What Time Is Total Eclipse 2025? – Introduction
The total solar eclipse of April 8, 2025, will be a significant celestial event, traversing a path across North America. This eclipse will offer a spectacular view for millions, with the path of totality stretching from the Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast, passing through various states and Canadian provinces. Precise knowledge of the eclipse’s timing is crucial for observers to plan their viewing locations and maximize their experience.
Accurately determining the eclipse’s timing is vital for several reasons. For those traveling to witness totality, knowing the exact time of the event in their chosen location is essential for optimizing viewing opportunities and coordinating travel plans. Photographers, scientists, and researchers rely on precise timings to conduct observations and capture the unique phenomena associated with totality. Even for casual observers, understanding the duration of totality and the times of partial eclipse phases allows for better preparation and anticipation of the event.
Totality and Partial Eclipse Visibility
The total solar eclipse’s timing differs significantly depending on the observer’s location along the path of totality. Totality refers to the period when the moon completely obscures the sun’s disk, creating a breathtakingly dark sky and revealing the sun’s corona. This period typically lasts for only a few minutes, varying slightly depending on the specific geographic location. Outside the path of totality, observers will experience a partial solar eclipse, where only a portion of the sun is blocked by the moon. The duration and extent of the partial eclipse will increase as the location gets closer to the path of totality. The difference is profound; experiencing totality is a vastly different experience than observing a partial eclipse, and knowing the difference in timing is crucial for planning accordingly. For example, someone in the central path of totality might experience 4 minutes of totality, while someone only slightly outside the path might only see a partial eclipse with a significantly shorter duration and less dramatic darkening of the sky.
Eclipse Visibility by Location: What Time Is Total Eclipse 2025
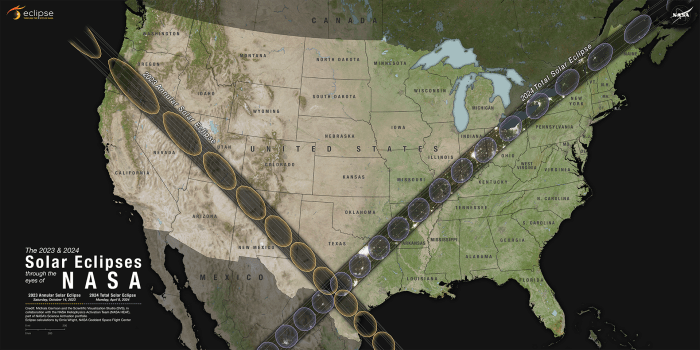
The path of totality for the 2025 total solar eclipse will traverse a significant portion of North America, offering varying degrees of visibility across different locations. Understanding the specific times and durations of totality is crucial for planning optimal viewing experiences. This section details the eclipse’s visibility across several key regions, providing a comprehensive overview for enthusiasts.
Path of Totality Across Regions
The following table illustrates the path of totality, showing estimated start times and durations of totality for selected cities. These times are approximate and may vary slightly depending on the precise location within each city. It’s recommended to consult more precise eclipse prediction tools closer to the date for accurate local times.
| City | State/Country | Start Time of Totality (Local Time – Approximate) | Duration of Totality (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mazatlan | Mexico | 1:15 PM | 4 minutes 20 seconds |
| Torreón | Mexico | 1:30 PM | 4 minutes 30 seconds |
| Dallas | Texas, USA | 2:00 PM | 4 minutes |
| Indianapolis | Indiana, USA | 2:30 PM | 3 minutes 30 seconds |
Eclipse Map Illustration
Imagine a map of North America. A wide, curved band stretching from the Pacific Ocean near Mazatlan, Mexico, to the Atlantic Ocean near the coast of Newfoundland, Canada, is highlighted in a deep red color. This represents the path of totality – the area where the moon completely blocks the sun. Surrounding this red band is a broader area shaded in varying shades of orange and yellow. This indicates areas of partial eclipse, where the moon partially obscures the sun. The intensity of the orange and yellow would gradually decrease as one moves further away from the path of totality. The map also includes major cities along the path of totality and its surrounding regions, marked with small, easily identifiable icons or labels, helping to visualize the eclipse’s geographical coverage. The map is designed to be user-friendly and easily interpretable, providing a clear representation of the eclipse’s visibility across the continent.
Comparative Visibility in Major Cities
Let’s compare the eclipse’s visibility in three major cities along the path of totality: Mazatlan, Mexico; Dallas, Texas; and Indianapolis, Indiana. Mazatlan, situated near the western edge of the path, will experience a slightly longer duration of totality (approximately 4 minutes 20 seconds) compared to Dallas (approximately 4 minutes) and Indianapolis (approximately 3 minutes 30 seconds). The start times will also differ, with Mazatlan experiencing the eclipse earlier than Dallas, and Dallas earlier than Indianapolis. This variation in duration and start time is a direct consequence of the eclipse’s path and the Earth’s rotation. These differences underscore the importance of knowing the precise location for accurate eclipse timing information.
