Next Total Solar Eclipse After April 2025
Total solar eclipses are awe-inspiring celestial events that occur when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the Sun’s light for a brief period. These events are relatively rare for any given location on Earth, as the precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth is necessary. Understanding the mechanics behind these events requires considering the orbits of both the Moon and Earth.
Total solar eclipses are a fascinating interplay of celestial mechanics. The Moon orbits the Earth in an elliptical path, meaning its distance from Earth varies. Similarly, Earth’s orbit around the Sun is also elliptical. A total solar eclipse only occurs when the Moon is close enough to Earth (at its perigee) to appear large enough in the sky to completely obscure the Sun’s disk. If the Moon were farther away, it would only partially cover the Sun, resulting in a partial eclipse. The Moon’s umbral shadow, the darkest part of its shadow, is the area where a total eclipse is visible. The path of totality, the narrow strip on Earth where the total eclipse can be seen, is determined by the trajectory of the Moon’s umbral shadow as it sweeps across the Earth’s surface.
Types of Solar Eclipses
There are three main types of solar eclipses: total, partial, and annular. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon completely blocks the Sun’s disk, creating a dramatic darkening of the sky and revealing the Sun’s corona. A partial solar eclipse happens when only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon; the degree of obscuration varies depending on the observer’s location. Finally, an annular eclipse occurs when the Moon is at or near its apogee (farthest point from Earth), appearing smaller than the Sun’s disk. This results in a “ring of fire” effect, where a bright ring of the Sun remains visible around the Moon’s silhouette. The difference between these types hinges solely on the relative sizes of the Sun and Moon as seen from Earth, which in turn depends on the Moon’s distance from Earth at the time of the eclipse. The August 21, 2017, eclipse across the United States was a total solar eclipse, while an annular eclipse occurred on October 14, 2023.
Pinpointing the Next Total Eclipse: When Is The Next Total Eclipse After April 2025
The next total solar eclipse after April 2025 will occur on August 12, 2026. This celestial event will be a spectacle visible across a significant portion of the globe, offering a unique opportunity for observers in its path to witness the breathtaking phenomenon of totality.
The path of totality for the August 12, 2026, total solar eclipse will traverse a wide swathe of Earth, beginning in the North Atlantic Ocean and then sweeping across Iceland, northern Spain, and parts of North Africa before concluding in the Arabian Peninsula. The eclipse will be visible as a partial eclipse over a much wider area, encompassing a large portion of Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
Geographic Path of Totality
Imagine a ribbon of darkness, approximately 100 miles wide, tracing a dynamic arc across the Earth’s surface. This ribbon represents the path of totality, where the moon completely blocks the sun, plunging the landscape into an eerie twilight. In Iceland, the eclipse will begin near the coast, with the shadow moving swiftly eastward. The totality will continue across the North Atlantic, offering spectacular views from the ocean itself. As the path crosses Spain, the shadow will pass over various cities and towns, creating unique viewing opportunities. The shadow then moves southward, casting its darkness over parts of North Africa and finally ending its journey over the Arabian Peninsula. The experience of totality varies slightly depending on the specific location, with differences in the duration and the angle of the sun during the eclipse.
Duration of Totality
The duration of totality, the period when the sun is completely obscured by the moon, will vary depending on the observer’s location along the path. In some areas, particularly near the central line of the path of totality, observers might experience totality lasting for up to approximately 1 minute and 40 seconds. However, in areas closer to the edges of the path, the duration will be shorter, potentially only a few seconds of complete darkness. For instance, an observer in northern Spain might see a slightly shorter period of totality than someone situated closer to the center of the path in the North Atlantic. This variation is due to the geometry of the moon’s shadow as it sweeps across the Earth’s surface. Precise timing and duration data are available from various astronomical resources, providing specific information for locations along the eclipse’s path.
