Next Total Solar Eclipse After 2025
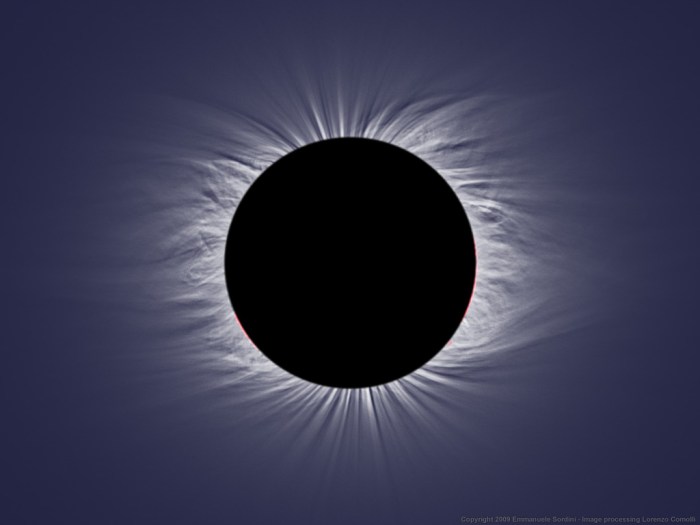
Total solar eclipses are awe-inspiring celestial events where the Moon completely blocks the Sun’s disk, revealing the Sun’s corona – its outer atmosphere. These events hold cultural and scientific significance, inspiring wonder and providing opportunities for valuable research into solar physics. Their rarity in any given location adds to their mystique and makes them highly anticipated occurrences.
Total solar eclipses occur due to a precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. The Moon’s orbit is not perfectly circular, and its distance from Earth varies. A total eclipse is only possible when the Moon is at or near its perigee (closest point to Earth), appearing large enough in the sky to fully obscure the Sun’s disk. The alignment must also be nearly perfect for the umbral shadow – the darkest part of the Moon’s shadow – to fall on Earth’s surface. Slight variations in these factors result in different types of solar eclipses.
Types of Solar Eclipses
The relative positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth determine the type of solar eclipse observed. Understanding these differences helps clarify why some eclipses are total, while others are partial or annular.
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon completely covers the Sun’s disk, as described above. This allows the Sun’s corona to be visible, a breathtaking sight. A partial solar eclipse happens when only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon. The Sun appears as a crescent, and the extent of obscuration varies depending on the observer’s location. Finally, an annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon is at or near its apogee (farthest point from Earth), appearing smaller than the Sun. In this case, the Moon doesn’t completely cover the Sun, leaving a bright ring of sunlight visible around the Moon’s silhouette – the “ring of fire.” The 2023 annular solar eclipse, visible across parts of North America, is a prime example of this phenomenon. The path of totality, or annularity in the case of an annular eclipse, is relatively narrow, meaning these spectacular events are only visible from specific geographic locations.
Predicting the Next Total Solar Eclipse

Predicting solar eclipses, a feat achieved with remarkable accuracy, relies on a deep understanding of celestial mechanics and sophisticated computational tools. Astronomers leverage precise knowledge of the movements of the Sun, Moon, and Earth to calculate the precise timing and location of these celestial events. This involves complex calculations accounting for the elliptical orbits of both the Moon and Earth, as well as other subtle gravitational influences.
Astronomers use a combination of established mathematical models and powerful computational software to predict solar eclipses. These models are based on Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation and Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion, which describe the gravitational interactions between celestial bodies and their orbital paths. These fundamental principles provide the basis for predicting the positions of the Sun and Moon with high accuracy.
Methods for Predicting Solar Eclipses
The process begins with determining the precise positions of the Sun and Moon in the sky at any given time. This involves using highly accurate ephemerides—tables of celestial positions—which are created using sophisticated numerical integration techniques. These techniques solve the equations of motion for the Sun, Moon, and Earth, taking into account the gravitational forces exerted by these bodies and other planets. The resulting ephemerides provide the coordinates of these celestial bodies with extremely high precision, forming the foundation for eclipse predictions. Once the positions are determined, the geometry of the Sun, Moon, and Earth is analyzed to determine whether a solar eclipse will occur and, if so, its type (total, partial, or annular) and path.
