Total Solar Eclipse 2025
The total solar eclipse of 2025 will be a spectacular celestial event, offering a unique opportunity for observers along its path of totality to witness the sun’s corona and experience the dramatic darkening of the daytime sky. The path of totality will traverse several countries, offering varying viewing experiences depending on location.
Path of Totality: Geographical Coverage and Duration
The path of totality for the 2025 total solar eclipse will begin in the northern hemisphere, crossing over parts of North America, including the United States and Canada, before continuing into Europe. Specific regions within these continents will experience the eclipse’s totality, while others will witness only a partial eclipse. Major cities along the path of totality will vary depending on the specific time and location of the eclipse. While a precise list of every city is impossible to provide without specific date/time data, regions like the northern United States and parts of Canada are expected to see the eclipse in its totality. The exact path and duration will be refined as the date approaches, based on more precise astronomical calculations. This path, however, will not be as easily accessible as others due to the geographic distribution and population density of the regions.
Path of Totality Map and Duration Variations
Imagine a map depicting North America and parts of Europe. A relatively narrow band, the path of totality, snakes across this map. This band is not uniform in width; it varies slightly across its length. The darkest portion of the band, representing the longest duration of totality, will likely be concentrated in a specific region, perhaps over a sparsely populated area of the US or Canada. Areas closer to the edges of this band will experience shorter durations of totality. The duration of totality will differ depending on the specific location within the path, ranging from a few seconds in some areas at the edges to potentially several minutes in the central regions. This variation is due to the geometry of the sun, moon, and Earth during the eclipse. A detailed map showing the isochrones (lines of equal duration) would clearly show this gradient of totality durations. For example, a location in central North America within the central path of totality might experience totality for over four minutes, while a location near the edge might only experience totality for a minute or less.
Accessibility of Viewing Locations
Accessibility along the path of totality will vary significantly. Some sections will pass over sparsely populated areas, offering relatively undisturbed viewing experiences but requiring significant travel to reach. Other sections will cross densely populated urban areas, potentially presenting challenges related to finding suitable viewing locations with minimal light pollution and ample space for observation. Factors such as infrastructure, including roads, parking availability, and public transportation, will also influence accessibility. For example, a remote area in northern Canada, while offering potentially longer durations of totality, might require considerable planning and specialized transportation to reach. Conversely, a location within a major city might be more easily accessible but could offer shorter totality durations and a less pristine viewing experience due to light pollution.
Viewing the Eclipse Safely
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but observing it without proper eye protection can lead to serious and permanent eye damage. The sun’s intense radiation can cause solar retinopathy, a condition that can result in blurred vision, blind spots, and even complete vision loss. Protecting your eyes is paramount during this celestial event.
The Dangers of Unsafe Solar Eclipse Viewing
Looking directly at the sun, even for a short period, during a partial or annular eclipse is extremely hazardous. The sun’s rays are so powerful that they can damage the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This damage can occur without any immediate sensation of pain, making it even more dangerous. Unlike other forms of eye injury, damage from solar radiation often has no immediate symptoms and may not be noticed until hours or days later, when vision problems start to appear. The damage is often irreversible.
Safe Solar Eclipse Viewing Glasses
Proper eye protection is crucial. ISO 12312-2 certified solar eclipse glasses are essential. These glasses have special filters that block out over 99.999% of visible light and 100% of harmful ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation. Avoid using homemade filters or ordinary sunglasses, as they are not sufficient to protect your eyes. Reputable manufacturers clearly label their glasses with the ISO 12312-2 certification. Some examples of features to look for include a snug fit to prevent stray light from entering, and durable construction to prevent scratching or damage to the filters. Glasses should also be comfortable to wear for extended periods.
Correct Use of Solar Eclipse Glasses
Always inspect your solar eclipse glasses before use. Check for any scratches or damage to the filters. Put them on before looking at the sun, and remove them only after you have turned away from the sun. Never look at the sun through binoculars, telescopes, or cameras without a specially designed solar filter attached to the front of the device. Such filters must be specifically designed for solar viewing and securely attached to avoid damage to the equipment and the eyes. Supervise children carefully when they are using solar eclipse glasses.
Safe Indirect Viewing Techniques
For a safe and engaging alternative, consider indirect viewing methods. A simple pinhole projector is an effective and easy-to-make option. Create a small hole in a piece of cardboard. Then, stand with your back to the sun and project the image of the sun onto a white surface held behind the cardboard. The pinhole will project a small, inverted image of the sun onto the surface, allowing you to safely observe the eclipse’s progress. Alternatively, you can use a colander to project multiple images of the sun onto a surface. This provides a fun, family-friendly way to watch the eclipse.