Viewing the Eclipse Safely
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety. Looking directly at the sun, even during a partial eclipse, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including solar retinopathy, which can lead to vision loss. This damage occurs because the sun’s intense radiation can burn the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. There’s no pain associated with this damage, making it even more dangerous. Therefore, using proper eye protection is paramount.
Safe solar viewing requires specialized filters that significantly reduce the sun’s brightness and harmful radiation. Improper eye protection, such as regular sunglasses or homemade filters, offers insufficient protection and can be extremely dangerous. Only certified solar filters should be used.
Safe Solar Viewing Glasses and Filters
Several types of safe solar viewing glasses and filters are available, all designed to block harmful ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR), and visible light. ISO 12312-2 is the international safety standard for eclipse viewers, and only glasses meeting this standard should be used. These glasses typically feature a special material, such as black polymer, that effectively blocks the sun’s harmful rays. Another option is a solar filter designed for telescopes or binoculars, which are usually made of a dense material like Mylar or aluminized polyester film. These filters should always be attached to the front of the optical instrument, never to the eyepiece. Remember, the filter must meet the ISO 12312-2 standard to be considered safe. Improperly filtered telescopes or binoculars can cause severe eye damage.
Safe Eclipse Viewing: A Step-by-Step Guide
Prior to the eclipse, acquire ISO 12312-2 certified solar viewing glasses from a reputable vendor. Avoid homemade filters or ordinary sunglasses, as these are not sufficient.
- Before looking at the sun, put on your ISO 12312-2 certified solar viewing glasses. Ensure they fit comfortably and completely cover your eyes.
- During the partial phases of the eclipse, observe the sun through your glasses. Do not remove them at any time during these phases.
- Only during the brief period of totality (when the sun is completely blocked by the moon), can you safely remove your glasses and observe the eclipse with the naked eye. This is only applicable during a total solar eclipse, not a partial one.
- As soon as the sun begins to reappear from behind the moon, immediately put your glasses back on.
- Continue wearing your glasses throughout the remainder of the partial eclipse.
- After the eclipse is over, carefully store your solar viewing glasses in a safe place for future use.
Never look at the sun directly without proper eye protection. Even a brief glance can cause permanent damage. The sun’s intensity is far too great for the human eye to handle without specialized filters. Following these steps will ensure you can enjoy the eclipse safely and protect your eyesight.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Trip
Planning a trip to witness a total solar eclipse requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure a safe, enjoyable, and memorable experience. The optimal viewing location, suitable accommodation options, and reliable transportation arrangements are all crucial elements to meticulously plan in advance. Failing to adequately plan any of these aspects can significantly impact the overall experience, potentially leading to disappointment or even safety concerns.
Location Selection for Optimal Eclipse Viewing
Choosing the right location is paramount. You need to be within the path of totality, the narrow band on Earth where the moon completely blocks the sun. Websites and apps dedicated to eclipse predictions provide detailed maps showing the path of totality. Factors beyond just being in the path of totality include weather predictions for the day of the eclipse – clear skies are essential. Consider locations with historical significance or other attractions to enhance your trip beyond the eclipse itself. For example, the 2017 total solar eclipse saw many people traveling to locations in Oregon, Idaho, and Wyoming not only for the eclipse but also to experience the natural beauty of these states.
Accommodation and Transportation Logistics
Accommodation booking should be well in advance, especially if the eclipse is highly anticipated. Hotels, campsites, and even vacation rentals can fill up quickly months or even a year before the event. Consider the proximity of your accommodation to the eclipse viewing site; you may need to factor in travel time to your chosen viewing spot, especially if it involves driving through potentially congested areas. Transportation options should also be pre-arranged; this could include car rentals, flights, or pre-booked shuttle services, depending on the location and your travel style. For example, renting a car might provide more flexibility to explore the area, while pre-booked shuttles might alleviate parking concerns near popular viewing sites.
Sample Eclipse Viewing Trip Itinerary
A sample itinerary could look like this:
Pre-Eclipse Activities (Day Before):
- Arrive at your chosen location and check into your accommodation.