Software and Algorithms Used in Eclipse Calculations
Specialized software packages, often developed by astronomical institutions and research groups, are employed for eclipse calculations. These programs incorporate highly refined algorithms based on the aforementioned principles. For example, NASA’s HORIZONS System is a widely used tool that provides precise ephemerides for a vast number of celestial objects, including the Sun and Moon. Such software typically uses numerical integration methods, like Runge-Kutta methods, to solve the equations of motion with great accuracy. These algorithms account for the perturbations caused by the gravitational forces of other planets, ensuring that the predicted positions of the Sun and Moon are as accurate as possible.
Factors Influencing the Accuracy of Eclipse Predictions
The accuracy of eclipse predictions is influenced by several factors. The precision of the ephemerides used is paramount. Inaccuracies in the ephemerides, stemming from incomplete understanding of gravitational influences or limitations in computational power, directly affect the accuracy of the eclipse prediction. Furthermore, the Earth’s irregular shape and its gravitational field variations (due to non-uniform mass distribution) introduce small uncertainties. Finally, the atmospheric refraction of sunlight can slightly alter the apparent position of the Sun and Moon, necessitating corrections in the calculations. Despite these influencing factors, modern eclipse predictions are remarkably accurate, often within a few seconds of the actual event. For instance, the prediction of the total solar eclipse of August 21, 2017, across the United States was incredibly precise, allowing for accurate mapping of the path of totality and the timing of the eclipse in various locations.
Upcoming Total Solar Eclipses
Predicting the exact path and duration of total solar eclipses requires sophisticated astronomical calculations. However, using established models and algorithms, we can provide a reasonably accurate forecast of upcoming events for the coming years. The following information details the dates, locations, and paths of totality for several total solar eclipses after 2025. Remember that slight variations may occur due to the complexities of celestial mechanics.
Total Solar Eclipse Dates and Locations
The table below lists several total solar eclipses occurring after 2025, along with their approximate paths of totality. The visibility of a total solar eclipse is restricted to a relatively narrow path, known as the path of totality. Locations outside this path will only experience a partial eclipse.
| Date | Path of Totality | Duration (Max) | Notable Locations |
|---|---|---|---|
| August 12, 2026 | North America (primarily the United States and Canada) | Approximately 4 minutes | Specific cities along the path will vary, but expect coverage across the North American continent. |
| August 22, 2028 | Europe, North Africa, and Asia | Approximately 2 minutes | Parts of Spain, Greece, Turkey, and other countries within the path will experience totality. |
| July 22, 2028 | South America | Approximately 4 minutes 30 seconds | Specific cities along the path will vary, but the path is expected to cross multiple South American countries. |
| July 12, 2029 | Pacific Ocean, and parts of Australia | Approximately 5 minutes | Locations along the Australian coast and possibly some Pacific islands will be in the path of totality. |
Path of Totality Maps
Visualizing the path of totality is crucial for eclipse enthusiasts planning their viewing locations. Below are descriptions of maps illustrating the path of totality for the three eclipses listed above:
Map 1: August 12, 2026 Eclipse: This map would show a relatively wide band crossing North America, starting in the Pacific Ocean, moving across the western United States, potentially covering parts of states such as California, Nevada, Utah, and Colorado, and then continuing through central Canada before ending in the Atlantic Ocean. The map’s color gradient would show the varying widths of the path of totality, potentially indicating areas of longer duration. The map would also include major cities and geographical landmarks to help viewers locate the path.
Map 2: August 22, 2028 Eclipse: This map would depict a more curved path, traversing across Europe, North Africa, and Asia. The path would start in Europe, potentially in Spain or Portugal, cross the Mediterranean Sea, and then proceed eastward, passing over parts of Turkey, and other countries in the region, finally concluding in Asia. The map’s shading would be used to highlight the area of total eclipse and differentiate it from regions experiencing partial eclipses.
Map 3: July 22, 2028 Eclipse: This map would focus on South America, showing a path that starts in the Pacific Ocean, moves across the continent, and ends in the Atlantic Ocean. The map would highlight specific cities and geographical features in South America through which the path of totality passes, allowing viewers to determine the best viewing locations.
