and dark, react in diverse ways to this unexpected shift. The intensity of these reactions varies depending on the species, their habitat, and the duration of totality.
Behavioral Changes in Animals During a Total Solar Eclipse
Animals exhibiting nocturnal behaviors may become active, mistaking the sudden darkness for nightfall. Birds, for example, may cease their singing and return to their roosts. Similarly, diurnal animals, active during the day, may display behaviors associated with nighttime, such as seeking shelter or becoming quieter. Insects, sensitive to light changes, may alter their activity patterns, with some becoming less active while others might increase their activity. Mammals, such as cows and horses, have been observed to exhibit unusual behavior, such as seeking shelter or displaying signs of agitation. These reactions highlight the deep-seated reliance of many animals on the predictable cycles of light and darkness.
Effects of a Total Solar Eclipse on Plant Life and Ecosystems
While the effects on plants might be less immediately noticeable than those on animals, a total solar eclipse does influence plant life. The sudden drop in light levels can trigger physiological responses in plants, though these effects are usually temporary and minor. Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light into energy, temporarily slows or stops during totality. The extent of this impact depends on factors like the duration of totality and the plant species’ sensitivity to light fluctuations. While a single eclipse is unlikely to have long-term ecological consequences, the cumulative effects of repeated eclipses over time could potentially influence plant growth and development, though more research is needed to fully understand this aspect.
Anecdotal Evidence of Wildlife Reactions During Past Eclipses
Numerous anecdotal accounts from observers during past total solar eclipses document various animal reactions. Reports from the 1999 European eclipse describe birds ceasing their songs and returning to their nests as darkness fell. Similarly, observations from the 2017 North American eclipse noted changes in animal activity, with some becoming quiet while others showed signs of confusion. While these are observational accounts and not rigorously controlled scientific studies, they consistently point towards a widespread impact of total solar eclipses on animal behavior, demonstrating the animals’ sensitivity to environmental changes, even those as brief as a total solar eclipse.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
This section addresses some common queries regarding total solar eclipses, providing clear and concise answers based on scientific understanding and observable phenomena. Understanding these aspects enhances the appreciation and safe observation of this spectacular celestial event.
Total Solar Eclipse Frequency
Total solar eclipses are not as rare as one might think, yet they are not commonplace either. They occur somewhere on Earth approximately every 18 months on average. However, any specific location on Earth will only experience a total solar eclipse roughly once every 375 years. This disparity arises because the Moon’s shadow, which creates the totality, is relatively small compared to the Earth’s surface. The path of totality, the narrow band where the total eclipse is visible, traverses only a small portion of the globe. For example, the total solar eclipse of April 8, 2024, was visible across a swathe of North America, while the next one in 2025 will trace a path across the Southern Hemisphere.
Solar and Lunar Eclipse Differences
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, casting its shadow on Earth. This can only happen during a new moon phase. A lunar eclipse, conversely, occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. This event can only take place during a full moon phase. The key difference lies in the celestial body being obscured: the Sun during a solar eclipse and the Moon during a lunar eclipse. Furthermore, solar eclipses are only visible from a limited area on Earth, while lunar eclipses are visible from a much larger portion of the night side of the Earth.
Temperature Changes During Totality
During a total solar eclipse, a noticeable drop in temperature occurs. The extent of the temperature change varies depending on several factors, including the time of year, weather conditions, and the duration of totality. However, a decrease of several degrees Celsius is typical. This is because the Sun, the primary source of heat, is completely blocked by the Moon. This sudden drop in temperature is often accompanied by a noticeable change in ambient light and a noticeable shift in wind patterns. Observers often report a feeling of a sudden twilight or even a brief coolness in the air.
Totality Duration
The duration of totality, the period when the Sun is completely obscured by the Moon, is highly variable. It can range from a few seconds to a maximum of around 7.5 minutes. The length of totality depends on several factors, including the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth, as well as the sizes of the Sun and Moon as seen from the Earth’s surface. The longer durations are rare events occurring only at certain geographic locations under specific astronomical alignments.