Safe Viewing Practices Infographic
Imagine a simple infographic with three panels.
Panel 1: A large, bold “X” over an image of a person looking directly at the sun without glasses. Text: “NEVER look directly at the sun without proper eye protection.”
Panel 2: An image of a person wearing ISO 12312-2 certified solar eclipse glasses, safely viewing the eclipse. Text: “Always use ISO 12312-2 certified solar eclipse glasses.”
Panel 3: An illustration of a pinhole projector in action, showing the projected image of the sun on a white surface. Text: “Use indirect viewing methods like a pinhole projector for safe viewing.”
Scientific Significance of the Eclipse
Total solar eclipses, fleeting moments of celestial alignment, offer invaluable opportunities for scientific advancement. The brief period of total darkness allows researchers to study aspects of the sun and its effects on Earth that are otherwise obscured by the overwhelming brightness of the solar disk. The 2025 total solar eclipse, with its path traversing specific regions, presents a unique chance to gather crucial data and further our understanding of solar phenomena.
The eclipse provides a rare window into the sun’s corona, its outermost atmosphere. This region, millions of degrees hotter than the sun’s surface, is a source of intense solar wind and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), events that can significantly impact Earth’s magnetosphere and technological infrastructure. During totality, the corona becomes visible, allowing scientists to study its structure, temperature, and magnetic field with unprecedented detail. This detailed observation helps refine models of solar activity and improve our ability to predict space weather events.
Corona Studies During Total Solar Eclipses, Total Sun Eclipse 2025
Observations of the corona during total solar eclipses have a long and rich history, contributing significantly to our understanding of the sun’s dynamic behavior. Early eclipse observations provided the first visual evidence of the corona’s existence, revealing its intricate structure of streamers and plumes. Modern observations, employing sophisticated instruments such as coronagraphs and spectrographs, have expanded our understanding of coronal heating mechanisms, the generation of solar wind, and the dynamics of CMEs. Data gathered during the 2025 eclipse will be compared with previous observations, furthering our understanding of long-term changes in solar activity. For example, comparing data from the 2025 eclipse with that from the 2017 eclipse across similar geographical locations could reveal subtle changes in the corona’s structure and dynamics over an eight-year period.
Citizen Scientist Participation in Eclipse Observation
Citizen scientists play a crucial role in collecting valuable data during total solar eclipses. Their widespread geographic distribution allows for simultaneous observations across the eclipse path, providing a more comprehensive dataset than what could be gathered by professional scientists alone. Organized citizen science projects often provide standardized protocols and data collection tools, ensuring data quality and consistency. Citizen scientists can contribute by photographing the corona, timing the duration of totality, or recording observations of changes in atmospheric conditions. The sheer volume of data collected by a network of citizen scientists can significantly enhance the scientific value of eclipse observations. For instance, coordinated observations of the corona’s shape and brightness across the eclipse path can help create a more complete three-dimensional model of the corona.
Comparison of Scientific Findings from Previous Eclipses
Past total solar eclipses have yielded groundbreaking discoveries. For example, the 1868 eclipse led to the discovery of helium, an element previously unknown on Earth. More recently, eclipses have been instrumental in confirming Einstein’s theory of general relativity and providing crucial data for understanding coronal mass ejections and their impact on Earth. The 2017 eclipse, for instance, provided valuable data on the sun’s corona, which was used to refine models of solar wind and space weather forecasting. By comparing the findings of the 2025 eclipse with previous observations, scientists can identify trends and patterns in solar activity, leading to a better understanding of the sun’s long-term behavior.
Potential Breakthroughs from the 2025 Eclipse
The 2025 total solar eclipse presents the potential for significant scientific breakthroughs. Advanced instrumentation and improved data analysis techniques could lead to a more detailed understanding of coronal heating mechanisms, the origin of solar wind, and the prediction of space weather events. The combination of professional and citizen science observations could reveal previously unknown features of the corona or uncover subtle changes in solar activity. For example, high-resolution imaging might reveal previously unseen fine structures within the corona, offering clues to the complex physical processes at play. Furthermore, analysis of spectral data could reveal the presence of unexpected elements or isotopes in the corona, expanding our understanding of the sun’s composition and evolution.
Historical and Cultural Perspectives on Eclipses
Solar and lunar eclipses, dramatic celestial events, have captivated humanity for millennia, leaving an indelible mark on our history and cultures. Their unpredictable nature and awe-inspiring visual impact have fostered a rich tapestry of interpretations, from fearful omens to profound spiritual experiences, shaping myths, rituals, and scientific understanding across diverse societies.