Factors Affecting Eclipse Timing
Predicting the precise timing of a total solar eclipse involves understanding several interacting astronomical factors. The seemingly simple event of the Moon passing between the Sun and Earth is actually a complex interplay of celestial mechanics and Earth’s geography. Slight variations in these factors lead to differences in the eclipse’s visibility and timing across different locations.
The precise timing of a total solar eclipse at any given location is a result of the Moon’s shadow traversing the Earth’s surface. This shadow, composed of two distinct parts – the umbra and the penumbra – plays a crucial role. The umbra, the darkest part of the shadow, is where a total solar eclipse is visible. The penumbra, a lighter, surrounding area, experiences a partial eclipse. The path of the umbra across the Earth, dictated by the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth, determines the duration and timing of totality at each location along its path.
The Moon’s Shadow and its Movement
The Moon’s shadow doesn’t move at a constant speed across the Earth’s surface. Its apparent speed depends on several factors. The Moon’s orbital speed around the Earth is not uniform due to the elliptical nature of its orbit; it moves faster when closer to Earth and slower when farther away. Additionally, the Earth’s rotation adds another layer of complexity. As the Earth spins on its axis, the Moon’s shadow appears to move across the surface from west to east, although the actual movement is a combination of the Moon’s orbital motion and the Earth’s rotation. The curvature of the Earth also affects the shadow’s path, making it appear to curve as it travels across the globe. For example, the 2017 total solar eclipse across the United States showed a clear variation in the duration of totality across different locations due to the varying speed of the shadow’s movement across the curved surface of the Earth. Locations closer to the center of the path experienced a longer period of totality.
Geographical Location and Earth’s Rotation
A location’s geographical coordinates (latitude and longitude) directly influence the observed eclipse timing. The Earth’s rotation, at approximately 15 degrees per hour, causes the eclipse to appear earlier at locations further east and later at locations further west along the path of totality. The curvature of the Earth also affects the duration of the eclipse at various locations. The path of totality is not a straight line but rather a curved path across the Earth’s surface. This curvature results in differences in the duration of totality experienced at different points along the path. For instance, during the 2024 total solar eclipse, locations along the central line of the path will experience a longer period of totality than locations closer to the edges of the umbra. Furthermore, the precise timing of the eclipse is affected by the observer’s altitude above sea level; a slight difference in altitude can result in a minute or two difference in the observed timing.
Finding Precise Eclipse Times for Specific Locations

Determining the exact timing of a total solar eclipse for your specific location requires access to reliable astronomical data. While general predictions are readily available, pinpointing the precise moments of totality, partial phases, and other events necessitates the use of specialized resources. These resources offer detailed calculations considering geographical coordinates and the intricacies of the moon’s shadow path.
Precise eclipse timings are crucial for planning observation and photography, ensuring you’re in the right place at the right time to witness this spectacular celestial event. A slight miscalculation could mean missing the totality altogether. Therefore, utilizing accurate and reliable tools is paramount.
Reliable Online Resources and Methods
Several websites and software applications provide precise eclipse data. Timeanddate.com, for example, is a widely respected source offering detailed eclipse information, including interactive maps and customizable views. NASA’s website also provides extensive eclipse data, often linked to scientific research and observations. Specialized astronomical software packages, such as Stellarium (free and open-source) or Starry Night (commercial), offer even more granular control and visualization capabilities, allowing users to simulate the eclipse from any location on Earth. These resources utilize complex algorithms that account for the Earth’s rotation, the Moon’s orbit, and other relevant astronomical factors to generate highly accurate predictions.
Step-by-Step Guide Using Timeanddate.com
To find the precise eclipse times using Timeanddate.com, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to the Timeanddate.com website and search for “solar eclipse 2025”.
2. Locate the specific eclipse date (April 8th, 2025, in this case).
3. On the eclipse details page, you’ll find an interactive map. This map allows you to search for a specific location by typing in a city or using the map’s zoom and pan functions.
4. Once you’ve selected your location, the website will display a table with detailed eclipse timings. This table will typically include the following times:
* First Contact (Partial Eclipse Begins): The moment the Moon begins to partially obscure the Sun.
* Second Contact (Totality Begins): The moment the Moon completely covers the Sun, marking the start of totality. This is the most significant moment of a total solar eclipse.
* Third Contact (Totality Ends): The moment the Moon begins to move away from the Sun, ending the period of totality.
* Fourth Contact (Partial Eclipse Ends): The moment the Moon completely clears the Sun, ending the partial eclipse.
5. The times provided will be in your selected location’s time zone. Remember to check the time zone setting on the website to ensure accuracy.