- Explore the local area, visiting points of interest or attractions.
- Attend a pre-eclipse event or presentation (if available).
- Gather any necessary eclipse viewing supplies (glasses, etc.).
- Confirm your transportation arrangements for the eclipse viewing site.
Eclipse Day:
- Wake up early and have breakfast.
- Travel to your chosen eclipse viewing location and secure your spot.
- Enjoy the partial eclipse phases leading up to totality.
- Experience the awe-inspiring spectacle of totality!
- Capture photos and videos (if desired).
Post-Eclipse Activities (Day After):
- Reflect on the experience and share your stories.
- Visit additional attractions in the area.
- Begin your journey home.
Tips for Maximizing Your Eclipse Viewing Experience
Preparation is key. Having appropriate eclipse glasses that meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard is non-negotiable. Pack sunscreen, hats, and comfortable clothing suitable for the weather conditions. A portable chair or blanket will ensure comfortable viewing, especially if you’re standing for an extended period. Consider bringing binoculars or a telescope for enhanced viewing (with appropriate solar filters). Be aware of potential challenges such as crowds, limited resources, and unpredictable weather. Having backup plans for accommodation or viewing locations can mitigate these risks. For example, having a backup viewing spot a short distance away can help if your initial choice becomes too crowded.
The Science Behind Eclipses
A solar eclipse is a captivating celestial event that occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow on our planet. This seemingly simple alignment of three celestial bodies holds a wealth of scientific intrigue, impacting both our environment and our cultural understanding of the cosmos. Understanding the mechanics of this event reveals fascinating insights into the dynamics of our solar system.
The precise geometry of a solar eclipse is crucial. The Sun’s diameter is approximately 400 times larger than the Moon’s, but it’s also about 400 times farther away. This remarkable coincidence allows the Moon, at specific points in its orbit, to almost perfectly obscure the Sun’s disk from our perspective on Earth. This creates the dramatic effect of a total solar eclipse, where the Sun’s corona, its outermost atmosphere, becomes visible. Partial solar eclipses occur when the Moon only partially blocks the Sun’s light.
Environmental and Wildlife Effects of Solar Eclipses
During a total solar eclipse, the sudden drop in sunlight triggers measurable changes in the environment. Temperatures can decrease noticeably, sometimes by several degrees Celsius. Wind patterns may shift subtly as the air cools. Animal behavior is also dramatically affected. Birds may cease their singing and return to their nests, believing it to be nightfall. Nocturnal animals may become active, mistaking the temporary darkness for the evening hours. These behavioral changes, documented across various species during numerous eclipses, provide valuable insights into the biological responses of organisms to environmental shifts. For example, studies have shown that cows in pastures may begin to seek shelter and prepare for the night.
Historical and Cultural Significance of Solar Eclipses, When Is The Next Total Eclipse After April 2025
Throughout history, solar eclipses have held profound cultural and religious significance across various civilizations. Many ancient cultures viewed eclipses as ominous signs, often associating them with divine wrath or impending doom. Ancient accounts, such as those from Babylonian astronomers who meticulously recorded eclipse occurrences, offer invaluable glimpses into the early attempts to understand and predict these events. In some cultures, eclipses were interpreted as battles between celestial deities, while others saw them as symbolic of rebirth or transformation. These diverse interpretations highlight the deep-seated human fascination with celestial phenomena and the profound impact they have had on shaping our beliefs and understanding of the world. The historical records of eclipses also serve as important data points for astronomers, helping to refine our understanding of the Moon’s orbit and the Earth’s rotation.