Ancient Accounts of Eclipses
Ancient civilizations lacked the scientific understanding we possess today, leading to varied interpretations of eclipses. The Babylonians, meticulous record-keepers, meticulously documented eclipses for centuries, developing sophisticated prediction methods. Their cuneiform tablets reveal detailed observations, contributing significantly to early astronomical knowledge. In contrast, many cultures viewed eclipses as ominous signs, often associating them with divine anger or impending doom. For instance, some Native American tribes believed a celestial beast was devouring the sun, prompting rituals to scare it away. Ancient Chinese texts describe eclipses as a dragon consuming the sun, with court astronomers held responsible for failing to predict and appease this celestial dragon.
Cultural Significance and Myths
Eclipses played a crucial role in shaping the myths and beliefs of various societies. In Norse mythology, eclipses were linked to the actions of the wolf Sköll, who chased and devoured the sun or moon. Greek mythology attributed eclipses to the actions of gods or celestial beings, often interpreting them as signs of divine displeasure or impending events. Many cultures developed elaborate rituals and ceremonies to ward off the perceived negative effects of eclipses, including making loud noises to scare away evil spirits or offering sacrifices to appease the gods. The Vikings, for example, believed that eclipses signaled a time of great vulnerability, and would take precautions to protect themselves from supernatural forces.
Reactions to Eclipses Across Cultures: A Comparison
While some cultures viewed eclipses with fear and dread, others approached them with a sense of wonder and curiosity. The contrasting reactions reflect the diverse cosmological beliefs and social structures of different societies. While some cultures interpreted eclipses as portents of disaster or war, others saw them as opportunities for spiritual reflection or renewal. The level of fear or acceptance often depended on the specific culture’s worldview and its understanding of the cosmos. For example, the Inca civilization associated eclipses with the wrath of their gods, initiating rituals to appease them, while the ancient Egyptians viewed them as celestial events of less ominous significance, though still worthy of careful observation.
Timeline of Notable Historical Eclipses
Several eclipses stand out in history due to their impact on human events or scientific understanding. The eclipse of 585 BC, accurately predicted by Thales of Miletus, is considered a pivotal moment in the history of astronomy and is credited with ending a war between the Medes and Lydians. The eclipse of 1133 AD, vividly documented in historical records, was a significant event in Europe. The eclipse of 1919, observed by Arthur Eddington during a solar eclipse, provided crucial evidence supporting Einstein’s theory of general relativity, revolutionizing our understanding of gravity.
Historical Observations and Scientific Understanding
Historical observations of eclipses, even those lacking sophisticated instruments, provided invaluable data for developing our understanding of celestial mechanics. The meticulous records kept by ancient civilizations, though often imbued with mythological interpretations, contributed to the gradual refinement of astronomical models. These early observations, coupled with later scientific advancements, enabled the development of accurate eclipse prediction methods, transforming what was once viewed as a mysterious and fearsome event into a predictable and scientifically understood phenomenon. The ongoing study of historical eclipse records continues to contribute to our knowledge of past celestial events and their impact on Earth.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Trip
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a truly unforgettable experience, but careful planning is crucial to ensure a smooth and enjoyable trip. This guide will help you navigate the various aspects of planning your eclipse viewing adventure in 2025. Consider this your roadmap to a successful and awe-inspiring celestial event.
Choosing a Viewing Location
Selecting the right location is paramount. The path of totality, the area where the sun will be completely obscured by the moon, is relatively narrow. Within this path, you’ll want to consider several factors. Weather forecasts for the day of the eclipse are incredibly important; clear skies are essential for optimal viewing. Historical weather data for the potential locations can help you assess the likelihood of clear skies. Accessibility is another key consideration; you’ll need to factor in ease of travel to and from your chosen location, as well as the availability of amenities such as lodging and food. Population density within the path of totality also impacts the viewing experience; some areas will be significantly more crowded than others. Researching the specific location’s infrastructure and crowd estimates can be crucial to your planning.
Accommodation and Transportation
Securing accommodation well in advance is vital, especially if you’re planning to travel to a popular viewing location. Many hotels and rental properties book up months, even years, in advance of major celestial events. Transportation options should also be planned early. If driving, consider potential traffic congestion, especially closer to the eclipse date. Public transportation options, if available, should be researched. Having a backup plan for transportation is wise, in case of unexpected delays or issues. For example, if relying on a rental car, booking well in advance and ensuring insurance coverage are essential.