Observing a Total Solar Eclipse Safely
Witnessing a total solar eclipse is a breathtaking experience, but it’s crucial to prioritize eye safety. Directly viewing the sun, even during a partial eclipse, can cause serious and permanent eye damage, including blindness. This section details the necessary precautions to ensure a safe and enjoyable viewing experience.
Observing a total solar eclipse requires specialized eye protection at all times except during the brief period of totality, when the moon completely blocks the sun’s disk. Even the smallest sliver of the sun visible can inflict damage to your eyes. Never rely on homemade filters or ordinary sunglasses; they offer inadequate protection.
Recommended Safety Equipment
Safe solar viewing necessitates the use of certified and appropriately rated equipment. Improper eye protection can lead to severe retinal burns and vision impairment. It’s essential to use only ISO 12312-2 compliant filters.
- ISO 12312-2 compliant solar viewing glasses: These glasses are specifically designed to block harmful solar radiation. They should be from a reputable manufacturer and in perfect condition, free of scratches or damage. Discard any glasses that show signs of wear and tear. Look for the ISO 12312-2 certification mark on the glasses.
- Solar viewers: Handheld solar viewers, similar in principle to solar glasses, provide another safe viewing option. These are often made of specially treated materials that filter out harmful UV and IR radiation. Ensure these are also ISO 12312-2 compliant.
- Solar projection: A safe method involves projecting the sun’s image onto a screen using a pinhole projector. This involves creating a small hole in a piece of cardboard and projecting the image onto another piece of cardboard. This method allows for group viewing without the need for individual protective eyewear. However, it requires a bit of careful setup.
- Telescopes and binoculars with solar filters: If using optical equipment, it is imperative to attach certified solar filters *before* viewing. Never look through a telescope or binoculars without the proper solar filter attached. These filters are specifically designed for use with optical equipment and should be checked for any damage before use.
Potential Dangers of Unsafe Solar Viewing
Looking directly at the sun during an eclipse without proper protection can cause severe and irreversible damage to the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This damage, known as solar retinopathy, can manifest as blurred vision, blind spots, or even complete loss of vision. The sun’s intense radiation can burn the retina without causing immediate pain, making the damage insidious and potentially undetectable until significant harm has occurred. The effects may not be immediately apparent, but can become noticeable hours or even days later. The 2017 total solar eclipse saw a number of cases reported of individuals experiencing vision problems after unsafe viewing.
Never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection during any phase of a solar eclipse, including partial phases.
The Impact of Total Solar Eclipses: When Will The Next Total Solar Eclipse Be After 2025
Total solar eclipses, while awe-inspiring natural phenomena, hold significant scientific, historical, and cultural weight. Their occurrence provides invaluable opportunities for scientific advancement and offer a glimpse into the diverse ways humans have interacted with and interpreted celestial events throughout history. The impact extends far beyond simple observation, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it.
The scientific significance of total solar eclipses is undeniable. These events provide a unique opportunity to study the sun’s corona, the outermost part of its atmosphere, which is usually obscured by the brighter light of the sun’s surface. During a total eclipse, the moon blocks the sun’s disk, allowing scientists to observe the corona’s structure, temperature, and magnetic fields with specialized instruments. This research contributes significantly to our understanding of solar physics, space weather, and the sun’s influence on Earth. For example, observations during past eclipses have helped refine models of coronal mass ejections (CMEs), powerful bursts of solar material that can disrupt satellite communications and power grids on Earth. Furthermore, the brief period of darkness allows for observation of stars and planets normally invisible during the day, offering valuable data for astronomical studies.
Scientific Research During Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses provide a unique natural laboratory for scientific research. The brief period of totality allows scientists to study the sun’s corona, a region typically too faint to observe directly. Observations during eclipses have led to significant discoveries about the sun’s magnetic field, temperature variations within the corona, and the dynamics of coronal mass ejections. These studies are crucial for understanding space weather and its potential impact on Earth. The alignment of the sun, moon, and Earth during a total eclipse also offers a rare opportunity to test theories of general relativity, as predicted by Einstein. Precise measurements of the bending of starlight around the sun during an eclipse have provided strong evidence supporting this theory. In addition, the sudden darkness allows astronomers to study the faint light of stars and planets normally obscured by daylight.