Future Total Solar Eclipses
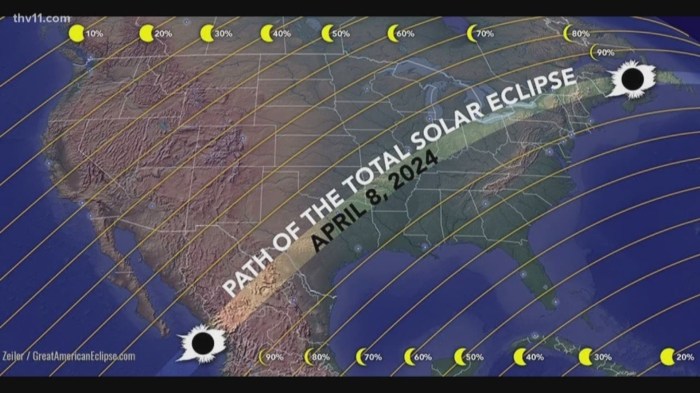
Planning to witness the awe-inspiring spectacle of a total solar eclipse? The next decade offers several opportunities to experience this celestial event. Understanding the paths of totality and optimal viewing locations will significantly enhance your eclipse-viewing experience. This section provides a preview of upcoming total solar eclipses, highlighting key aspects for planning your observation.
Upcoming Total Solar Eclipses in the Next Decade
Predicting the exact path and duration of total solar eclipses requires precise astronomical calculations. However, we can reliably forecast the approximate dates and general geographic regions where these eclipses will be visible. The following list presents a selection of total solar eclipses expected within the next ten years, offering a glimpse into future opportunities for eclipse enthusiasts. Keep in mind that these are projections, and slight variations may occur as calculations are refined.
- August 12, 2026: A total solar eclipse will cross North America, offering excellent viewing opportunities across a significant portion of the continent. The path of totality will traverse a relatively densely populated area, making it easily accessible for many observers.
- August 22, 2028: This total solar eclipse will be visible from a path crossing Europe and Asia. The path of totality will pass over various countries, offering diverse viewing locations and cultural experiences.
- July 22, 2028: This total solar eclipse will traverse the Southern Hemisphere. The path of totality will cross over parts of Australia and the Southern Ocean.
- July 12, 2029: This eclipse will be visible from the Atlantic Ocean, crossing over parts of South America.
- July 2, 2030: This total solar eclipse will traverse the Southern Hemisphere, specifically the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
- June 25, 2038: A total solar eclipse will cross over the Arctic region and parts of Europe and Asia.
- June 15, 2039: This total solar eclipse will be visible from the Pacific Ocean and parts of North America.
Comparison of Totality Paths
The paths of totality for these eclipses vary significantly. Some will traverse densely populated areas, offering convenient viewing opportunities for many, while others will cross remote regions, requiring more extensive travel planning. For example, the 2026 North American eclipse will offer relatively easy access for a large population, unlike the 2028 eclipse, which will require travel to more remote locations in Europe and Asia to witness totality. The duration of totality also varies, influencing the length of time observers have to experience the complete eclipse. Each eclipse presents unique geographical challenges and rewards for observers.
Optimal Viewing Locations
Identifying optimal viewing locations depends on several factors, including weather patterns, accessibility, and the specific path of totality. For example, regions with a high probability of clear skies on the eclipse day are preferred. Accessibility includes considering factors like transportation, accommodation, and overall ease of reaching the viewing location. The 2026 eclipse, crossing North America, might offer many accessible locations with relatively good weather predictability in certain regions, compared to the 2028 eclipse, where remote areas in the path of totality might require careful logistical planning. Detailed eclipse maps and forecasts, typically available closer to the event, are invaluable tools for selecting the best viewing spots.
FAQ
Total solar eclipses are awe-inspiring celestial events, and understanding them better enhances the experience. This section addresses some common questions about these phenomenal occurrences.
Causes of a Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow on our planet. This alignment is incredibly precise; the Sun, Moon, and Earth must be in a nearly perfect straight line. The Moon’s apparent size, as seen from Earth, is just large enough to completely block the Sun’s disk during a total eclipse. The Moon’s orbit is not perfectly circular, so the distance between the Earth and Moon varies. This means that sometimes the Moon appears slightly smaller than the Sun, resulting in an annular eclipse (where a ring of sunlight is visible around the Moon), rather than a total eclipse.