Corona Appearance During Totality
The Sun’s corona, its outermost atmosphere, is only visible during a total solar eclipse. The corona appears as a pearly white or silvery halo surrounding the eclipsed Sun. Its appearance is quite dynamic and complex, exhibiting streamers, plumes, and loops of plasma extending millions of kilometers into space. The brightness and structure of the corona can vary considerably from one eclipse to another, reflecting changes in the Sun’s activity and magnetic field. Observing the corona is one of the most awe-inspiring aspects of witnessing a total solar eclipse.
Illustrative Descriptions (for images)
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is an experience that transcends mere observation; it’s a visceral engagement with the celestial mechanics of our solar system, leaving an indelible mark on the observer’s memory. The following descriptions aim to capture the visual spectacle and emotional impact of this extraordinary event.
The dramatic shift in light and color during totality is unlike anything experienced on Earth. The transition from bright daylight to a deep twilight is swift and breathtaking.
Sky Appearance During Totality
As the moon completely obscures the sun, the sky transforms dramatically. The familiar blue of daytime gives way to a deep, almost unnatural twilight. The horizon glows with a vibrant, almost otherworldly light, a mixture of oranges, reds, and purples that intensifies the further away from the sun one looks. The effect is surreal, as if the setting sun were mirrored on every point of the horizon simultaneously. Stars and planets become visible, adding to the uncanny atmosphere. The air itself seems to cool, and a palpable sense of awe settles over the landscape.
Corona Appearance During Totality
The sun’s corona, normally invisible to the naked eye, becomes the centerpiece of the spectacle during totality. It’s a breathtaking halo of pearly white light, extending outwards from the eclipsed sun in a complex, dynamic structure. The corona’s size and shape vary with each eclipse, influenced by the sun’s current activity. Streamers of light, brighter and denser than the surrounding corona, often radiate outwards, creating a visually stunning spectacle. The corona’s brightness contrasts sharply with the darkened sky, creating a stark and unforgettable image. Its ethereal glow is a testament to the sun’s immense power and the intricate dynamics of our star.
Emotional Impact of Witnessing a Total Solar Eclipse
The emotional response to a total solar eclipse is deeply personal, but a sense of awe and wonder is almost universally reported. The sudden darkness, the eerie silence, and the unearthly beauty of the corona combine to create a profoundly moving experience. Many observers describe feelings of humility in the face of the cosmos, a sense of connection to something larger than themselves. The sheer spectacle can be overwhelming, leaving a lasting impression on the observer’s psyche, a memory that is often described as life-altering. The feeling is frequently described as a profound sense of wonder, a mixture of fear and excitement, and a deep respect for the power of nature. The experience is frequently described as a spiritual or transformative event, leaving observers with a renewed appreciation for the universe and their place within it.
The Total Solar Eclipse of 2025 is a significant astronomical event, promising a breathtaking spectacle for observers in its path. For those eager to witness the celestial wonder, or even relive the experience later, a fantastic resource is available: Photos Of Total Solar Eclipse 2025 , offering a collection of stunning images. These photos help capture the awe-inspiring beauty and scientific significance of the Total Eclipse Solar 2025.
The Total Solar Eclipse of 2025 is a significant astronomical event, generating considerable excitement among astronomy enthusiasts. A key question for many is whether specific locations will experience totality, and to find out if Columbus, Ohio will be in the path of totality, you can check this helpful resource: Will Columbus Ohio Be In Total Eclipse 2025.
Knowing this information is crucial for planning viewing opportunities during the Total Eclipse Solar 2025.
The Total Solar Eclipse of 2025 is a significant astronomical event, promising a breathtaking spectacle for observers in its path. Understanding the celestial event’s impact goes beyond the scientific; many explore its spiritual significance, delving into its symbolic meaning. For those interested in this perspective, consider exploring the insights offered at Total Eclipse 2025 Meaning Spiritual to gain a deeper understanding.
Returning to the astronomical event itself, the Total Solar Eclipse of 2025 is anticipated to be a truly memorable celestial occurrence.
The Total Eclipse Solar 2025 event is generating significant excitement among astronomy enthusiasts. To properly prepare for viewing this celestial spectacle, understanding the precise path of totality is crucial. You can find a detailed map illustrating the Total Solar Eclipse Path April 8 2025 , which will help you determine optimal viewing locations for the Total Eclipse Solar 2025 experience.
Planning ahead ensures you won’t miss this rare opportunity.