Historical and Cultural Impact of Total Solar Eclipses, When Will The Next Total Solar Eclipse Be After 2025
Throughout history, total solar eclipses have profoundly impacted various cultures and societies. Many ancient civilizations viewed these events as either ominous signs or significant religious or mythological occurrences. Some cultures interpreted them as portents of disaster or the wrath of the gods, leading to rituals and ceremonies aimed at appeasing celestial forces. Other cultures saw eclipses as moments of profound spiritual significance, associating them with cycles of life, death, and rebirth. The ancient Chinese, for example, believed that a celestial dragon was devouring the sun during an eclipse, and they would beat drums and clang cymbals to scare it away. In contrast, some Native American tribes viewed eclipses as a time for reflection and renewal. The differing interpretations highlight the rich tapestry of human beliefs and the diverse ways in which people have sought to understand the world around them.
Cultural Interpretations of Total Solar Eclipses
The diverse interpretations of total solar eclipses across different cultures reflect the varying cosmological beliefs and worldviews of those societies. Ancient Mesopotamian texts describe eclipses as portents of war, famine, or the death of a ruler. Ancient Egyptian records, while less abundant, suggest similar interpretations. In contrast, some cultures, such as the Vikings, viewed eclipses as battles between celestial beings. The Inca civilization associated eclipses with the sun god Inti and performed rituals to ensure his return. These contrasting perspectives highlight the fact that the scientific understanding of eclipses is a relatively recent development. For centuries, they were interpreted through the lens of mythology, religion, and folklore, shaping cultural narratives and beliefs. Even today, the awe-inspiring spectacle of a total solar eclipse continues to inspire wonder and fascination, reminding us of the power and mystery of the cosmos.
Planning Your Eclipse Viewing Trip
Planning a trip to witness a total solar eclipse requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure a safe and memorable experience. Success hinges on meticulous preparation, encompassing the selection of a viewing location, the gathering of essential equipment, and the arrangement of practical logistics like accommodation and transportation.
Essential Items for Eclipse Viewing
A well-prepared eclipse viewing kit is crucial for a successful and safe observation. Neglecting essential items can significantly detract from the experience, or worse, compromise safety. The following checklist covers the most important items:
- Eye Protection: ISO 12312-2 certified solar viewing glasses are absolutely essential. These glasses are specifically designed to filter out harmful solar radiation. Never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection.
- Camera Equipment (Optional): If you plan on photographing the eclipse, ensure your camera has the necessary filters and settings. A tripod is highly recommended for stable shots.
- Binoculars or Telescope (Optional): For a closer look (with appropriate solar filters!), binoculars or a telescope can enhance the viewing experience. Remember, solar filters are crucial for all optical equipment.
- Comfortable Seating: You’ll likely be standing or sitting for an extended period, so comfortable seating is recommended. A folding chair or even a blanket are good options.
- Sunscreen, Hat, and Water: Protection from the sun is paramount, especially during midday. Bring ample sunscreen, a hat, and plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Weather-Appropriate Clothing: Check the forecast and pack clothing suitable for the anticipated conditions. Layers are always a good idea.
- Snacks: Having some snacks on hand can help keep energy levels up throughout the day.
- First-aid Kit: A small first-aid kit is always a good idea for minor injuries or ailments.
Choosing a Viewing Location
Selecting the optimal viewing location is paramount for a successful eclipse viewing experience. The choice depends on several critical factors, including weather patterns and accessibility. Factors such as cloud cover probability and ease of access should be carefully considered. For example, a location with a historically high percentage of clear days during that time of year is preferable to one known for frequent cloud cover. Accessibility involves considering proximity to accommodation, transportation options, and the overall convenience of the site.
Logistical Aspects of Eclipse Viewing
Planning the logistical aspects of your trip is as crucial as choosing the viewing location itself. Careful consideration of accommodation and transportation will ensure a smooth and stress-free experience.
- Accommodation: Book accommodation well in advance, especially if traveling to a popular eclipse viewing location. Consider options ranging from hotels and motels to campsites, depending on your preferences and budget. For the 2017 Great American Eclipse, many locations experienced significant increases in hotel prices and availability due to the high demand.
- Transportation: Plan your transportation to and from the viewing location carefully. Traffic congestion is common during eclipse events, so factor in extra travel time. Consider carpooling or using public transportation if feasible. The 2017 eclipse saw significant traffic jams in many areas, with some travelers experiencing delays of several hours.