Sample Eclipse Viewing Trip Itinerary
This sample itinerary assumes a three-day trip centered around the eclipse:
- Day 1: Arrive at your chosen location. Check into your accommodation. Explore the local area, perhaps visiting a museum or historical site. Enjoy a relaxing dinner, preparing yourself for the main event.
- Day 2: The Eclipse Day! Set up your viewing location early to secure a good spot. Engage in pre-eclipse activities, such as attending a local eclipse viewing event or participating in educational programs. Witness the total solar eclipse! Afterward, celebrate with fellow eclipse enthusiasts.
- Day 3: Enjoy any remaining sightseeing opportunities. Depart from your viewing location.
Essential Items Checklist
Preparing a comprehensive checklist is key to a stress-free eclipse experience.
- Eclipse glasses: These are absolutely essential for safe viewing. Ensure they meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard.
- Sunscreen and hat: Protect yourself from the sun’s rays.
- Comfortable clothing and footwear: You might be standing or sitting for extended periods.
- Camera and tripod (optional): Capture the incredible spectacle.
- Binoculars or telescope (optional): Enhance your viewing experience.
- Snacks and water: Stay hydrated and energized.
- First-aid kit: Be prepared for minor injuries.
- Portable charger: Keep your devices powered.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Total Sun Eclipse 2025
This section addresses some common queries regarding the upcoming total solar eclipse in 2025. Understanding these points will help you prepare for and enjoy this spectacular celestial event.
Total Solar Eclipse Description
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and the Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light. This creates a temporary period of darkness during the daytime, even though the Sun is still shining. The Sun’s corona, its outer atmosphere, becomes visible as a faint, ethereal glow surrounding the completely obscured solar disk. Depending on atmospheric conditions, various effects can be observed, including the darkening of the sky, a drop in temperature, and the appearance of stars and planets in the daytime sky. The path of totality, the area where the total eclipse is visible, is a relatively narrow band across the Earth’s surface.
Frequency of Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events at any given location. While they occur somewhere on Earth roughly every 18 months, the same location might not witness a total solar eclipse for many decades, or even centuries. The specific frequency depends on the complex interplay of the Sun, Moon, and Earth’s orbits. For example, while several partial solar eclipses may be visible in a given region each year, a total eclipse is a much rarer occurrence.
2025 Total Solar Eclipse Viewing Locations
The 2025 total solar eclipse will be visible across a path traversing parts of North America, specifically passing over regions of Mexico, the United States, and Canada. The exact path of totality will vary in width and precise location, and detailed maps showing the path’s progression are readily available from various astronomical organizations and websites. Specific cities and towns along this path will experience the total eclipse for a short period, while areas further away will only see a partial eclipse.
Safe Eclipse Viewing Practices
Never look directly at the Sun during a solar eclipse without proper eye protection. Doing so can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. Certified solar viewing glasses, which meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard, are essential for safe observation. These glasses significantly reduce the Sun’s intensity to a safe level. Improvised methods, such as using sunglasses or exposed film, are inadequate and dangerous. Indirect viewing methods, such as projecting the Sun’s image onto a screen using a pinhole camera, are also safe alternatives.
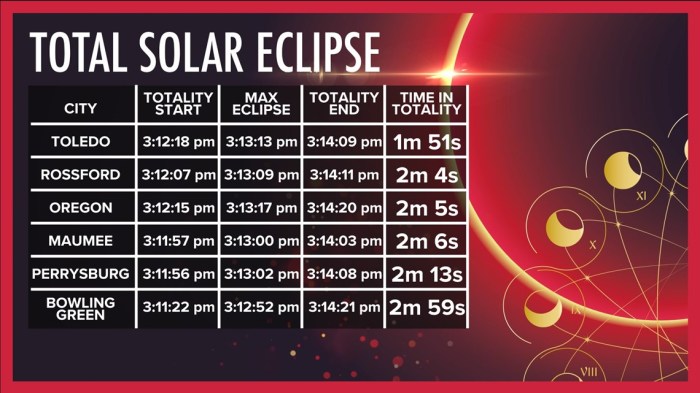
Total Solar Eclipse Duration in Mazatlan, Mexico
The total duration of the 2025 total solar eclipse in Mazatlan, Mexico, is estimated to be approximately 4 minutes and 26 seconds. This duration can vary slightly depending on the precise location within the city and the accuracy of predictive models. It is important to note that this is an estimate, and minor variations may occur. This specific location was chosen due to its expected prime viewing position along the path of totality. Other locations within the path of totality will have varying durations, with some experiencing longer periods of totality.