Frequency of Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events at any given location on Earth. While they occur somewhere on the planet roughly every 18 months, the path of totality—the area where the Sun is completely obscured—is narrow, typically only a few hundred kilometers wide. This means that a specific location might only experience a total solar eclipse every few hundred years. The predictability of these eclipses is high; astronomers can calculate their paths and timings years, even decades, in advance using sophisticated models of celestial mechanics. For example, the total solar eclipse of August 21, 2017, was widely predicted and observed across a significant portion of the United States.
Reliable Sources of Eclipse Information
Several reputable sources provide accurate and up-to-date information about upcoming eclipses. NASA’s website is an excellent starting point, offering detailed information on eclipse paths, timings, and related scientific data. Other trustworthy sources include major observatories (like the Royal Observatory Greenwich or the National Solar Observatory) and well-established astronomy websites and magazines. It’s crucial to rely on these established sources to avoid misinformation. Always cross-reference information from multiple reliable sources to ensure accuracy.
Differences Between Solar and Lunar Eclipses
Solar and lunar eclipses are distinct events. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon blocks the Sun’s light from reaching Earth. A lunar eclipse, on the other hand, happens when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. During a lunar eclipse, the Moon typically appears reddish due to the scattering of sunlight through the Earth’s atmosphere. The key difference lies in which celestial body is being shadowed: the Sun in a solar eclipse and the Moon in a lunar eclipse. Lunar eclipses are generally visible over a much wider area than solar eclipses.
Myths and Legends Associated with Solar Eclipses
Throughout history, many cultures have developed myths and legends surrounding solar eclipses. Some ancient civilizations viewed them as ominous signs, associating them with battles, disasters, or the anger of gods. For example, in some Norse mythology, a solar eclipse was attributed to the wolf Sköll swallowing the Sun. Conversely, other cultures celebrated solar eclipses as sacred events, viewing them as a time for spiritual reflection or renewal. These diverse interpretations highlight the profound impact that these celestial events have had on human societies and beliefs across different cultures and time periods.
When Is The Next Total Eclipse After April 2025 – Determining when the next total eclipse occurs after April 2025 requires looking ahead on the celestial calendar. The highly anticipated April 8 Total Solar Eclipse 2025 is a significant event, but future total solar eclipses will follow, with their dates readily available from reputable astronomical sources. Planning to witness these awe-inspiring events requires advance preparation and research into their specific paths and times.
Planning your next eclipse viewing? While the April 2025 eclipse is exciting, the next total solar eclipse after that will occur later in the year. To help you prepare, you might find the details on the path of totality for the Total Solar Eclipse 2025 Path In Mexico useful, as it’s a significant event in itself.
Understanding this path will give you a better idea of the timing and viewing opportunities for future total eclipses.
Determining when the next total eclipse occurs after April 2025 requires consulting astronomical data. For those in New York interested in witnessing this celestial event, planning is key; you’ll want to find the optimal viewing location, and for that, check out this helpful guide on the Best Place In New York To See Total Solar Eclipse 2025 to ensure you don’t miss it.
After securing your spot, you can then confidently anticipate the next total solar eclipse’s date and time.
Planning for the next total solar eclipse after April 2025 requires some foresight. Determining the exact date necessitates consulting astronomical resources. However, considerations extend beyond celestial events; for example, you might want to think about your eclipse viewing party’s menu, and check out this helpful resource on Total Eclipse 2025 Food for inspiration. This will help ensure your viewing experience is complete and memorable, leaving you ready for the next celestial spectacle.
Planning your next eclipse viewing? To determine when the next total eclipse occurs after April 2025, you’ll first want to understand the path of the 2025 event. For a detailed look at the trajectory of that eclipse, check out this excellent resource: Eclipse Solar Total 2025 Trayectoria. Understanding the 2025 path helps predict future total solar eclipse dates and locations.