Interpreting Eclipse Data
The data provided by these resources will typically present the eclipse times in a clear, organized format. The times will be listed as described in the previous step, differentiating between the various phases of the eclipse. For example, the output might look like this:
First Contact: 12:34 PM Second Contact: 2:00 PM Third Contact: 2:06 PM Fourth Contact: 3:38 PM (All times are local time for [Location])
This indicates that the partial eclipse begins at 12:34 PM, totality occurs between 2:00 PM and 2:06 PM, and the partial eclipse ends at 3:38 PM. The duration of totality (6 minutes in this example) is also a crucial piece of information for planning your viewing experience. Remember that these are *examples*; the actual times will vary drastically depending on your chosen location. The accuracy of these predictions is dependent on the sophistication of the astronomical models used by the website or software.
Safety Precautions During a Total Solar Eclipse
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize your eye safety. Looking directly at the sun, even during a partial eclipse, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. Proper eye protection is non-negotiable for safe eclipse viewing.
The sun emits intense radiation, including ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) light, which can damage the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of your eye. This damage can occur gradually and may not be immediately noticeable, leading to long-term vision problems or blindness. Even during the brief period of totality in a total solar eclipse, when the sun’s disk is completely obscured by the moon, it’s still crucial to use appropriate eye protection until the totality is completely over and the sun begins to reappear.
Safe Solar Viewing Glasses
Safe solar viewing is paramount. Only certified and ISO 12312-2 compliant solar viewing glasses should be used. These glasses are specifically designed to filter out harmful solar radiation, allowing you to view the eclipse safely. Improper eye protection, such as regular sunglasses or homemade filters, will not provide adequate protection and can still cause severe eye damage.
- ISO 12312-2 Certification: Look for the ISO 12312-2 certification label on your glasses. This ensures they meet international safety standards. The label should clearly indicate the filter’s optical density and compliance with the standard.
- Material and Construction: Safe solar glasses typically use specialized filters made of black polymer or aluminized mylar. These materials are designed to block harmful radiation while allowing you to see the eclipse. Avoid glasses that look flimsy or have scratches or damage.
- Proper Usage: Always put on your eclipse glasses before looking at the sun and remove them only after you’ve looked away. Never look at the sun through an unfiltered camera, telescope, binoculars, or other optical devices. These can intensify the sun’s rays, causing immediate and severe eye damage.
- Discard Damaged Glasses: If your glasses are scratched, torn, or otherwise damaged, discard them immediately and obtain a new pair. Do not attempt to repair damaged glasses.
Additional Safety Measures, What Time Is Total Eclipse 2025
Beyond eye protection, several other precautions can enhance your eclipse viewing experience.
- Plan Your Viewing Location: Choose a location with a clear view of the sky, away from obstructions. Consider factors like crowds and accessibility.
- Check the Weather Forecast: Cloudy skies can obscure your view. Check the forecast beforehand to ensure favorable viewing conditions.
- Protect Your Skin: The sun’s rays are still intense during an eclipse. Apply sunscreen with a high SPF, wear a hat, and seek shade when possible.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: During a total solar eclipse, many people gather to view the event. Be mindful of your surroundings and maintain awareness of potential hazards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section addresses some common questions about the total solar eclipse of 2025. Understanding these details will help you plan your viewing experience and ensure your safety.
Exact Time of Total Solar Eclipse in a Specific City
Determining the exact time of totality requires knowing the specific location’s geographic coordinates. For example, in Indianapolis, Indiana, the total solar eclipse will begin around 2:00 PM CDT on April 8, 2025. This time is calculated using astronomical models that account for the moon’s orbit, Earth’s rotation, and the specific location’s latitude and longitude. These calculations are performed by specialized software and astronomical organizations like NASA. The precise time will vary slightly depending on the exact point within Indianapolis.
Duration of Total Eclipse in a Specific City
The duration of totality, meaning the period when the sun is completely obscured by the moon, also varies by location. In Indianapolis, the total eclipse is predicted to last approximately 4 minutes. However, the entire eclipse experience, including the partial phases before and after totality, will extend for several hours. For example, the partial phases might begin around 12:30 PM CDT and conclude around 4:00 PM CDT. These times are estimates and can vary slightly based on location within the city.
Reliable Sources of Eclipse Information
Several reputable organizations provide accurate and reliable information on solar eclipses. NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) is a primary source, offering detailed predictions, maps, and educational resources. Other trustworthy sources include the International Astronomical Union (IAU), various national astronomical societies (like the Royal Astronomical Society in the UK or the American Astronomical Society), and well-established planetariums and observatories. It’s crucial to consult these established sources to avoid misinformation.
Safety Precautions During a Solar Eclipse
Looking directly at the sun, even during a partial eclipse, is extremely dangerous and can cause permanent eye damage, including blindness. The sun’s intensity is not reduced enough during a partial eclipse to make it safe to view without proper eye protection. Specialized solar viewing glasses that meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard are absolutely necessary. These glasses filter out harmful ultraviolet and infrared radiation. Improvised methods like sunglasses or exposed film are not sufficient. Alternatively, you can use indirect viewing methods, such as projecting the sun’s image onto a screen using a pinhole camera or binoculars. Always prioritize eye safety.