- Contingency Plans: Have backup plans in place in case of unexpected events, such as bad weather or transportation issues. This could involve having an alternate viewing location or accommodation options.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section addresses some common queries regarding total solar eclipses, clarifying their causes, frequency, and predictability, as well as providing resources for reliable information about future events. Understanding these aspects enhances the appreciation and planning for witnessing this awe-inspiring celestial phenomenon.
Causes of a Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse occurs due to a precise alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. The Moon, orbiting the Earth, passes directly between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow on our planet. For a total eclipse to happen, the Moon must be at or near its perigee (closest point to Earth) to appear large enough in the sky to completely obscure the Sun’s disk. This alignment isn’t a perfect straight line; a slight misalignment still allows for a partial or annular eclipse. The shadow cast by the Moon has two main parts: the umbra (the darkest part, where the total eclipse is visible) and the penumbra (a lighter shadow where a partial eclipse is seen).
Duration of a Total Solar Eclipse
The duration of totality – the period when the Sun is completely blocked by the Moon – varies significantly depending on the location on Earth where the eclipse is observed. Several factors influence this duration, including the Moon’s distance from Earth and the relative speeds of the Moon and Earth. Totality can last from a few seconds to a maximum of about 7.5 minutes. Locations within the path of totality closer to the center of the umbra will experience longer durations than those near the edges. For example, the total solar eclipse of July 22, 2009, had a maximum duration of totality of around 6 minutes and 39 seconds.
Frequency of Total Solar Eclipses
Total solar eclipses are relatively rare events at any given location on Earth. While a total solar eclipse occurs somewhere on Earth roughly every 18 months, the same location might not experience one for hundreds of years. This is because the Moon’s orbit is tilted relative to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. The frequency of total solar eclipses globally is more frequent than at a specific location, with approximately two to five total solar eclipses occurring annually. However, the visibility of these eclipses is geographically limited.
Reliable Sources for Future Eclipse Information
Several reputable sources provide accurate and up-to-date information about future solar eclipses. NASA’s website is an excellent resource, offering detailed predictions, maps, and explanations. Other credible sources include timeanddate.com and eclipsewise.com, which offer interactive maps and comprehensive data on past, present, and future eclipses. These websites utilize sophisticated astronomical calculations to generate precise predictions, making them reliable sources for eclipse enthusiasts and researchers alike.
When Will The Next Total Solar Eclipse Be After 2025 – Planning to witness a total solar eclipse? To determine when the next one will occur after 2025, you’ll first need to know the specifics of the 2025 event; you can find the exact time by checking this helpful resource: What Time Is The Total Solar Eclipse 2025. Understanding the 2025 eclipse’s timing helps predict future events and allows for better preparation for the next spectacular celestial show.
Planning for future celestial events? While the next total solar eclipse after 2025 is still some years away, it’s worth noting that 2025 offers a significant event for those in the Northeast: you can find details about the visibility of the Total Eclipse 2025 from Long Island, NY, by checking out this resource: Total Eclipse 2025 Long Island Ny.
After this exciting 2025 event, future eclipse viewing will require more extensive travel planning to experience totality.
Planning to witness the celestial spectacle? Determining when the next total solar eclipse occurs after 2025 requires looking ahead on the astronomical calendar. To help you prepare for the 2025 event, you can find specific viewing locations by using this helpful resource: Total Eclipse 2025 Zip Code. This will assist in your planning for future eclipses as well, ensuring you’re ready for the next breathtaking total solar eclipse.
Planning to witness a total solar eclipse? While many are eagerly awaiting the 2024 event, you might be curious about what follows. To understand future eclipses, it’s helpful to first examine past ones; for instance, precise timing information for North Carolina in 2025 can be found here: Total Eclipse 2025 Time Nc. This detailed information helps predict the timing of subsequent total solar eclipses, allowing for better preparation and anticipation of future celestial events.
Determining when the next total solar eclipse will occur after 2025 requires considering global visibility. For those interested in viewing this celestial event from a specific region, a helpful resource is available to find out the Next Total Solar Eclipse In India After 2025 , which can provide a localized perspective. Understanding regional variations helps refine predictions for the next worldwide total solar eclipse after 2025.